Abstract
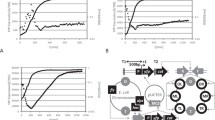
The sopAB operon and the sopC sequence, which acts as a centromere, are essential for stable maintenance of the mini-F plasmid. Immunoprecipitation experiments with purified SopA and SopB proteins have demonstrated that these proteins interact in vitro. Expression studies using the lacZ gene as a reporter revealed that the sopAB operon is repressed by the cooperative action of SopA and SopB. Using immunofluorescence microscopy, we found discrete fluorescent foci of SopA and SopB in cells that produce both SopA and SopB in the presence of the sopC DNA segment, but not in the absence of sopC, suggesting the SopA-SopB complex binds to sopC segments. SopA was exclusively found to colocalize with nucleoids in cells that produced only SopA, while, in the absence of SopA, SopB was distributed in the cytosolic spaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 July 1997 / Accepted: 3 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, M., Mori, H., Onogi, T. et al. Autoregulation of the partition genes of the mini-F plasmid and the intracellular localization of their products in Escherichia coli . Mol Gen Genet 257, 392–403 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050663