Abstract
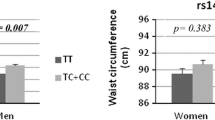
Body weight regulation is influenced neuronally via the hypothalamus, which strongly expresses TRPV4. TRPV4 deficiency in mice confers resistance against diet-induced obesity. We investigated the association between TRPV4 gene variants and body mass index (BMI) in Taiwanese subjects. A sample population of 617 Taiwanese subjects was enrolled, and ten TRPV4 gene polymorphisms were selected and genotyped. After adjusting for clinical covariates, significant associations were observed between three studied polymorphisms and BMI using a dominant model (P = 4.83 × 10−4, P = 1.17 × 10−4, and P = 3.37 × 10−4 for rs3742037, rs10735104, and rs3742035, respectively). Obesity as defined according to both the Asian and National Institutes of Health (NIH) criteria was significantly associated with rs10735104 (P = 0.003 and P = 0.037, respectively) in a dominant model. Genotypes at the TRPV4 locus independently affect BMI and obesity status in Taiwanese subjects. This association may broaden our understanding of the role of neuronal influence on body weight regulation. The regulation of TRPV4 channels in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue could also be a new therapeutic target for preventing the development of obesity.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SNPs:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- TRP:
-
Transient receptor potential
- TRPV4:
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 4
- NIH:
-
National Institutes of Health
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
References
Atwood LD, Heard-Costa NL, Cupples LA, Jaquish CE, Wilson PW, D’Agostino RB (2002) Genomewide linkage analysis of body mass index across 28 years of the Framingham Heart Study. Am J Hum Genet 71:1044–1050
Cecil JE, Tavendale R, Watt P, Hetherington MM, Palmer CN (2008) An obesity-associated FTO gene variant and increased energy intake in children. N Engl J Med 359:2558–2566
Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ et al (2009) A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet 41:527–534
Clapham DE, Montell C, Schultz G, Julius D (2003) International Union of Pharmacology. XLIII. Compendium of voltage-gated ion channels: transient receptor potential channels. Pharmacol Rev 55:591–596
Croteau-Chonka DC, Marvelle AF, Lange EM, Lee NR, Adair LS (2011) Genome-wide association study of anthropometric traits and evidence of interactions with age and study year in Fiipino women. Obesity 19(5):1019–1027
Delany NS, Hurle M, Facer P et al (2001) Identification and characterization of a novel human vanilloid receptor-like protein, VRL-2. Physiol Genomics 4:165–174
den Hoed M, Ekelund U, Brage S et al (2010) Genetic susceptibility to obesity and related traits in childhood and adolescence: influence of loci identified by genome-wide association studies. Diabetes 59:2980–2988
Farooqi IS (2006) Genetic aspects of severe childhood obesity. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 3:528–536
Finkelstein EA, Trogdon JG, Brown DS, Allaire BT, Dellea PS, Kamal-Bahl SJ (2008) The lifetime medical cost burden of overweight and obesity: implications for obesity prevention. Obesity 16:1843–1848
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH (2007) Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. J Am Med Assoc 298:2028–2037
Gao X, Wu L, O’Neil RG (2003) Temperature-modulated diversity of TRPV4 channel gating activation by physical stresses and phorbol ester derivatives through protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem 278:27129–27137
Gevaert T, Vriens J, Segal A et al (2007) Deletion of the transient receptor potential cation channel TRPV4 impairs murine bladder voiding. J Clin Invest 117:3453–3462
Heid IM, Jackson AU, Randall JC et al (2010) Meta-analysis identifies 13 new loci associated with waist-hip ratio and reveals sexual dimorphism in the genetic basis of fat distribution. Nat Genet 42:949–960
Hsu LA, Ko YL, Hsu KH, Ko YH, Lee YS (2002) Genetic variations in the cholesteryl ester transfer protein gene and high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in Taiwanese Chinese. Hum Genet 110:57–63
Kaneko Y, Szallasi A (2014) Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels: a clinical perspective. Br J Pharmacol 171:2474–2507
Ko YL, Hsu LA, Hsu KH, Ko YH, Lee YS (2004) The interactive effects of hepatic lipase gene promoter polymorphisms with sex and obesity on high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol levels in Taiwanese-Chinese. Atherosclerosis 172:135–142
Kusudo T, Wang Z, Mizuno A, Suzuki M, Yamashita H (2012) TRPV4 deficiency increases skeletal muscle metabolic capacity and resistance against diet-induced obesity. J Appl Physiol 112:1223–1232
Lee H, Iida T, Mizuno A, Suzuki M, Caterina MJ (2005) Altered thermal selection behavior in mice lacking transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J Neurosci 25:1304–1310
Li Y, Sandra K, Jun W et al (2012) TRPV4 is a regulator of adipose oxidative metabolism, inflammation, and energy homeostasis. Cell 152:96–110
Liedtke W, Friedman JM (2003) Abnormal osmotic regulation in trpv4−/− mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13698–13703
Liedtke W, Choe Y, Marti-Renom MA et al (2000) Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell 103:525–535
Lindgren CM, Heid IM, Randall JC et al (2009) Genome-wide association scan meta-analysis identifies three loci influencing adiposity and fat distribution. PLoS Genet 5:e1000508
Ma D, Li S, Lucas EK, Cowell RM, Lin JD (2010) Neuronal inactivation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) protects mice from diet-induced obesity and leads to degenerative lesions. J Biol Chem 285:39087–39095
Maes HH, Neale MC, Eaves LJ (1997) Genetic and environmental factors in relative body weight and human adiposity. Behav Genet 27:325–351
National Institute of Health (1998) National Heart Lung and Blood Institute: clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. Obes Res 6:51S–209S
Nilius B, Vriens J, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T (2004) TRPV4 calcium entry channel: a paradigm for gating diversity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C195–C205
O’ Conor C, Griffin T, Liedtke W, Guilak F (2013) Increased susceptibility of TRPV4 deficient mice to obesity and obesity-induced osteoarthritis with very high fat diet. Ann Rheu Dis 72:300–304
Ohnishi M, Kato S, Akiyoshi J, Atfi A, Razzaque MS (2011) Dietary and genetic evidence for enhancing glucose metabolism and reducing obesity by inhibiting Klotho functions. FASEB J 25:201–2039
Pang Z, Wu NN, Zhao W et al (2011) The central cannabinoid CB1 receptor is required for diet-induced obesity and rimonabant’s antiobesity effects in mice. Obesity 19:1923–1934
Park JH, Wacholder S, Gail MH et al (2011) Estimation of effect size distribution from genome-wide association studies and implications for future discoveries. Nat Genet 42(7):570–575
Rock MJ, Prenen J, Funari VA et al (2008) Gain-of-function mutations in TRPV4 cause autosomal dominant brachyolmia. Nat Genet 40:999–1003
Scherag A, Jarick I, Grothe J et al (2010) Investigation of a genome wide association signal for obesity: synthetic association and haplotype analyses at the melanocortin 4 receptor gene locus. PLoS One 5:e13967
Schumacher MA, Jong BE, Frey SL, Sudanagunta SP, Capra NF, Levine JD (2000) The stretch-inactivated channel, a vanilloid receptor variant, is expressed in small-diameter sensory neurons in the rat. Neuro sci Lett 287:215–218
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI et al (2010) Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal eighteen new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet 42:937–948
Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Kodaira K, Imai M (2003) Impaired pressure sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. J Biol Chem 278:22664–22668
Thaler JP, Yi CX, Schur EA et al (2012) Obesity is associated with hypothalamic injury in rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 122:153–162
Tian W, Fu Y, Garcia-Elias A et al (2009) A loss-of-function nonsynonymous polymorphism in the osmoregulatory TRPV4 gene is associated with human hyponatremia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14034–14039
Todaka H, Taniguchi J, Satoh J, Mizuno A, Suzuki M (2004) Warm temperature-sensitive transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) plays an essential role in thermal hyperalgesia. J Biol Chem 279:35133–35138
Voets T, Talavera K, Owsianik G, Nilius B (2005) Sensing with TRP channels. Nat Chem Biol 1:85–92
Wang K, Li WD, Zhang CK et al (2011) A genome-wide association study on obesity and obesity-related traits. PLoS One 6:e18939
Wheeler E, Huang N, Bochukova EG, Keogh JM, Lindsay S et al (2013) Genome-wide SNP and CNV analysis idenitifies common and low-frequency variants associated with severe early-onset obesity. Nat Genet 45:513–517
WHO expert consultation (2004) Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 363:157–163
Willer CJ, Speliotes EK, Loos RJ et al (2009) Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat Genet 41:25–34
Wu TL, Tsao KC, Chang CP, Li CN, Sun CF, Wu JT (2002) Development of ELISA on microplate for serum C-reactive protein and establishment of age-dependent normal reference range. Clin Chim Acta 322:163–168
Yang X, Deignan JL, Qi H et al (2009) Validation of candidate causal genes for obesity that affect shared metabolic pathways and networks. Nat Genet 41:415–423
Zhu G, Gulsvik A, Bakke P, ICGN Investigators et al (2009) Association of TRPV4 gene polymorphisms with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hum Mol Genet 18:2053–2062
Zimoń M, Baets J, Auer-Grumbach M et al (2010) Dominant mutations in the cation channel gene transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 cause an unusual spectrum of neuropathies. Brain 133:1798–1809
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC101-2314-B-303-023-MY3), and a grant from the Buddhist Tzu Chi General Hospital (TCRD-I100-01-01) to YL Ko.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, DM., Wu, S., Hsu, LA. et al. Associations between TRPV4 genotypes and body mass index in Taiwanese subjects. Mol Genet Genomics 290, 1357–1365 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-0996-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-0996-8