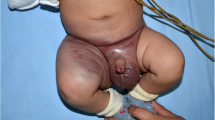
Abstract
Background
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE) is a locally aggressive vascular tumor that usually occurs in infants. It is commonly associated with Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon which is directly responsible for the significant morbidity and mortality, including hemodynamic instability, local invasion, and compression of vital structures. Treatment is particularly difficult for those who had no response to conventional therapies. This paper wants to share experience of mTOR inhibitors sirolimus in the treatment of refractory KHE.
Materials and methods
Six cases of refractory KHE were diagnosed and treated in Children’s Hospital of Fudan University from Jan 2010–June 2013; all of them were treated with sirolimus in June 2012 after failing multiple other therapies.
Results
In six patients, gender was equally distributed between male and female patients. The mean age at the time of initial diagnosed as KHE was 3.1 ± 1.8 months. All of them had been pretreated with at least 2 medical therapies. All of them showed significant improvement in clinical status with tolerable side effects. The average time to response was 5.3 ± 1.0 days; the average stabilization time of platelet was 15.1 ± 8.0 days; and the average time for sirolimus treated as single agent was 1.7 ± 0.4 months. No recurrence of their symptoms happened.
Conclusions
Sirolimus appears to be effective and safe in patients with life-threatening KHE and represents a promising tool in treating refractory KHE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarado Y et al (2011) Clinical activity of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in solid tumors. Target Oncol 6(2):69–94
Castilho R, Squarize C, Gutkind J (2013) Exploiting PI3 K/mTOR signaling to accelerate epithelial wound healing. Oral Dis 19(6):551–558
Croteau SE et al (2013) Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: atypical features and risks of Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon in 107 referrals. J Pediatr 162(1):142–147
DeFatta RJ et al (2005) Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: case report and literature review. Laryngoscope 115(10):1789–1792
Deb G (2003) Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and therapy with interferon-alpha. Med Pediatr Oncol 41(6):593
Debelenko LV et al (2005) D2-40 immunohistochemical analysis of pediatric vascular tumors reveals positivity in Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. Mod Pathol 18(11):1454–1460
Dresse MF et al (1991) Successful treatment of Kasabach–Merritt syndrome with prednisone and epsilon-aminocaproic acid. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 8(4):329–334
Fahrtash F, McCahon E, Arbuckle S (2010) Successful treatment of kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma with vincristine. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 32(6):506–510
Falger JC et al (2006) Conversion from calcineurin inhibitor to sirolimus in pediatric chronic allograft nephropathy. Pediatr Transplant 10(5):565–569
Fasolo A, Sessa C (2011) Current and future directions in mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors development. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 20(3):381–394
Flores MV et al (2010) Visualization of embryonic lymphangiogenesis advances the use of the zebrafish model for research in cancer and lymphatic pathologies. Dev Dyn 239(7):2128–2135
Fuchimoto Y et al (2012) Vincristine, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide chemotherapy resolves Kasabach–Merritt syndrome resistant to conventional therapies. Pediatr Int 54(2):285–287
Garcia CD et al (2006) Conversion to sirolimus in pediatric renal transplantation recipients. Transplant Proc 38(6):1901–1903
Garcia-Monaco R et al (2012) Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma with Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon: successful treatment with embolization and vincristine in two newborns. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23(3):417–422
Haisley-Royster C et al (2002) Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon: a retrospective study of treatment with vincristine. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 24(6):459–462
Hammill AM et al (2011) Sirolimus for the treatment of complicated vascular anomalies in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 57(6):1018–1024
Hu B et al (1998) Kasabach–Merritt syndrome-associated kaposiform hemangioendothelioma successfully treated with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and actinomycin D. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 20(6):567–569
Huber S et al (2007) Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin impedes lymphangiogenesis. Kidney Int 71(8):771–777
Issaka RB et al (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factors C and D induces proliferation of lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells through autocrine crosstalk with endothelium. Am J Pathol 175(4):1410–1420
Jiang RS, Hu R (2012) Successful treatment of Kasabach–Merritt syndrome arising from kaposiform hemangioendothelioma by systemic corticosteroid therapy and surgery. Int J Clin Oncol 17(5):512–516
Kaylani S, Theos AJ, Pressey JG (2013) Treatment of infantile hemangiomas with sirolimus in a patient with PHACE syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol 30(6):e194–e197
Kobayashi S et al (2007) Rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin, suppresses lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Sci 98(5):726–733
Le Huu AR et al (2010) Expression of prox1, lymphatic endothelial nuclear transcription factor, in Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. Am J Surg Pathol 34(11):1563–1573
Lopez V et al (2009) Successful management of Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma with Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon using vincristine and ticlopidine. Pediatr Dermatol 26(3):365–366
Low IC, Yang RY, Symmans PJ (2013) Microscopic Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma with extensive lymphangiomatosis: an extraordinary example of an unusual entity. Int J Surg Pathol 21(3):297–302
Trenor CR (2011) Sirolimus for refractory vascular anomalies. Pediatr Blood Cancer 57(6):904–905
Vinayak S, Carlson RW (2013) mTOR inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park), 27(1):38–44, 46, 48 passim
Wander SA et al (2013) PI3K/mTOR inhibition can impair tumor invasion and metastasis in vivo despite a lack of antiproliferative action in vitro: implications for targeted therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138(2):369–381
Yadav D et al (2011) Neonatal Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 32(4):238–241
Yasui N et al (2013) Kasabach–Merritt phenomenon: a report of 11 cases from a single institution. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 35(7):554–558
Acknowledgments
This manuscript is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81071903). We thank Xiuzhen Dai for language improvement.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kai, L., Wang, Z., Yao, W. et al. Sirolimus, a promising treatment for refractory Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 471–476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1549-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1549-3