Abstract
Introduction
The special types of breast cancer seem to have not only distinct morphological features but also distinct biological features.
Materials and methods
Women diagnosed with a first primary invasive breast cancer in the 2004–2005 period were identified through Tuscan Cancer Registry. Information on age, tumor size, lymph node status, histological type and grade, hormonal receptors, HER2 immunohistochemical expression were collected. Five subtypes were defined: luminal A, luminal B HER2+, luminal B HER2−, triple negative, and HER2 positive. The association between the histological type and molecular subgroups was assessed by a Fisher’s exact test, and a multinomial logistic regression model was used.
Results
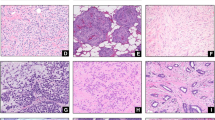
Out of 1,487 patients, 34 % were luminal A subtype, 25 % luminal B HER2−, 11 % luminal B HER2+, 19 % triple negative, and 10.2 % HER2+; 58.5 % of cancers were ductal NOS types. With luminal A as reference, histological types distribution was significantly different between the subgroups. Mucinous, tubular, and cribriform histotypes were found among luminal A cancers more than in other subgroups; all medullary carcinomas were triple negative cancers. Pathological stage at diagnosis was more advanced, and histological grade was lower among subgroups other than luminal A.
Conclusions
Significant association between breast cancer histotypes and molecular subgroups was found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson WF, Pfeiffer RM, Dores GM, Sherman ME (2006) Comparison of age distribution patterns for different histopathologic types of breast carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers 15(10):1899–1905
Caldarella A, Crocetti E, Bianchi S, Vezzosi V, Urso C, Biancalani M, Zappa M (2011) Female breast cancer status according to ER, PR and HER2 expression: a population based analysis. Pathol Oncol Res 17(3):753–758
Colleoni M, Rotmensz N, Maisonneuve P, Mastropasqua MG, Luini A, Veronesi P, Intra M, Montagna E, Cancello G, Cardillo A, Mazza M, Perri G, Iorfida M, Pruneri G, Goldhirsch A, Viale G (2012) Outcome of special types of luminal breast cancer. Annals Oncol 23(6):1428–1436
Cristofanilli M, Gonzalez-Angulo A, Sneige N, Kau SW, Broglio K, Theriault RL, Valero V, Buzdar AU, Kuerer H, Buccholz TA, Hortobagyi GN (2005) Invasive lobular carcinoma classic type: response to primary chemotherapy and survival outcomes. J Clin Oncol 23(1):41–48
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Fritz A, Percy C, Jack A, Shanmugaratnam K, Sobin L, Parkin DM, Whelan S (2000) International classification of diseases for oncology, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Goldrisch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, Panel members (2011) Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22:1736–1747
Gruver AM, Portier BP, Tubbs RR (2011) Molecualr pathology of breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135:544–557
Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ (2012) WHO classification of tumours, vol 4. IARC WHO Classification of Tumours, no 4
Li CI, Uribe DJ, Daling JR (2005) Clinical characteristics of different histologic types of breast cancer. Br J Cancer 93:1046–1052
Louwman MWJ, Vriezen M, van Beek MWPM, Tutein Nolthenius-Puylaert CBJE, van der Sangen MJC, Roumen RM, Kiemeney LALM, Coebergh JWW (2007) Uncommon breast tumors in perspective: incidence, treatment and survival in the Netherlands. Int J Cancer 121:127–135
Metzger-Filho O, Tutt A, de Azambuja E, Saini KS, Viale G, Loi S, Bradbury I, Bliss JM, Azim HA Jr, Di Leo A, Baselga J, Sotiriou C, Piccard-Gebhart M (2012) Dissecting the heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer. JCO 30:1879–1887
Nagao T, Kinoshita T, Hojo T, Tsuda K, Fujimara Y (2012) The differences in the histological types of breast cancer and the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: the relationship between the outcome and the clinicopathological characteristics. Breast 21(3):289–295
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Powe DG, Green AR, Habashy H, Grainge MJ, Robertson JF, Blamey R, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Lee AH, Ellis IO (2008) Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: response to hormonal therapy and outcomes. Eur J Cancer 44:73–83
Schnitt SJ (2010) Classification and prognosis of invasive breast cancer: from morphology to molecular taxonomy. Mod Pathol 23:S60–S64
Simpson PT, Reis Filho JS, Lakhani SR (2010) Breast pathology: beyond morphology. Sem Diagn Pathol 27:91–96
Vincent-Salomon A, Gruel N, Lucchesi C, MacGrogan G, Dendale R, Sigal-Zafrani B, Longy M, Raynal V, Pierron G, de Mascarel I, Taris C, Stopp-Lyonnel D, Pierga JY, Salmon R, Sastre-Garau X, Fourquet A, Delattre O, de Cremoux P, Aurias A (2007) Identification of typical medullary breast carcinoma as a genomic sub-group of basal-like carcinomas, a heterogeneous new molecular entity. Breast Cancer Res 9(2):R24
Vu-Nishino H, Tavassoli FA, Ahrens WA, Haffty BG (2005) Clinicopathologic features and log-term outcome of patients with medullary breast carcinoma managed with breast-conserving therapy (BCT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62(4):1040–1047
Weigelt R, Reis-Filho JS (2009) Histological and molecular types of breast cancer: is there a unifying taxonomy? Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(12):718–730
Weigelt B, Horlings HM, Kreike B, Hayes MM, Hauptmann M, Wessels LFA, de Jong D, Van de Vijver MJ, Van’t Veer LJ, Peterse JL (2008) Refinement of breast cancer classification by molecular characterization of histological special types. J Pathol 216:141–150
Yerushalmi R, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA (2009) Breast carcinoma-rare types: review of the literature. Annals Oncol 20:1763–1770
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caldarella, A., Buzzoni, C., Crocetti, E. et al. Invasive breast cancer: a significant correlation between histological types and molecular subgroups. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 617–623 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1365-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1365-1