Abstract
Purpose
Low-dose multislice-CT (MSCT) detects many early-stage lung cancers with good prognosis, but whether it decreases lung cancer mortality and at which costs is yet insufficiently explored. Scope of the present study is to examine within a common European effort whether MSCT screening is capable to reduce the lung cancer mortality by at least 20 % and at which amount of undesired side effects this could be achieved.
Methods
Overall 4,052 heavy smoking men and women were recruited by a population-based approach and randomized into a screening arm with five annual MSCT screens and an initial quit-smoking counseling, and a control arm with initial quit-smoking counseling and five annual questionnaire inquiries.
Results
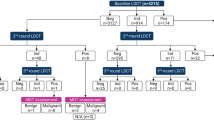
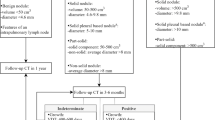
In the first screening round, 2,029 participants received a MSCT providing 1,488 negative and 540 suspicious screens with early recalls (early recall rate 26.6 %) leading to 31 biopsies (biopsy rate 1.5 %) and 22 confirmed lung cancers (detection rate 1.1 %). Among the lung cancers, 15 were adenocarcinomas, 3 squamous cell carcinomas, one small-cell lung cancer, and 3 others, whereby 18 were in clinical stage I, one in stage II, and 3 in stage III. One interval cancer occurred.
Conclusions
The indicated performance indicators fit into the range observed in comparable trials. The study continues finalizing the second screening round and for the first participants even the last screening round. The unresolved issue of the precise amount of side effects and the high early recall rate precludes currently the recommendation of MSCT as screening tool for lung cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach PB, Kelley MJ, Tate RC, McCrory DC (2003) Screening for lung cancer. A review of the current literature. Chest 123:72s–82s
Bach PB, Jett JR, Pastorino U, Tockman MS, Swensen SJ, Begg CB (2007) Computed tomography screening and lung cancer outcomes. JAMA 297:953–961
Baldwin DR, Duffy SW, Wald NJ, Page R, Hansel DM, Field JK (2011) UK Lung Screen (UKLS) nodule management protocol: modelling of a single screen randomised controlled trial of low-dose CT screening for lung cancer. Thorax 66:308–313
Diederich S, Thomas M, Semik M, Lenzen H, Roos N, Weber A, Heindel W, Wormanns D (2004) Screening for early lung cancer with low-dose spiral computed tomography: results of annual follow-up examinations in asymptomatic smokers. Eur Radiol 14:691–702
Henschke CI, McCauley DI, Yankelevitz DF, Naidich DP, McGuiness G, Miettinen OS, Libby DM, Pasmantier MW, Koizumi J, Altorki NK, Smith JP (1999) Early lung cancer action project: overall design and findings from baseline screening. The Lancet 354:99–105
Heuer C, Becker N (1999) Smoking prevalence and lung cancer mortality in germany. J Epidem Biostat 4:45–52
Hoffmann D, Pilz L (2005) RANDI—Online randomization for small-scale clinical trials. GMS (http://www.egms.de/en/meetings/gmds2005/05gmds361.shtml)
Infante M, Lutman FR, Cavuto S, et al. for the DANTE Study Group (2008) Lung cancer screening with spiral CT Baseline results of the randomized DANTE trial. Lung Cancer 59:355–63
Investigators I-ELCAP (2006) Survival of patients with stage I lung cancer detected on CT screening. NEJM 355(17):1763–1771
Lopez Pegna A, Picozzi G, Mascalchi M, Carrozzi FM, Carozzi L, Comin C, Spinelli C, Falaschi F, Grazzini M, Innocenti F, Ronchi C, Paci E (2009) Design, recruitment and baseline results of the ITALUNG trial for lung cancer screening with low-dose CT. Lung Cancer 64:34–40
NLST Research Team (2011) Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. NEJM 365:395–409
Pastorino U (2006) Early detection of lung cancer. Respiration 73:5–13
Pedersen JH, Ashraf H, Dirksen A, Bach K, Hansen H, Toennesen P, Thorsen H, Brodersen J, Skov BG, Døssing M, Mortensen J, Richter K, Clementsen P, Seersholm N (2009) The Danish randomized lung cancer CT screening trial—overall design and results of the prevalence round. J Thorac Oncol 4:608–614
van Iersel CA, de Koning HJ, Draisma G, Mali WP, Scholten ET, Nackaerts K, Prokop M, Habbema JD, Oudkerk M, van Klaveren RJ (2007) Risk-based selection from the general population in a screening trial: selection criteria, recruitment and power for the Dutch-Belgian randomised lung cancer multi-slice CT screening trial (NELSON). Int J Cancer 120:868–874
van Klaveren RJ (2011) Lung cancer screening. EJC 47(3):S147–S155
van Klaveren RJ, Habbema JDF, Pedersen JH, de Koning HJ, Oudkerk M, Hoosteden HC (2001) Lung cancer screening by low-dose spiral computed tomography. Eur Respir J 18:857–866
van Klaveren RJ, Oudkerk M, Prokop M, Scholten ET, Nackaerts K, Vernhout R, van Iersel CA, van den Bergh KA, van ‘t Westeinde S, van der Aalst C, Thunnissen E, Xu DM, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Gietema HA, de Hoop BJ, Groen HJ, de Bock GH, van Ooijen P, Weenink C, Verschakelen J, Lammers JW, Timens W, Willebrand D, Vink A, Mali W, de Koning HJ (2009) Management of lung nodules detected by volume CT scanning. N Engl J Med 361:2221–2229
Acknowledgments
Numerous colleagues contributed to the success of the study. The MSCTs were carried out by Jessica Engelhart and Martina Jochim. The database was set up and managed (2007–2011) by Simon Roether. Data entry, invitation of participants, and time schedule coordination by Angelika Bari and Andrea Albrecht, quit-smoking counseling by Monika Bade and Vera Bähr, processing and storage of blood specimen by Kirsten Lenner-Fertig and Ulrike von Seydlitz-Kurzbach. The study was supported in 2007–2010 by the German Research Foundation (BE 2486/2-1) and the Dietmar-Hopp-Stiftung, and is currently (2010–2013) supported by the German Research Foundation (BE 2486/2-2), and the members of the German Center for Lung Research by the German Research Ministry (BMBF-DZL).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, N., Motsch, E., Gross, ML. et al. Randomized study on early detection of lung cancer with MSCT in Germany: study design and results of the first screening round. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 1475–1486 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1228-9