Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the function of the KIAA0008 gene, one of the leading genes in the signature associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis selected by cDNA microarray, and especially its possible roles in invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods
Expression levels of KIAA0008 in 27 primary tumors and 23 matched non-tumor liver tissues from HCC patients, and four HCC cell lines with different metastatic potentials were detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR. Recombinant expression plasmid vectors of the KIAA0008 gene were constructed and transfected into HCC cells. The subcellular localization of the KIAA0008 gene product and in vitro effects of KIAA0008 overexpression on proliferation and invasion of HCC cell line were also investigated.
Results
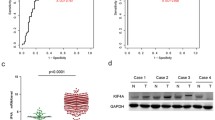
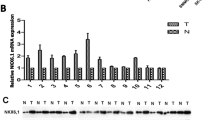
Expression levels of KIAA0008 in HCC tissues were statistically higher than those of paired non-tumorous liver tissues (P<0.001, paired Wilcoxon test), and in HCCs with high invasiveness these were statistically higher than those with low invasiveness (P=0.002, Mann-Whitney test). In the four HCC cell lines with an identical genetic background and stepwise higher invasiveness potentials, its expression was consistent with their invasiveness potential. The KIAA0008 gene product was concentrated on the nucleus and cell membrane of HCC cells, without any distribution in the cytoplasm. Overexpression of KIAA0008 in the MHCC97L cell line resulted in increased cell proliferation, colony formation, and invasion.
Conclusions
KIAA0008 expression is associated with invasiveness of HCC; overexpression of KIAA0008 leads to a more invasive phenotype of HCC cell lines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassal S, Nomura N, Venter D, Brand K, McKay MJ, van der Spek PJ (2001) Characterization of a novel human cell-cycle-regulated homologue of Drosophila dlg1. Genomics 77:5–7
Cance WG, Stewart AK, Menck HR (2000) The national cancer data base report on treatment patterns for hepatocellular carcinomas: improved survival of surgically resected patients, 1985–1996. Cancer 88:912–920
El-Serag HB, Mason AC (1999) Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med. 340:745–750
Giannelli G, Fransvea E, Marinosci F, Bergamini C, Colucci S, Schiraldi O, Antonaci S (2002)Transforming growth factor-beta1 triggers hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness via alpha3beta1 integrin. Am J Pathol 161:183–193
Gildea JJ, Seraj MJ, Oxford G, Harding MA, Hampton GM, Moskaluk CA, Frierson HF, Conaway MR, Theodorescu D (2002) RhoGDI2 is an invasion and metastasis suppressor gene in human cancer. Cancer Res 62:6418–6423
Li Y, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Chen J, Xue Q, Chen J, Gao DM, Bao WH (2001) Establishment of cell clones with different metastatic potential from the metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line MHCC97. World J Gastroenterol 7:630–636
Li Y, Tang Y, Ye L, Liu B, Liu K, Chen J, Xue Q (2003) Establishment of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line with unique metastatic characteristics through in vivo selection and screening for metastasis-related genes through cDNA microarray. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:43–51
Li Y, Tian B, Yang J, Zhao L, Wu X, Ye SL, Liu YK, Tang ZY (2004) Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol (In press)
MacDonald TJ, Brown KM, LaFleur B, Peterson K, Lawlor C, Chen Y, Packer RJ, Cogen P, Stephan DA (2001) Expression profiling of medulloblastoma: PDGFRA and the RAS/MAPK pathway as therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. Nat Genet 29:143–152
Nomura N, Miyajima N, Sazuka T, Tanaka A, Kawarabayasi Y, Sato S, Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, Tabata S (1995) Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. I. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0001-KIAA0040) deduced by analysis of randomly sampled cDNA clones from human immature myeloid cell line KG-1. DNA Res 1:27–35
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94:153–156
Sun FX, Tang ZY, Liu KD, Ye SL, Xue Q, Gao DM, Ma ZC (1996) Establishment of a metastatic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice via orthotopic implantation of histologically intact tissues. Int J Cancer 66:239–243
Tang ZY (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma--cause, treatment and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 7:445–454
Taylor-Robinson SD, Foster GR, Arora S, Hargreaves S, Thomas HC (1997) Increase in primary liver cancer in the UK, 1979–94. Lancet 350:1142–1143
Tian J, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Lin ZY, Chen J, Xue Q (1999) New human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line with highly metastatic potential (MHCC97) and its expressions of the factors associated with metastasis. Br J Cancer 81:814–821
Tominaga S, Kuroishi T, Aoki S (1998) (UICC) (eds) Cancer mortality statistics in 33 countries 1953–1992. Roppo Shupan, Nagoya, pp 69
Wang J, Chen S (2002) Screening and identification of gastric adenocarcinoma metastasis-related genes using cDNA microarray coupled to FDD-PCR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 128:547–553
Ye QH, Qin LX, Forgues M, He P, Kim JW, Peng AC, Simon R, Li Y, Robles AI, Chen Y, Ma ZC, Wu ZQ, Ye SL, Liu YK, Tang ZY, Wang XW (2003) Predicting hepatitis B virus-positive metastatic hepatocellular carcinomas using gene expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med 9:416–423
Yu Y, Khan J, Khanna C, Helman L, Meltzer PS, Merlino G (2004) Expression profiling identifies the cytoskeletal organizer ezrin and the developmental homeoprotein Six-1 as key metastatic regulators. Nat Med 10:175–181
Zhang Z, Futamura M, Vikis HG, Wang M, Li J, Wang Y, Guan KL, You M (2003) Positional cloning of the major quantitative trait locus underlying lung tumor susceptibility in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12642–12647
Zhou XD, Tang ZY, Yang BH, Lin ZY, Ma ZC, Ye SL, Wu ZQ, Fan J, Qin LX, Zheng BH (2001) Experience of 1000 patients who underwent hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 91:1479–1486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the National Foundation for the Excellent Younger Researcher of China (30325041), the “863” R & D High-tech Key Project (2002BA711A02–4), the “973” State Key Basic Research Program Grant of China (G1998051211), the Fund for the Innovative Research Group in Shanghai, and the Fund for Outstanding Scholars of the New Era of the Ministry of Education in China (2003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Qin, LX., Ye, QH. et al. KIAA0008 gene is associated with invasive phenotype of human hepatocellular carcinoma—a functional analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130, 719–727 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0595-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0595-2