Abstract
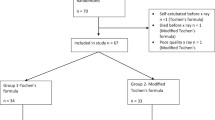
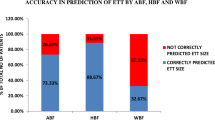
The objectives were to estimate the incidence of inadequate placement of the endotracheal tube (ET) using Tochen’s formula (6 + birth weight) and to correlate optimum ET length with anthropometric measurements in neonates. A cross-sectional analytical study was conducted in 50 neonates. Neonates requiring intubation for ventilation, with a confirmatory chest radiograph, were intubated using Tochen’s formula, after which tube placement was verified by auscultation. The incidence of inadequate placement and optimum length of ET insertion were estimated from chest radiographs. Anthropometric parameters were measured and correlated with the optimum length and regression equations generated. The incidence of inadequate placement of the ET was 40 % (20 of 50). The incidence of inadequate placement was higher (5 of 6, 83 %) in extremely low birth weight (ELBW) infants, and in extreme preterm infants (5 of 5, 100 %). It was found that all the anthropometric parameters correlated well (r between 0.71 and 0.84) with the optimum ET length. Conclusion: The incidence of inadequate placement was high, especially in the ELBWs’ and extreme preterm infants. Birth weight, sternal length, and shoulder umbilical length correlated significantly with optimum ET length and may guide optimal ET placement.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AL:
-
Arm length
- BW:
-
Birth weight
- DV:
-
The principal investigator
- ELBW:
-
Extremely low birth weight
- ET:
-
Endotracheal tube
- FL:
-
Foot length
- LBW:
-
Low birth weight
- NICU:
-
Neonatal intensive care unit
- NL:
-
Neonatal length
- NRP:
-
Neonatal Resuscitation Program
- NTL:
-
Nasal tragal length
- OFC:
-
Occipitofrontal head circumference
- SL:
-
Sternal length
- SN:
-
The neonatal consultant
- SUL:
-
Sternal umbilical length
- ShUL:
-
Shoulder umbilical length
- T1:
-
First thoracic vertebra
- T2:
-
Second thoracic vertebra
- T3:
-
Third thoracic vertebra
- T4:
-
Fourth thoracic vertebra
- T5:
-
Fifth thoracic vertebra
References
Amarilyo G, Mimouni FB, Oren A, Tsyrkin S, Mandel D (2009) Orotracheal tube insertion in extremely low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 154:764–765
Blayney M, Costello S, Perlman M, Lui K, Frank J (1991) A new system for location of endotracheal tube in preterm and term neonates. Pediatrics 87:44–47
Coldiron JS (1968) Estimation of nasotracheal tube length in neonates. Pediatrics 41:823–828
Conrardy PA, Goodman LR, Lainge F, Singer MM (1976) Alteration of endotracheal tube position. Flexion and extension of the neck. Crit Care Med 4:7–12
Embleton ND, Deshpande SA, Scott D, Wright C, Milligan DW (2001) Foot length, an accurate predictor of nasotracheal tube length in neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 85:F60–648
Heller RM, Cotton RB (1985) Early experience with illuminated endotracheal tubes in premature and term infants. Pediatrics 75:664–666
Kattwinkel J (2012) Textbook of neonatal resuscitation, 6th edn. American Academy of Pediatrics, Elk Grove Village, IL
Kempley ST, Moreiras JW, Petrone FL (2008) Endotracheal tube length for neonatal intubation. Resuscitation 77:369–373
Mainie P, Carmichael A, McCullough S, Kempley ST (2006) Endotracheal tube position in neonates requiring emergency interhospital transfer. Am J Perinatol 23:121–124
Peterson J, Johnson N, Deakins K, Wilson-Costello D, Jelovsek JE, Chatburn R (2006) Accuracy of the 7-8-9 Rule for endotracheal tube placement in the neonate. J Perinatol 26:333–336
Rotschild A, Chitayat D, Puterman ML, Phang MS, Ling E, Baldwin V (1991) Optimal positioning of endotracheal tubes for ventilation of preterm infants. Am J Dis Child 145:1007–1012
Shukla HK, Hendricks-Munoz KD, Atakent Y, Rapaport S (1997) Rapid estimation of insertional length of endotracheal intubation in newborn infants. J Pediatr 131:561–564
Slovis TL, Poland R (1986) Endotracheal tubes in neonates: sonographic positioning. Radiology 160:262–263
Tochen ML (1979) Orotracheal intubation in the newborn infant: a method for determining depth of tube insertion. J Pediatr 95:1050–1051
Todres ID (1993) Pediatric airway control and ventilation. Ann Emerg Med 22:440–444
Whyte KL, Levin R, Powls A (2007) Clinical audit: optimal positioning of endotracheal tubes in neonates. Scott Med J 52:25–27
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This study has been approved by the institutional ethical review board and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Written informed consent was taken from the parents or guardians of the neonate before collecting data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Patrick Van Reempts
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatwavedi, D., Nesargi, S.V., Shankar, N. et al. Evaluation of body parameters for estimation of endotracheal tube length in Indian neonates. Eur J Pediatr 174, 245–249 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2388-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2388-1