Abstract
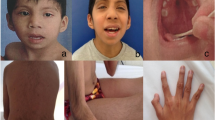
We report a child with a de novo interstitial deletion, 46,XY, int del(9)(9q22.31-q31.2). Cytogenetic and molecular analysis defined the boundaries of the lost region, of paternal origin, from D9S1796 to D9S938. The clinical picture included macrocephaly, frontal bossing, bilateral epicanthus, down-slanted palpebral fissures, low-set ears, hypoplastic nostrils, micrognathia, scoliosis, right single palmar crease, small nails, slender fingers, bilaterally flexed 5th finger, delayed bone age, abnormal metacarpophalangeal pattern (MCPP) profile and sole pits. No major malformation was recorded. The deleted region includes, among others, the PTCH and ROR2 genes. Mutations of the former cause the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS) while mutations in the ROR2 gene have been found both in Robinow syndrome and in brachydactyly type 1B (BDB1). As the patient shows some clinical manifestation of both syndromes, we conclude that phenotypic changes related to haploinsufficiency of PTCH and ROR2 are recognisable in our patient even at a young age and in the presence of the more complex phenotype due to the deletion's large size. Thus the efforts to identify the genes included in a deletion are worthy as they may result in better care of the patient as, in this case, monitoring the possible development of tumours associated with NBCCS.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NBCCS :
-
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
- BDB1 :
-
brachydactyly type 1B
- MCPP :
-
metacarpophalangeal pattern
- STRPs :
-
short tandem repeats
References
Afzal AR, Rajab A, Fenske CD, Oldridge M, Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E, Tuysuz B, Murday VA, Patton MA, Wilkie AO, Jeffery S (2000) Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat Genet 25:419–422
Boonen SE, Tümer Z, Tommerup N, Stahl D, Rosenberg T, Kreiborg S, Kalscheuer V, Brøndum-Nielsen K (2002) Gorlin syndrome in a patient with deletion of the distal part of chromosome 9q and fine mapping of the break points with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Eur J Hum Gen 10(supp1):117 (Abs P0201)
Butler MG, Gale DD, Meaney FJ, Wadlington WB, Robinow M (1987) Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile analysis in Robinow syndrome. Am J Med Genet 27:219–223
Garn SM, Hertzog KP, Poznanski AK, Nagy JM (1972) Metacarpophalangeal length in the evaluation of skeletal malformation. Radiology 105:375–381
Guttenbach M, Engel W, Schmid M (1997) Analysis of structural and numerical chromosome abnormalities in sperm of normal men and carriers of constitutional chromosome aberrations. A review. Hum Genet 100:1–21
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A, Vorechovsky I, Holmberg E, Unden AB, Gillies S, Negus K, Smyth I, Pressman C, Leffell DJ, Gerrard B, Goldstein AM, Dean M, Toftgard R, Chenevix-Trench G, Wainwright B, Bale AE (1996) Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 85:841–851
Oldridge M, Fortuna AM, Maringa M, Propping P, Mansour S, Pollitt C, DeChiara TM, Kimble RB, Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos GD, Wilkie AO (2000) Dominant mutations in ROR2, encoding an orphan receptor tyrosine kinase, cause brachydactyly type B. Nat Genet 24:275–278
Olivieri C, Mira E, Delù G, Pagella F, Zambelli A, Malvezzi L, Buscarini E, Danesino C (2002) Identification of 13 new mutations in the ACVRL1 gene in a group of 52 unselected Italian patients affected by hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Med Genet 39:E39
Schinzel A (2001) Catalogue of unbalanced chromosome aberrations in man, 2nd edn. de Gruyter, Berlin
Shimkets R, Gailani MR, Siu VM, Yang-Feng T, Pressman CL, Levanat S, Goldstein A, Dean M, Bale AE (1996) Molecular analysis of chromosome 9q deletions in two Gorlin syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet 59:417–422
Takeuchi S, Takeda K, Oishi I, Nomi M, Ikeya M, Itoh K, Tamura S, Ueda T, Hatta T, Otani H, Terashima T, Takada S, Yamamura H, Akira S, Minami Y (2000) Mouse Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for the heart development and limb formation. Genes Cells 5:71–78
Van Bokhoven H, Celli J, Kayserili H, Van Beusekom E, Balci S, Brussel W, Skovby F, Kerr B, Percin EF, Akarsu N, Brunner HG (2000) Mutation of the gene encoding the ROR2 tyrosine kinase causes autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome. Nat Genet 25:423–426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olivieri, C., Maraschio, P., Caselli, D. et al. Interstitial deletion of chromosome 9, int del(9)(9q22.31-q31.2), including the genes causing multiple basal cell nevus syndrome and Robinow/brachydactyly 1 syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 162, 100–103 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-002-1116-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-002-1116-4