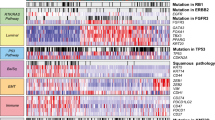
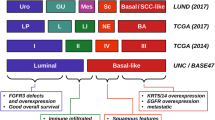
Abstract
Empowered by the recent advances in next generation sequencing and bioinformatics technology, an unprecedented wave of integrated transcriptomic and genomic studies have impacted the field of bladder cancer. These studies not only have confirmed previously charted genetic pathways in bladder cancer development but also have led to the discovery of numerous additional crucial driver genetic alterations. As a result, a novel genomic-based taxonomy is emerging that promises to better define clinically relevant intrinsic subtypes of bladder cancer. The current review is an update on the above advances and their significant implications on the future of bladder cancer patient management.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F (2016) Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol
Kinde I, Munari E, Faraj SF, Hruban RH, Schoenberg M, Bivalacqua T et al (2013) TERT promoter mutations occur early in urothelial neoplasia and are biomarkers of early disease and disease recurrence in urine. Cancer Res 73(24):7162–7167
Mitra AP (2016) Molecular substratification of bladder cancer: moving towards individualized patient management. Ther Adv Urol 8(3):215–233
Netto GJ, Tafe LJ (2016) Emerging bladder cancer biomarkers and targets of therapy. Urol Clin North Am 43(1):63–76
Millán-Rodríguez F, Chéchile-Toniolo G, Salvador-Bayarri J, Palou J, Algaba F, Vicente-Rodríguez J (2000) Primary superficial bladder cancer risk groups according to progression, mortality and recurrence. J Urol 164(3 Pt 1):680–684
Dinney CPN, McConkey DJ, Millikan RE, Wu X, Bar-Eli M, Adam L et al (2004) Focus on bladder cancer. Cancer Cell 6(2):111–116
Wu X-R (2005) Urothelial tumorigenesis: a tale of divergent pathways. Nat Rev Cancer 5(9):713–725
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner SP, Malmström PU, Choi W et al (2016) Bladder cancer. Lancet Lond Engl
Gui Y, Guo G, Huang Y, Hu X, Tang A, Gao S et al (2011) Frequent mutations of chromatin remodeling genes in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Nat Genet 43(9):875–878
Kim J, Akbani R, Creighton CJ, Lerner SP, Weinstein JN, Getz G et al (2015) Invasive bladder cancer: genomic insights and therapeutic promise. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 21(20):4514–4524
Solomon DA, Kim J-S, Bondaruk J, Shariat SF, Wang Z-F, Elkahloun AG et al (2013) Frequent truncating mutations of STAG2 in bladder cancer. Nat Genet 45(12):1428–1430
Balbás-Martínez C, Sagrera A, Carrillo-de-Santa-Pau E, Earl J, Márquez M, Vazquez M et al (2013) Recurrent inactivation of STAG2 in bladder cancer is not associated with aneuploidy. Nat Genet 45(12):1464–1469
Höglund M (2007) On the origin of syn- and metachronous urothelial carcinomas. Eur Urol 51(5):1185–1193
van Tilborg AA, de Vries A, de Bont M, Groenfeld LE, van der Kwast TH, Zwarthoff EC (2000) Molecular evolution of multiple recurrent cancers of the bladder. Hum Mol Genet 9(20):2973–2980
Nordentoft I, Lamy P, Birkenkamp-Demtröder K, Shumansky K, Vang S, Hornshøj H et al (2014) Mutational context and diverse clonal development in early and late bladder cancer. Cell Rep 7(5):1649–1663
Lamy P, Nordentoft I, Birkenkamp-Demtröder K, Thomsen MBH, Villesen P, Vang S et al (2016) Paired exome analysis reveals clonal evolution and potential therapeutic targets in urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Res 76(19):5894–5906
Malats N, Bustos A, Nascimento CM, Fernandez F, Rivas M, Puente D et al (2005) P53 as a prognostic marker for bladder cancer: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol 6(9):678–686
Chatterjee SJ, Datar R, Youssefzadeh D, George B, Goebell PJ, Stein JP et al (2004) Combined effects of p53, p21, and pRb expression in the progression of bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 22(6):1007–1013
Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y (2007) Predictive value of cell cycle biomarkers in nonmuscle invasive bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol 177(2):481–487 discussion 487
van Rhijn BWG, Zuiverloon TCM, Vis AN, Radvanyi F, van Leenders GJLH, Ooms BCM et al (2010) Molecular grade (FGFR3/MIB-1) and EORTC risk scores are predictive in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 58(3):433–441
van Rhijn BWG, Vis AN, van der Kwast TH, Kirkels WJ, Radvanyi F, Ooms ECM et al (2003) Molecular grading of urothelial cell carcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 and MIB-1 is superior to pathologic grade for the prediction of clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 21(10):1912–1921
Quintero A, Alvarez-Kindelan J, Luque RJ, Gonzalez-Campora R, Requena MJ, Montironi R et al (2006) Ki-67 MIB1 labelling index and the prognosis of primary TaT1 urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Clin Pathol 59(1):83–88
Margulis V, Lotan Y, Karakiewicz PI, Fradet Y, Ashfaq R, Capitanio U et al (2009) Multi-institutional validation of the predictive value of Ki-67 labeling index in patients with urinary bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(2):114–119
Lopez-Beltran A, Luque RJ, Alvarez-Kindelan J, Quintero A, Merlo F, Carrasco JC et al (2004) Prognostic factors in stage T1 grade 3 bladder cancer survival: the role of G1-S modulators (p53, p21Waf1, p27kip1, cyclin D1, and cyclin D3) and proliferation index (ki67-MIB1). Eur Urol 45(5):606–612
Kim PH, Cha EK, Sfakianos JP, Iyer G, Zabor EC, Scott SN et al (2015) Genomic predictors of survival in patients with high-grade urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 67(2):198–201
di Martino E, Tomlinson DC, Knowles MA (2012) A decade of FGF receptor research in bladder cancer: past, present, and future challenges. Adv Urol 2012:429213
van Rhijn BWG, van der Kwast TH, Liu L, Fleshner NE, Bostrom PJ, Vis AN et al (2012) The FGFR3 mutation is related to favorable pT1 bladder cancer. J Urol 187(1):310–314
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden APM, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L et al (2006) Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol 49(3):465–477
Catto JWF, Azzouzi A-R, Rehman I, Feeley KM, Cross SS, Amira N et al (2005) Promoter hypermethylation is associated with tumor location, stage, and subsequent progression in transitional cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 23(13):2903–2910
Yates DR, Rehman I, Abbod MF, Meuth M, Cross SS, Linkens DA et al (2007) Promoter hypermethylation identifies progression risk in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 13(7):2046–2053
Lindgren D, Sjödahl G, Lauss M, Staaf J, Chebil G, Lövgren K, et al (2012) Integrated genomic and gene expression profiling identifies two major genomic circuits in urothelial carcinoma. PLoS ONE 7(6)
Lindgren D, Frigyesi A, Gudjonsson S, Sjödahl G, Hallden C, Chebil G et al (2010) Combined gene expression and genomic profiling define two intrinsic molecular subtypes of urothelial carcinoma and gene signatures for molecular grading and outcome. Cancer Res 70(9):3463–3472
Choi W, Porten S, Kim S, Willis D, Plimack ER, Hoffman-Censits J et al (2014) Identification of distinct basal and luminal subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with different sensitivities to frontline chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 25(2):152–165
Damrauer JS, Hoadley KA, Chism DD, Fan C, Tiganelli CJ, Wobker SE et al (2014) Intrinsic subtypes of high-grade bladder cancer reflect the hallmarks of breast cancer biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(8):3110–3115
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2014) Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder carcinoma. Nature 507(7492):315–322
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Ochoa A, Siefker-Radtke A, Czerniak B, Dinney CPN (2015) Therapeutic opportunities in the intrinsic subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 29(2):377–394
Dadhania V, Zhang M, Zhang L, Bondaruk J, Majewski T, Siefker-Radtke A et al (2016) Meta-analysis of the luminal and basal subtypes of bladder cancer and the identification of signature immunohistochemical markers for clinical use. EBioMedicine 12:105–117
Dyrskjøt L, Thykjaer T, Kruhøffer M, Jensen JL, Marcussen N, Hamilton-Dutoit S et al (2003) Identifying distinct classes of bladder carcinoma using microarrays. Nat Genet 33(1):90–96
Dyrskjøt L, Kruhøffer M, Thykjaer T, Marcussen N, Jensen JL, Møller K et al (2004) Gene expression in the urinary bladder: a common carcinoma in situ gene expression signature exists disregarding histopathological classification. Cancer Res 64(11):4040–4048
Dyrskjøt L, Zieger K, Kruhøffer M, Thykjaer T, Jensen JL, Primdahl H et al (2005) A molecular signature in superficial bladder carcinoma predicts clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 11(11):4029–4036
Dyrskjøt L, Zieger K, Real FX, Malats N, Carrato A, Hurst C et al (2007) Gene expression signatures predict outcome in non-muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma: a multicenter validation study. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 13(12):3545–3551
Biton A, Bernard-Pierrot I, Lou Y, Krucker C, Chapeaublanc E, Rubio-Pérez C et al (2014) Independent component analysis uncovers the landscape of the bladder tumor transcriptome and reveals insights into luminal and basal subtypes. Cell Rep 9(4):1235–1245
Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490(7418):61–70
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2012) Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 489(7417):519–525
Ho PL, Kurtova A, Chan KS (2012) Normal and neoplastic urothelial stem cells: getting to the root of the problem. Nat Rev Urol 9(10):583–594
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Dinney CPN (2015) Genetic subtypes of invasive bladder cancer. Curr Opin Urol 25(5):449–458
Hedegaard J, Lamy P, Nordentoft I, Algaba F, Høyer S, Ulhøi BP et al (2016) Comprehensive transcriptional analysis of early-stage urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Cell 30(1):27–42
Lerner SP, DJ MC, Hoadley KA, Chan KS, Kim WY, Radvanyi F et al (2016) Bladder cancer molecular taxonomy: summary from a consensus meeting. Bladder Cancer 2(1):37–47
Carneiro BA, Meeks JJ, Kuzel TM, Scaranti M, Abdulkadir SA, Giles FJ (2015) Emerging therapeutic targets in bladder cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 41(2):170–178
Montironi R, Santoni M, Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L, Moch H, Scarpelli M (2015) Morphologic and molecular backgrounds for personalized management of genito-urinary cancers: an overview. Curr Drug Targets 16(2):96–102
Gartrell BA, Sonpavde G (2013) Emerging drugs for urothelial carcinoma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 18(4):477–494
Bellmunt J, Teh BT, Tortora G, Rosenberg JE (2013) Molecular targets on the horizon for kidney and urothelial cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10(10):557–570
Fahmy M, Mansure JJ, Brimo F, Yafi FA, Segal R, Althunayan A et al (2013) Relevance of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in the prognosis of patients with high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Hum Pathol 44(9):1766–1772
Chaux A, Compérat E, Varinot J, Hicks J, Lecksell K, Solus J et al (2013) High levels of phosphatase and tensin homolog expression are associated with tumor progression, tumor recurrence, and systemic metastases in pT1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: a tissue microarray study of 156 patients treated by transurethral resection. Urology 81(1):116–122
Gonzalez-Roibon ND, Chaux A, Al-Hussain T, Osunkoya AO, Bezerra SM, Hicks J et al (2013) Dysregulation of mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in plasmacytoid variant of urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Hum Pathol 44(4):612–622
Schultz L, Chaux A, Albadine R, Hicks J, Kim JJ, De Marzo AM et al (2011) Immunoexpression status and prognostic value of mTOR and hypoxia-induced pathway members in primary and metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 35(10):1549–1556
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS, Loriot Y, Cruz C et al (2014) MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature 515(7528):558–562
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y, Smith WB, Fedorov O et al (2010) Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468(7327):1067–1073
Fedorov O, Lingard H, Wells C, Monteiro OP, Picaud S, Keates T et al (2014) [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]phthalazines: inhibitors of diverse bromodomains. J Med Chem 57(2):462–476
Hay DA, Fedorov O, Martin S, Singleton DC, Tallant C, Wells C et al (2014) Discovery and optimization of small-molecule ligands for the CBP/p300 bromodomains. J Am Chem Soc 136(26):9308–9319
Mooso BA, Vinall RL, Mudryj M, Yap SA, deVere White RW, Ghosh PM (2015) The role of EGFR family inhibitors in muscle invasive bladder cancer: a review of clinical data and molecular evidence. J Urol 193(1):19–29
Hayashi T, Seiler R, Oo HZ, Jäger W, Moskalev I, Awrey S et al (2015) Targeting HER2 with T-DM1, an antibody cytotoxic drug conjugate, is effective in HER2 over expressing bladder cancer. J Urol 194(4):1120–1131
Bajorin DF, Sharma P, Quinn DI, Plimack ER, Hoffman-Censits JH, O’Donnell PH, et al (2016) Phase 2 trial results of DN24-02, a HER2-targeted autologous cellular immunotherapy in HER2+ urothelial cancer patients (pts). J Clin Oncol 34(4513)
Richards DA, Braiteh FS, Garcia AA, Denlinger CS, Conkling PR, Edenfield WJ et al (2014) A phase 1 study of MM-111, a bispecific HER2/HER3 antibody fusion protein, combined with multiple treatment regimens in patients with advanced HER2-positive solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 32(651):5
Hussain MHA, MacVicar GR, Petrylak DP, Dunn RL, Vaishampayan U, Lara PN et al (2007) Trastuzumab, paclitaxel, carboplatin, and gemcitabine in advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor-2/neu-positive urothelial carcinoma: results of a multicenter phase II National Cancer Institute trial. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 25(16):2218–2224
Hansel DE, Swain E, Dreicer R, Tubbs RR (2008) HER2 overexpression and amplification in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder is associated with MYC coamplification in a subset of cases. Am J Clin Pathol 130(2):274–281
Dees EC, Infante JR, Cohen RB, O’Neil BH, Jones S, von Mehren M et al (2011) Phase 1 study of MLN8054, a selective inhibitor of aurora A kinase in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67(4):945–954
Dees EC, Cohen RB, von Mehren M, Stinchcombe TE, Liu H, Venkatakrishnan K et al (2012) Phase I study of aurora A kinase inhibitor MLN8237 in advanced solid tumors: safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and bioavailability of two oral formulations. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 18(17):4775–4784
Lin C-C, Su W-C, Yen C-J, Hsu C-H, Su W-P, Yeh K-H et al (2014) A phase I study of two dosing schedules of volasertib (BI 6727), an intravenous polo-like kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Br J Cancer 110(10):2434–2440
Thomsen MBH, Nordentoft I, Lamy P, Høyer S, Vang S, Hedegaard J et al (2016) Spatial and temporal clonal evolution during development of metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Mol Oncol 10(9):1450–1460
Dinney CPN, Hansel D, McConkey D, Shipley W, Hagan M, Dreicer R et al (2014) Novel neoadjuvant therapy paradigms for bladder cancer: results from the National Cancer Center Institute forum. Urol Oncol 32(8):1108–1115
Zargar H, Espiritu PN, Fairey AS, Mertens LS, Dinney CP, Mir MC et al (2015) Multicenter assessment of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 67(2):241–249
Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM, Speights VO, Vogelzang NJ, Trump DL et al (2003) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 349(9):859–866
International Collaboration of Trialists, Medical Research Council Advanced Bladder Cancer Working Party (now the National Cancer Research Institute Bladder Cancer Clinical Studies Group), European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Genito-Urinary Tract Cancer Group, Australian Bladder Cancer Study Group, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group, Finnbladder et al (2011) International phase III trial assessing neoadjuvant cisplatin, methotrexate, and vinblastine chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: long-term results of the BA06 30894 trial. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 29(16):2171–2177
Plimack ER, Dunbrack RL, Brennan TA, Andrake MD, Zhou Y, Serebriiskii IG et al (2015) Defects in DNA repair genes predict response to neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol 68(6):959–967
Xylinas E, Hassler MR, Zhuang D, Krzywinski M, Erdem Z, Robinson BD, et al (2016) An epigenomic approach to improving response to neoadjuvant cisplatin chemotherapy in bladder cancer. Biomolecules 6(3)
Rosenberg JE, Hoffman-Censits J, Powles T, van der Heijden MS, Balar AV, Necchi A et al (2016) Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 387(10031):1909–1920
Netto GJ (2016) Role for anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitor in advanced urothelial carcinoma. Lancet Lond Engl 387(10031):1881–1882
Bellmunt J, de Wit R, Vaughn DJ, Fradet Y, Lee J-L, Fong L, et al (2017) Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med 17
Mitra AP, Cote RJ (2009) Molecular pathogenesis and diagnostics of bladder cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 4:251–285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors adhere to institutional ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
The authors received no funding.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eich, ML., Dyrskjøt, L. & Netto, G.J. Toward personalized management in bladder cancer: the promise of novel molecular taxonomy. Virchows Arch 471, 271–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-017-2119-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-017-2119-x