Abstract
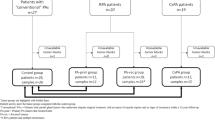
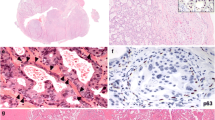
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is the most common salivary gland neoplasm, and while mostly benign, recurrences (RPA) and malignant transformation to carcinoma ex-PA (CXPA) do occur. Cell cycle proteins important in its tumorigenesis have been studied as markers for PA with a high risk of RPA or CXPA. The aim of the present study was to investigate cell cycle markers p-16, cyclin D1, CDK4, E2F, and retinoblastoma (Rb) in this context. Expression of p16, cyclin D1, E2F, CDK4, and Rb was studied by immunohistochemistry in 24 cases of PA, 21 of RPA, and 2 of CXPA. The presence of HPV was assessed by in situ hybridization. Immunostaining for p16 and cyclin D1 was negative or weakly positive in most cases of PA while strongly positive in the majority of RPA and both CXPA cases. Staining for Rb and CDK4 was either negative or weakly positive in PA, RPA, and CXPA. Expression of E2F was stronger in RPA and CXPA than in PA. Nuclear reactivity for HPV was not observed in any case. In conclusion, the strong staining for p16, cyclinD1, and E2F in RPA and CXPA, while weak or negative in PA, suggests that these proteins might be involved in recurrence and malignant transformation of PA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oliveira F, Duarte E, Taveira C et al (2009) Salivary gland tumor: a review of 599 cases in a Brazilian population. Head Neck Pathol 3:271–275
Li L, Li Y, Wen Y et al (2008) Clinical analysis of salivary gland tumor cases in West China in past 50 years. Oral Oncol 44:187–192
Chidzonga M, Lopez-Perez V, Portilla-Alvarez A (1995) Salivary gland tumours in Zimbabwe: report of 282 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 24:293–297
Barnes L, Everson JW, Reichart P et al (2005) World Health Organization classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics head and neck tumours. IARC Press, Lyon
Suh M, Hah J, Kwon S et al (2009) Clinical manifestations of recurrent parotid pleomorphic adenoma. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 2:193–197
Chen A, Granchi P, Garcia J (2007) Local-regional recurrence after surgery without postoperative irradiation for carcinomas of the major salivary glands: implications for adjuvant therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:982–987
Duck S, Mcconnel F (1993) Malignant degeneration of pleomorphic adenoma–clinical implications. Am J Otolaryngol 14:175–178
Fleming WB (1987) Recurrent pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid. Aust N Z J Surg 57:173–176
Soares AB, Altemani A, de Araújo VC (2011) Study of histopathological, morphological and immunohistochemical features of recurrent pleomorphic adenoma: an attempt to predict recurrence of pleomorphic adenoma. J Oral Pathol Med 40:352–358
Cohen JA, Geradts J (1997) Loss of RB and MTS1/CDKN2 (p16) expression in human sarcomas. Hum Pathol 28:893–898
Yuan J, Knorr J, Altmannsberger M et al (1999) Expression of p16 and lack of pRB in primary small cell lung cancer. J Pathol 189:358–362
Feakins RM, Nickols CD, Bidd H et al (2003) Abnormal expression of pRb, p16, and cyclin D1 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its lymph node metastases: relationship with pathological features and survival. Hum Pathol 34:1276–1282
Schwerer MJ, Sailer A, Kraft K et al (2003) Expression of retinoblastoma gene product in respiratory epithelium and sinonasal neoplasms: relationship with p16 and cyclin D1 expression. Histol Histopathol 18:143–151
Ihrler S, Weiler C, Hirschmann A et al (2007) Intraductal carcinoma is the precursor of carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma and is often associated with dysfunctional p53. Histopathology 51:362–371
Altemani A, Martins M, Freitas L, Soares F, Araújo N, Araújo V (2005) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA): immunoprofile of the cells involved in carcinomatous progression. Histopathology 46:635–641
Soares AB, Ponchio L, Juliano PB et al (2007) Lymphatic vascular density and lymph angiogenesis during tumour progression of carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. J Clin Pathol 60:995–1000
Soares AB, Demasi AP, Altemani A et al (2011) Increased mucin 1 expression in recurrence and malignant transformation of salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma. Histopathology 58:377–382
Soares AB, Demasi AP, Tincani AJ et al (2012) The increased PDGF-A, PDGF-B and FGF-2 expression in recurrence of salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma. J Clin Pathol 65:272–277
Salzman R, Stárek I, Kučerová L et al (2014) Neither expression of VEGF-C/D nor lymph vessel density supports lymphatic invasion as the mechanism responsible for local spread of recurrent salivary pleomorphic adenoma. Virchows Arch 464:29–34
El-Mofty SK, Lu DW (2003) Prevalence of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in squamous cell carcinoma of the palatine tonsil, and not the oral cavity, in young patients: a distinct clinicopathologic and molecular disease entity. Am J Surg Pathol 27:1463–1470
Etges A, Nunes FD, Ribeiro KCB et al (2004) Immunohistochemical expression of retinoblastoma pathway proteins in normal salivary glands and in salivary gland tumours. Oral Oncol 40:326–331
Di Vinci A, Perdelli L, Banelli B et al (2005) p16(INK4a) promoter methylation and protein expression in breast fibroadenoma and carcinoma. Int J Cancer 114:414–421
Ferrazzo KL, Neto MM, Santos E et al (2009) Differential expression of galectin-3, beta-catenin, and cyclin d1 in adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma of salivary glands. J Oral Pathol Med 38:701–707
Etges A, Pinto DS, Kowalski LP et al (2003) Salivary duct carcinoma: immunohistochemical profile of an aggressive salivary gland tumour. J Clin Pathol 56:914–918
Vékony H, Röser K, Löning T et al (2008) Deregulated expression of p16INK4a and p53 pathway members in benign and malignant myoepithelial tumours of the salivary glands. Histopathology 53:658–666
Jour G, West K, Ghali V et al (2013) Differential expression of p16(ink4a) and cyclin d1 in benign and malignant salivary gland tumors: a study of 44 cases. Head Neck Pathol 7:224–231
Weber A, Langhanki L, Schütz A, Wittekind C, Bootz F, Tannapfel A (2002) Alterations of the INK4a-ARF gene locus in pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. J Pathol 198:326–334
Patel RS, Rose B, Bawdon H, Hong A, Lee CS, Fredericks S, Gao K, O’Brien CJ (2007) Cyclin D1 and p16 expression in pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Histopathology 51:691–696
Maruya S, Kurotaki H, Shimoyama N et al (2003) Expression of p16 protein and hypermethylation status of its promoter gene in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 65:26–32
Hu YA, Zhang CY, Tian Z et al (2011) Aberrant protein expression and promoter methylation of p16 gene are correlated with malignant transformation of salivary pleomorphic adenoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135:882–889
Rittà M, De Andrea M, Mondini M et al (2009) Cell cycle and viral and immunologic profiles of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma as predictable variables of tumor progression. Head Neck 31:318–327
Motokura T, Arnold A (1993) PRAD1/cyclin D1 proto-oncogene: genomic organization, 5′ DNA sequence, and sequence of a tumor-specific rearrangement breakpoint. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 7:89–95
Masuda M, Hirakawa N, Nakashima T et al (1996) Cyclin D1 overexpression in primary hypopharyngeal carcinomas. Cancer 78:390–395
Shin KY, Kong G, Kim WS et al (1997) Overexpression of cyclin D1 correlates with early recurrence in superficial bladder cancers. Br J Cancer 75:1788–1792
Yasumatsu R, Kuratomi Y, Nakashima et al (2004) Cyclin D1 expression does not affect cell proliferation in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 261:526–530
Liu T, Zhu E, Wang L et al (2005) Abnormal expression of Rb pathway-related proteins in salivary gland acinic cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 36:962–970
Greer R, Said S, Shroyer K et al (2007) Overexpression of cyclin D1 and cortactin is primarily independent of gene amplification in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol 43:735–741
Kishimoto I, Mitomi H, Ohkura Y et al (2008) Abnormal expression of p16 (INK4a), cyclin D1, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and retinoblastoma protein in gastric carcinomas. J Surg Oncol 98:60–66
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J et al (2007) Molecular biology of the cell. Artmed, Porto Alegre
Parry D, Bates S, Mann DJ et al (1995) Lack of cyclin D-Cdk complexes in Rb-negative cells correlates with high levels of p16INK4/MTS1 tumour suppressor gene product. EMBO J 14:503–511
Lukas J, Aagaard L, Strauss M et al (1995) Oncogenic aberrations of p16INK4/CDKN2 and cyclin D1 cooperate to deregulate G1 control. Cancer Res 55:4818–4823
Shintani S, Mihara M, Nakahara Y et al (2000) Infrequent alternations of RB pathway (Rb-p16INK4A-cyclinD1) in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary glands. Anticancer Res 20:2169–2175
Kishi M, Nakamura M, Nishimine M et al (2004) Genetic and epigenetic alteration profiles for multiple genes in salivary gland carcinomas. Oral Oncol 41:161–169
Tarakji B (2011) Immunohistochemical expression of pRb in pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 16:e323–e329
Bringold F, Serrano M (2000) Tumor suppressors and oncogenes in cellular senescence. Exp Gerontol 35:317–329
Ralhan R, Mathew R, Arora S et al (2000) Frequent alterations in the expression of tumor suppressor genes p16INK4A and pRb in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in the Indian population. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:655–660
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Jeruza Pinheiro da Silveira Bossonaro and Nadir Freitas for their excellent technical expertise and assistance. Dr. Amy Brown is acknowledged for her help with the final English revision. This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) (number 12/00757-1).
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza, A.A., Altemani, A., Passador-Santos, F. et al. Dysregulation of the Rb pathway in recurrent pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary glands. Virchows Arch 467, 295–301 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1804-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1804-x