Abstract
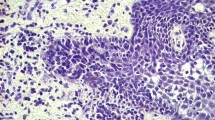
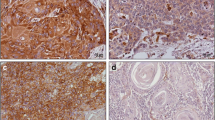
Podoplanin is involved in actin remodeling of the cytoskeleton of tumor cells and may promote tumor cell invasion by increasing cell motility and formation of filopodia-like membrane protrusions. Podoplanin is expressed in a variety of tumors, but its role in head and neck cancer, particularly in oral squamous cell carcinoma, remains unclear. We studied podoplanin expression by immunohistochemistry in 92 oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) using a monoclonal antibody against an epitope of podoplanin (D2-40). In terms of the number of stained cells, 34 OSCC (38 %) had low podoplanin expression (less than 33 % of cells), 33 (36 %) showed moderate expression (between 34 and 66 % of cells), and 21 (22 %) showed high expression. The intensity of immunostaining was strong in 26 (28 %) cases, moderate in 36 (40 %), and weak or negative in the remaining 30 tumors (32 %). Immunohistochemical expression of podoplanin was associated with a tumor histological grade. A diffuse pattern of podoplanin expression significantly decreased in moderately differentiated (37 %) and poorly differentiated (20 %) carcinomas compared to well-differentiated (43 %) carcinomas. In addition, the focal expression of podoplanin in the invasion front of the tumor, without expression in the tumor center, was observed in 72 % of well-differentiated tumors, 27 % of moderate tumors, and 0 % of poorly differentiated tumors. Moreover, a trend was found toward an association of diffuse podoplanin staining with the development of second primary carcinomas (13 %), in contrast to its expression in the invasion front (3 %). No association was observed between podoplanin expression and nodal metastasis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vormittag L, Thurnher D, Geleff S, Pammer J, Heiduschka G, Brunner M, Grasl MC, Erovic BM (2009) Co-expression of Bmi-1 and podoplanin predicts overall survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with radio(chemo)therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:913–918
Zbaren P, Lehmann W (1987) Frequency and sited of distant metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. An analysis of 101 cases at autopsy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:762–764
Kreppel M, Scheer M, Drebber U, Ritter L, Zöller JE (2010) Impact of podoplanin expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: clinical and histopathologic correlations. Virchows Arch 456:473–482
Wicki A, Christofori G (2007) The potential role of podoplanin in tumour invasion. Br J Cancer 96:1–5
Schacht V, Dadras SS, Johnson LA, Jackson DG, Hong YK, Detmar M (2005) Up-regulation of the lymphatic marker podoplanin, a mucin-type transmembrane glycoprotein, in human squamous cell carcinomas and germ cell tumors. Am J Pathol 166:913–921
Huber GF, Fritzsche FR, Züllig L, Storz M, Graf N, Haerle SK, Jochum W, Stoeckli SJ, Moch H (2011) Podoplanin expression correlates with sentinel lymph node metastasis in early squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and oropharynx. Int J Cancer 129:1404–1409
Martín-Villar E, Scholl FG, Gamallo C, Yurrita MM, Muñoz-Guerra M, Cruces J, Quintanilla M (2005) Characterization of human PA2.26 antigen (T1alpha-2, podoplanin), a small membrane mucin induced in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 113:899–910
Martín-Villar E, Megías D, Castel S, Yurrita MM, Vilaró S, Quintanilla M (2006) Podoplanin binds ERM proteins to activate RhoA and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 21):4541–4553
Wicki A, Lehembre F, Wick N, Hantusch B, Kerjaschki D, Christofori G (2006) Tumor invasion in the absence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition: podoplanin-mediated remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Cell 9:261–272
Dumoff KL, Chu C, Xu X, Pasha T, Zhang PJ, Acs G (2005) Low D2-40 immunoreactivity correlates with lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Mod Pathol 18:97–104
Yuan P, Temam S, El-Naggar A, Zhou X, Liu DD, Lee JJ, Mao L (2006) Overexpression of podoplanin in oral cancer and its association with poor clinical outcome. Cancer 107:563–569
Chuang WY, Yeh CJ, Wu YC, Chao YK, Liu YH, Tseng CK, Chang HK, Liu HP, Hsueh C (2009) Tumor cell expression of podoplanin correlates with nodal metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Histol Histopathol 24:1021–1027
de Vicente JC, Rodrigo JP, Rodríguez-Santamarta T, Lequerica-Fernández P, Allonca E, García-Pedrero JM (2013) Podoplanin expression in oral leukoplakia: tumorigenic role. Oral Oncol 49:598–603
Kreppel M, Drebber U, Wedemeyer I, Eich HT, Backhaus T, Zöller JE, Scheer M (2011) Podoplanin expression predicts prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy. Oral Oncol 47:873–878
Kyzas PA, Geleff S, Batistatou A, Agnantis NJ, Stefanou D (2005) Evidence for lymphangiogenesis and its prognostic implications in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol 206:170–177
Rodrigo JP, García-Carracedo D, González MV, Mancebo G, Fresno MF, García-Pedrero J (2010) Podoplanin expression in the development and progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Cancer 9:48
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG, Balch CM, Haller DG, Morrow M (2002) American Joint Committee on Cancer staging manual, 6th edn. Springer, New York
Goldstein BY, Chang SC, Hashibe M, La Vecchia C, Zhang ZF (2010) Alcohol consumption and cancers of the oral cavity and pharynx from 1988 to 2009: an update. Eur J Cancer Prev 19:431–465
Remmele W, Schicketanz KH (1993) Immunohistochemical determination of estrogen and progesterone receptor content in human breast cancer. Computer-assisted image analysis (QIC score) vs. subjective grading (IRS). Pathol Res Pract 189:862–866
Dumoff KL, Chu CS, Harris EE, Holtz D, Xu X, Zhang PJ, Acs G (2006) Low podoplanin expression in pretreatment biopsy material predicts poor prognosis in advanced-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix treated by primary radiation. Mod Pathol 19:708–716
Schacht V, Ramirez MI, Hong YK, Hirakawa S, Feng D, Harvey N, Williams M, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF, Oliver G, Detmar M (2003) T1alpha/podoplanin deficiency disrupts normal lymphatic vasculature formation and causes lymphedema. EMBO J 22:3546–3556
Sleeman JP, Krishnan J, Kirkin V, Baumann P (2001) Markers for the lymphatic endothelium: in search of the holy grail? Microsc Res Tech 55:61–69
Hirakawa S, Hong YK, Harvey N, Schacht V, Matsuda K, Libermann T, Detmar M (2003) Identification of vascular lineage-specific genes by transcriptional profiling of isolated blood vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 162:575–586
Funayama A, Cheng J, Maruyama S, Yamazaki M, Kobayashi T, Syafriadi M, Kundu S, Shingaki S, Saito C, Saku T (2011) Enhanced expression of podoplanin in oral carcinomas in situ and squamous cell carcinomas. Pathobiology 78:171–180
Maula SM, Luukkaa M, Grénman R, Jackson D, Jalkanen S, Ristamäki R (2003) Intratumoral lymphatics are essential for the metastatic spread and prognosis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck region. Cancer Res 63:1920–1926
Nakayama Y, Matsumoto K, Nagato M, Inoue Y, Katsuki T, Minagawa N, Shibao K, Tsurudome Y, Hirata K, Higure A, Sako T, Nagata N (2007) Significance of lymphangiogenesis as assessed by immunohistochemistry for podoplanin in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 27:619–625
Margaritescu C, Raica M, Pirici D, Simionescu C, Mogoanta L, Stinga AC, Stinga AS, Ribatti D (2010) Podoplanin expression in tumor-free resection margins of oral squamous cell carcinomas: an immunohistochemical and fractal analysis study. Histol Histopathol 25:701–711
Liang P, Hong JW, Ubukata H, Liu HR, Watanabe Y, Katano M, Motohashi G, Kasuga T, Nakada I, Tabuchi T (2006) Increased density and diameter of lymphatic microvessels correlate with lymph node metastasis in early stage invasive colorectal carcinoma. Virchows Arch 448:570–575
Schoppmann SF, Bayer G, Aumayr K, Taucher S, Geleff S, Rudas M, Kubista E, Hausmaninger H, Samonigg H, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Horvat R, Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group (2004) Prognostic value of lymphangiogenesis and lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg 240:306–312
Van der Auwera I, Van den Eynden GG, Colpaert CG, Van Laere SJ, van Dam P, Van Marck EA, Dirix LY, Vermeulen PB (2005) Tumor lymphangiogenesis in inflammatory breast carcinoma: a histomorphometric study. Clin Cancer Res 11:7637–7642
Roma AA, Magi-Galluzzi C, Kral MA, Jin TT, Klein EA, Zhou M (2006) Peritumoral lymphatic invasion is associated with regional lymph node metastases in prostate adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 19:392–398
Shimada Y, Ishii G, Nagai K, Atsumi N, Fujii S, Yamada A, Yamane Y, Hishida T, Nishimura M, Yoshida J, Ikeda N, Ochiai A (2009) Expression of podoplanin, CD44, and p63 in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Sci 100:2054–2059
Zhao D, Pan J, Li XQ, Wang XY, Tang C, Xuan M (2008) Intratumoral lymphangiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. J Oral Pathol Med 37:616–625
de Sousa SF, Gleber-Netto FO, de Oliveira-Neto HH, Batista AC, Nogueira Guimarães Abreu MH, de Aguiar MC (2012) Lymphangiogenesis and podoplanin expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma and the associated lymph nodes. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 20:588–594
Muñoz-Guerra MF, Marazuela EG, Martín-Villar E, Quintanilla M, Gamallo C (2004) Prognostic significance of intratumoral lymphangiogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer 100:553–560
Ohno F, Nakanishi H, Abe A, Seki Y, Kinoshita A, Hasegawa Y, Tatematsu M, Kurita K (2007) Regional difference in intratumoral lymphangiogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinomas evaluated by immunohistochemistry using D2-40 and podoplanin antibody: an analysis in comparison with angiogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med 36:281–289
Cueni LN, Hegyi I, Shin JW, Albinger-Hegyi A, Gruber S, Kunstfeld R, Moch H, Detmar M (2010) Tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to lymph nodes induced by cancer cell expression of podoplanin. Am J Pathol 177:1004–1016
Chung MK, Min JY, So YK, Ko YH, Jeong HS, Son YI, Baek CH (2010) Correlation between lymphatic vessel density and regional metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Head Neck 32:445–451
Al-Hajj M, Clarke MF (2004) Self-renewal and solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene 23:7274–7282
Prince ME, Sivanandan R, Kaczorowski A, Wolf GT, Kaplan MJ, Dalerba P, Weissman IL, Clarke MF, Ailles LE (2007) Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:973–978
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Marino Santirso, who acted as the language consultant for the final edited version. The authors disclosed that they have no significant relationships with or financial interest in any commercial companies pertaining to this article. This study was supported by grants from the Plan Nacional de I + D + I 2013–2016 ISCIII (CP13/00013 and PI13/00259), RD12/0036/0015 of Red Temática de Investigación Cooperativa en Cáncer (RTICC), Spain, and the FEDER Funding Program from the European Union.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Vicente, J.C., Santamarta, T.R., Rodrigo, J.P. et al. Expression of podoplanin in the invasion front of oral squamous cell carcinoma is not prognostic for survival. Virchows Arch 466, 549–558 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1746-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-015-1746-3