Abstract
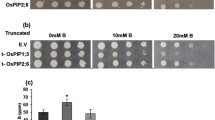
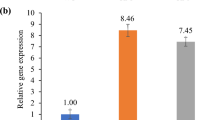
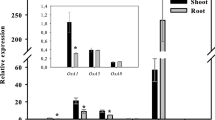
Boron (B) toxicity is responsible for low cereal crop production in a number of regions worldwide. In this report, we characterized two rice genes, OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7, for their involvement in B permeability and tolerance. Transcript analysis demonstrated that the expression of OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7 were downregulated in shoots and strongly upregulated in rice roots by high B treatment. Expression of both OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7 in yeast HD9 strain lacking Fps1, ACR3, and Ycf1 resulted in an increased B sensitivity. Furthermore, yeast HD9 strain expressing OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7 accumulated significantly higher B as compared to empty vector control, which suggests their involvement in B transport. Overexpression of OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7 in Arabidopsis imparted higher tolerance under B toxicity. Arabidopsis lines overexpressing OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7 showed significantly higher biomass production and greater root length, however there was no difference in B accumulation in long term uptake assay. Short-term uptake assay using tracer B (10B) in shoots and roots demonstrated increased 10B accumulation in Arabidopsis lines expressing OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7, compare to wild type control plants. Efflux assay of B in the roots showed that 10B was effluxed from the Arabidopsis transgenic plants overexpressing OsPIP2;4 or OsPIP2;7 during the initial 1-h of assay. These data indicate that OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7 are involved in mediating B transport in rice and provide tolerance via efflux of excess B from roots and shoot tissues. These genes will be highly useful in developing B tolerant crops for enhanced yield in the areas affected by high B toxicity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal A, Sankararamakrishnan R (2007) Homology modeling of major intrinsic proteins in rice, maize and Arabidopsis: comparative analysis of transmembrane helix association and aromatic/arginine selectivity filters. BMC Struct Biol 7:27
Bechtold N, Pelletier G (1993) In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. In: Martinez-Zapater J, Salinas J (eds) Arabidopsis protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 259–266
Bienert G, Thorsen M, Schüssler M, Nilsson H, Wagner A, Tamás M, Jahn T (2008) A subgroup of plant aquaporins facilitate the bi-directional diffusion of As(OH)3 and Sb(OH)3 across membranes. BMC Biol 6:1–15
Cabello-Hurtado F, Ramos J (2004) Isolation and functional analysis of the glycerol permease activity of two new nodulin-like intrinsic proteins from salt stressed roots of the halophyte Atriplex nummularia. Plant Sci 166:633–640
Chaumont F, Barrieu F, Jung R, Chrispeels MJ (2000) Plasma membrane intrinsic proteins from maize cluster in two sequence subgroups with differential aquaporin activity. Plant Physiol 122:1025–1034
Chiba Y, Mitani N, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2009) HvLsi1 is a silicon influx transporter in barley. Plant J 57:810–818
Dannel F, Pfeffer H, Romheld V (2000) Characterization of root boron pools, boron uptake and boron translocation in sunflower using the stable isotopes 10B and 11B. Aust J Plant Physiol 27:397–405
Dannel F, Pfeffer H, Romheld V (2002) Update on boron in higher plants—uptake, primary translocation and compartmentation. Plant Biol 4:193–204
Dhankher OP, Li Y, Rosen BP, Shi J, Salt D, Senecoff JF, Sashti NA, Meagher RB (2002) Engineering tolerance and hyperaccumulation of arsenic in plants by combining arsenate reductase and [gamma]-glutamylcysteine synthetase expression. Nat Biotech 20:1140–1145
Dordas C, Chrispeels MJ, Brown PH (2000) Permeability and channel-mediated transport of boric acid across membrane vesicles isolated from squash roots. Plant Physiol 124:1349–1361
Fetter K, Van Wilder V, Moshelion M, Chaumont F (2004) Interactions between plasma membrane aquaporins modulate their water channel activity. Plant Cell 16:215–228
Fitzpatrick KL, Reid RJ (2009) The involvement of aquaglyceroporins in transport of boron in barley roots. Plant Cell Environ 32:1357–1365
Garnett TP, Tester MA, Nable RO (1993) The control of boron accumulation by two genotypes of wheat. Plant Soil 155:305–308
Gerbeau P, Güclü J, Ripoche P, Maurel C (1999) Aquaporin nt-TIPa can account for the high permeability of tobacco cell vacuolar membrane to small neutral solutes. Plant J 18:577–587
Hanaoka H, Fujiwara T (2007) Channel-mediated boron transport in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 48:S227
Hanba YT, Shibasaka M, Hayashi Y, Hayakawa T, Kasamo K, Terashima I, Katsuhara M (2004) Overexpression of the barley aquaporin HvPIP2;1 increases internal CO2 conductance and CO2 assimilation in the leaves of transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol 45:521–529
Hayes JE, Reid R (2004) Boron tolerance in Barley is mediated by efflux of boron from the roots. Plant Physiol 136:3376–3382
Isayenkov SV, Maathuis FJM (2008) The Arabidopsis thaliana aquaglyceroporin AtNIP7;1 is a pathway for arsenite uptake. FEBS Lett 582:1625–1628
Kamiya T, Tanaka M, Mitani N, Ma JF, Maeshima M, Fujiwara T (2009) NIP1;1, an aquaporin homolog, determines the arsenite sensitivity of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 284:2114–2120
Kammerloher W, Fischer U, Piechottka GP, Schäffner AR (1994) Water channels in the plant plasma membrane cloned by immunoselection from a mammalian expression system. Plant J 6:187–199
Kato Y, Miwa K, Takano J, Wada M, Fujiwara T (2009) Highly boron deficiency-tolerant plants generated by enhanced expression of NIP5;1, a boric acid channel. Plant Cell Physiol 50:58–66
Li G, Zhang M, Cai W, Sun W, Su W (2008) Characterization of OsPIP2;7, a water channel protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1851–1858
Li R, Ago Y, Liu W, Mitani N, Feldmann J, McGrath SP, Ma JF, Zhao F (2009) The rice aquaporin Lsi1 mediates uptake of methylated arsenic species. Plant Physiol 150:2071–2080
Liu Z, Shen J, Carbrey JM, Mukhopadhyay R, Agre P, Rosen BP (2002) Arsenite transport by mammalian aquaglyceroporins AQP7 and AQP9. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:6053–6058
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Loomis WD, Durst RW (1992) Chemistry and biology of boron. Biofactors 3:229–239
Ma JF, Tamai K, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Konishi S, Katsuhara M, Ishiguro M, Murata Y, Yano M (2006) A silicon transporter in rice. Nature 440:688–691
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu X, Su Y, McGrath SP, Zhao F (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:9931–9935
Maciaszczyk-Dziubinska E, Migdal I, Migocka M, Bocer T, Wysocki R (2010) The yeast aquaglyceroporin Fps1p is a bidirectional arsenite channel. FEBS Lett 584:726–732
Marone M, Mozzetti S, De Ritis D, Pierelli L, Scambia G (2001) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis to assess the expression levels of multiple transcripts from the same sample. Biol Proced 3:19–25
Matoh T (1997) Boron in plant cell walls. Plant Soil 193:59–70
Maurel C, Verdoucq L, Luu D, Santoni V (2008) Plant aquaporins: membrane channels with multiple integrated functions. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:595–624
Mitani N, Chiba Y, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2009) Identification and characterization of maize and barley Lsi2-like silicon efflux transporters reveals a distinct silicon uptake system from that in rice. Plant Cell 21:2133–2142
Mitani-Ueno N, Yamaji N, Zhao F, Ma JF (2011) The aromatic/arginine selectivity filter of NIP aquaporins plays a critical role in substrate selectivity for silicon, boron, and arsenic. J Exp Bot 62:4391–4398
Miwa K, Takano J, Fujiwara T (2006) Improvement of seed yields under boron-limiting conditions through overexpression of BOR1, a boron transporter for xylem loading, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 46:1084–1091
Miwa K, Takano J, Omori H, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Fujiwara T (2007) Plants tolerant of high boron levels. Science 318:1417
Mosa KA, Kumar K, Chhikara S, Joseph M, Liu Z, Musante C, White JC, Dhankher OP (2012) Members of rice plasma membrane intrinsic protein subfamily are involved in arsenite permeability and tolerance in plants. Transgenic Res 21:1265–1277
Moshelion M, Becker D, Biela A, Uehlein N, Hedrich R, Otto B, Levi H, Moran N, Kaldenhoff R (2002) Plasma membrane aquaporins in the motor cells of Samanea saman: diurnal and circadian regulation. Plant Cell 14:727–739
Nable RO, Bañuelos GS, Paull JG (1997) Boron toxicity. Plant Soil 193:181–198
Nakagawa Y, Hanaoka H, Kobayashi M, Miyoshi K, Miwa K, Fujiwara T (2007) Cell-type specificity of the expression of OsBOR1, a rice efflux boron transporter gene, is regulated in response to boron availability for efficient boron uptake and xylem loading. Plant Cell 19:2624–2635
Oertli JJ, Kohl HC (1961) Some considerations about the tolerance of various plant species to excessive supplies of boron. Soil Sci 92:243–247
Pang Y, Li L, Ren F, Lu P, Wei P, Cai J, Xin L, Zhang J, Chen J, Wang X (2010) Overexpression of the tonoplast aquaporin AtTIP5;1 conferred tolerance to boron toxicity in Arabidopsis. J Genet Genomics 37:389–397
Ralston NV, Hunt CD (2001) Diadenosine phosphates and S-adenosylmethionine: novel boron binding biomolecules detected by capillary electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1527:20–30
Reid R (2007) Identification of boron transporter genes likely to be responsible for tolerance to boron toxicity in wheat and barley. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1673–1678
Reid R, Fitzpatrick K (2009) Influence of leaf tolerance mechanisms and rain on boron toxicity in barley and wheat. Plant Physiol 151:413–420
Sakurai J, Ishikawa F, Yamaguchi T, Uemura M, Maeshima M (2005) Identification of 33 rice aquaporin genes and analysis of their expression and function. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1568–1577
Schnurbusch T, Hayes J, Hrmova M, Baumann U, Ramesh SA, Tyerman SD, Langridge P, Sutton T (2010) Boron toxicity tolerance in barley through reduced expression of the multifunctional aquaporin HvNIP2;1. Plant Physiol 153:1706–1715
Siefritz F, Otto B, Bienert GP, Van Der Krol A, Kaldenhoff R (2004) The plasma membrane aquaporin NtAQP1 is a key component of the leaf unfolding mechanism in tobacco. Plant J 37:147–155
Sutton T, Baumann U, Hayes J, Collins NC, Shi B, Schnurbusch T, Hay A, Mayo G, Pallotta M, Tester M, Langridge P (2007) Boron-toxicity tolerance in barley arising from efflux transporter amplification. Science 318:1446–1449
Takano J, Noguchi K, Yasumori M, Kobayashi M, Gajdos Z, Miwa K, Hayashi H, Yoneyama T, Fujiwara T (2002) Arabidopsis boron transporter for xylem loading. Nature 420:337–340
Takano J, Wada M, Ludewig U, Schaaf G, Wirén NV, Fujiwara T (2006) The Arabidopsis major intrinsic protein NIP5;1 is essential for efficient boron uptake and plant development under boron limitation. Plant Cell 18:1498–1509
Tanaka M, Wallace IS, Takano J, Roberts DM, Fujiwara T (2008) NIP6;1 is a boric acid channel for preferential transport of boron to growing shoot tissues in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:2860–2875
Wallace IS, Roberts DM (2004) Homology modeling of representative subfamilies of arabidopsis major intrinsic proteins classification based on the aromatic/arginine selectivity filter. Plant Physiol 135:1059–1068
Weig A, Deswarte C, Chrispeels MJ (1997) The major intrinsic protein family of Arabidopsis has 23 members that form three distinct groups with functional aquaporins in each group. Plant Physiol 114:1347–1357
Wimmer MA, Mühling KH, Läuchli A, Brown PH, Gold-bach HE (2002) Boron toxicity: the importance of soluble boron. In: Gold- bach HE, Rerkasem B, Wimmer MA, Brown PH, Bell RW (eds) Boron in plant and animal nutrition. Kluwer, New York, pp 241–253
Yamada S, Katsuhara M, Kelly WB, Michalowski CB, Bohnert HJ (1995) A family of transcripts encoding water channel proteins: tissue-specific expression in the common ice plant. Plant Cell 7:1129–1142
Zhao F, Ago Y, Mitani N, Li R, Su Y, Yamaji N, McGrath SP, Ma JF (2010) The role of the rice aquaporin Lsi1 in arsenite efflux from roots. New Phytol 186:392–399
Acknowledgments
Authors are highly thankful to Dr. Barry Rosen for providing the HD9 yeast mutant strain. This research was partly supported by a grant (GAID #4808) from the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research in Egypt through the Egyptian Cultural and Educational Bureau, Washington DC to OPD and KAM (GM:714) and a Hatch grant (MAS00401) from the USDA to OPD via the University of Massachusetts Amherst. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Kumar, and K. A. Mosa contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K., Mosa, K.A., Chhikara, S. et al. Two rice plasma membrane intrinsic proteins, OsPIP2;4 and OsPIP2;7, are involved in transport and providing tolerance to boron toxicity. Planta 239, 187–198 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1969-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1969-y