Abstract
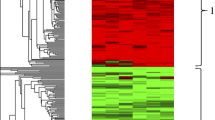
Changes in gene expression within roots of Glycine max (soybean), cv. Kent, susceptible to infection by Heterodera glycines (the soybean cyst nematode [SCN]), at 6, 12, and 24 h, and 2, 4, 6, and 8 days post-inoculation were monitored using microarrays containing more than 6,000 cDNA inserts. Replicate, independent biological samples were examined at each time point. Gene expression was analyzed statistically using T-tests, ANOVA, clustering algorithms, and online analytical processing (OLAP). These analyses allow the user to query the data in several ways without importing the data into third-party software. RT-PCR confirmed that WRKY6 transcription factor, trehalose phosphate synthase, EIF4a, Skp1, and CLB1 were differentially induced across most time-points. Other genes induced across most timepoints included lipoxygenase, calmodulin, phospholipase C, metallothionein-like protein, and chalcone reductase. RT-PCR demonstrated enhanced expression during the first 12 h of infection for Kunitz trypsin inhibitor and sucrose synthase. The stress-related gene, SAM-22, phospholipase D and 12-oxophytodienoate reductase were also induced at the early time-points. At 6 and 8 dpi there was an abundance of transcripts expressed that encoded genes involved in transcription and protein synthesis. Some of those genes included ribosomal proteins, and initiation and elongation factors. Several genes involved in carbon metabolism and transport were also more abundant. Those genes included glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and sucrose synthase. These results identified specific changes in gene transcript levels triggered by infection of susceptible soybean roots by SCN.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- hpi:
-
Hours post-infection
- dpi:
-
Days post-infection
- LCM:
-
Laser capture microdissection
References
Agrawal GK, Tamogami S, Han O, Iwahashi H, Rakwal R (2004) Rice octadecanoid pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 317:1–15
Alkharouf N, Matthews BF (2004) SGMD: the soybean genomics and microarray database. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D398–D400
Alkharouf N, Khan R, Matthews BF (2004) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from roots of resistant soybean infected by the soybean cyst nematode. Genome 47:380–388
Alkharouf N, Jamison C, Matthews BF (2005) Online analytical processing (OLAP): a fast and effective data mining tool for gene expression databases. J Biomed Biotechnol 2:181–188
de Almeida Engler J, De Vleesschauwer V, Burssens S, Celenza JL Jr, Inze D, Van Montagu M, Engler G, Gheysen G (1999) Molecular markers and cell cycle inhibitors show the importance of cell cycle progression in nematode-induced galls and syncytia. Plant Cell 11:793–808
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arz MC, Grambow HJ (1994) Polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C and evidence for inositol-phosphate-hydrolysing activities in the plasma-membrane fraction from light-grown wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaves. Planta 195:57–62
Bilban M, Buehler LK, Head S, Desoye G, Quaranta V (2002) Normalizing DNA microarray data. Curr Issues Mol Biol 4:57–64
Cebolla A, Vinardell JM, Kiss E, Olah B, Roudier F, Kondorosi A, Kondorosi E (1999) The mitotic inhibitor ccs52 is required for endoreduplication and ploidy-dependent cell enlargement in plants. EMBO J 18:4476–4484
Clark GB, Roux SJ (1995) Annexins of plant cells. Plant Physiol 109:1133–1139
Codd EF, Codd SB, Salley CT (1993) Providing OLAP (on-line analytical processing) to user-analysts: an IT mandate. Technical Report, EF Codd & Associates
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z (2003) Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol 51:21–37
Droge-Laser W, Kaiser A, Lindsay WP, Halkier BA, Loake GJ, Doerner P, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1997) Rapid stimulation of a soybean protein-serine kinase that phosphorylates a novel bZIP DNA-binding protein, G/HBF-1, during the induction of early transcription-dependent defenses. EMBO J 16:726–738
Durrant WE, Rowland O, Piedras P, Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JD (2000) cDNA-AFLP reveals a striking overlap in race-specific resistance and wound response gene expression profiles. Plant Cell 12:963–977
Duyvesteijn RG, van Wijk R, Boer Y, Rep M, Cornelissen BJ, Haring MA (2003) Frp1 is a Fusarium oxysporum F-box protein required for pathogenicity on tomato. Mol Microbiol 57:1051–1063
Endo BY (1964) Penetration and development of Heterodera glycines in soybean roots and related anatomical changes. Phytopathology 54:79–88
Endo BY (1965) Histological responses of resistant and susceptible soybean varieties, and backcross progeny to entry development of Heterodera glycines. Phytopathology 55:375–381
Endo B (1971) Synthesis of nucleic acids at infection sites of soybean roots parasitized by Heterodera glycines. Phytopathology 61:395–399
Endo BY (1991) Ultrastructure of initial responses of resistant and susceptible soybean roots to infection by Heterodera glycines. Rev Nematol 14:73–94
Foster AJ, Jenkinson JM, Talbot NJ (2003) Trehalose synthesis and metabolism are required at different stages of plant infection by Magnaporthe grisea. EMBO J 22:225–235
Gheysen G, Fenoll C (2002) Gene expression in nematode feeding sites. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:191–219
Grundler FMW, Bockenhoff A (1997) Physiology of nematode feeding and feeding sites. In: Fenoll C, Grundler FMW, Ohl SA (eds) Cellular and molecular aspects of plant–nematode interactions. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 107–119
Hermsmeier D, Mazarei M, Baum TJ (1998) Differential display analysis of the early compatible interaction between soybean and the soybean cyst nematode. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11(12):1258–1263
Heo WD, Lee SH, Kim MC, Kim JC, Chung WS, Chun HJ, Lee KJ, Park CY, Park HC, Choi JY, Cho MJ (1999) Involvement of specific calmodulin isoforms in salicylic acid-independent activation of plant disease resistance responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:766–771
Hegde P, Qi R, Abernathy K, Gay C, Dharap S, Gaspard R, Hughes JE, Snesrud E, Lee N, Quackenbush J (2000) A concise guide to cDNA microarray analysis. Biotechniques 29:548–556
Jammes F, Lecomte P, de Almeida-Engler J, Bitton F, Martin-Magniette ML, Renou JP, Abad P, Favery B (2005) Genome-wide expression profiling of the host response to root-knot nematode infection in Arabidopsis. Plant J 44:447–458
Jung C, Wyss U (1999) New approaches to control plant parasitic nematodes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:439–446
Kawasaki S, Borchert C, Deyholos M, Wang H, Brazille S, Kawai K, Galbraith D, Bohnert HJ (2001) Gene expression profiles during the initial phase of salt stress in rice. Plant Cell 13:889–905
Khan R, Alkharouf N, Beard HS, MacDonald M, Chouikha I, Meyer S, Grefenstette J, Knap H, Matthews BF (2004) Resistance mechanisms in soybean: gene expression profile at an early stage of soybean cyst nematode invasion. J Nematol 36:241–248
Kiegle E, Moore CA, Haseloff J, Tester MA, Knight MR (2000) Cell-type-specific calcium responses to drought, salt and cold in the Arabidopsis root. Plant J 23:267–278
Kiyosue T, Ryan CA (1997) A novel gene of tomato preferentially expressed in fruit encodes a protein with a Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding domain. Plant Mol Biol 35:969–972
Klink VP, MacDonald M, Alkharouf N, Matthews BF (2005) Laser capture microdissection (LCM) and expression analyses of Glycine max (soybean) syncytium containing root regions formed by the plant pathogen Heterodera glycines (soybean cyst nematode). Plant Mol Biol 59:969–983
Lange BM, Wildung MR, McCaskill D, Croteau R (1998) A family of transketolases that directs isoprenoid biosynthesis via a mevalonate-independent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2100–2104
Laxalt AM, Cassia RO, Sanllorenti PM, Madrid EA, Andreu AB, Daleo GR, Conde RD, Lamattina L (1996) Accumulation of cytosolic glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA under biological stress conditions and elicitor treatments in potato. Plant Mol Biol 30:961–972
Lee SH, Kim JC, Lee MS, Heo WD, Seo HY, Yoon HW, Hong JC, Lee SY, Bahk JD, Hwang I, Cho MJ (1995) Identification of a novel divergent calmodulin isoform from soybean which has differential ability to activate calmodulin-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem 270:21806–21812
Mahalingam R, Wang G, Knap HT (1999) Polygalacturonase and polygalacturonase inhibitor protein: gene isolation and transcription in Glycine max–Heterodera glycines interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 12:490–498
Mujer CV, Andrews DL, Manhart JR, Pierce SK, Rumpho ME (1996) Chloroplast genes are expressed during intracellular symbiotic association of Vaucheria litorea plastids with the sea slug Elysia chlorotica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12333–12338
Niebel A, Heungens K, Barthels N, Inze C, Van Montagu M, Gheysen G (1995) Characterization of a pathogen-induced potato catalase and its systemic expression upon nematode and bacterial infection. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:371–378
Niebel A, de Almeida Engler J, Hemerly A, Ferreira P, Inze D, Van Montagu M, Gheysen G (1996) Induction of cdc2a and cyc1At expression in Arabidopsis thaliana during early phases of nematode-induced feeding cell formation. Plant J 10:1037–1043
Ongena M, Duby F, Rossignol F, Fauconnier ML, Dommes J, Thonart P (2004) Stimulation of the lipoxygenase pathway is associated with systemic resistance induced in bean by a nonpathogenic Pseudomonas strain. Mole Plant Path Interact 17:1009–1018
Oztur ZN, Talame V, Deyholos M, Michalowski CB, Gozukirmizi DW, Tuberosa R, Bohnert HJ (2002) Monitoring large-scale changes in transcript abundance in drought- and salt-stressed barley. Plant Mol Biol 48:551–573
Park CY, Heo WD, Yoo JH, Lee JH, Kim MC, Chun HJ, Moon BC, Kim IH, Park HC, Choi MS, Ok HM, Cheong MS, Lee SM, Kim HS, Lee KH, Lim CO, Chung WS, Cho MJ (2004a) Pathogenesis-related gene expression by specific calmodulin isoforms is dependent on NIM1, a key regulator of systemic acquired resistance. Mol Cells 18:207–213
Park HC, Kim ML, Kang YH, Jeon JM, Yoo JH, Kim MC, Park CY, Jeong JC, Moon BC, Lee JH, Yoon HW, Lee SH, Chung WS, Lim CO, Lee SY, Hong JC, Cho MJ (2004b) Pathogen- and NaCl-induced expression of the SCaM-4 promoter is mediated in part by a GT-1 box that interacts with a GT-1-like transcription factor. Plant Physiol 135:2150–2161
Potenza C, Thomas SH, Sengupta-Gopalan C (2001) Genes induced during early response to Meloidogyne incognita in roots of resistant and susceptible alfalfa cultivars. Plant Sci 161:289–299
Puthoff DP, Nettleton D, Rodermel SR, Baum TJ (2003) Arabidopsis gene expression changes during cyst nematode parasitism revealed by statistical analyses of microarray expression profiles. Plant J 33:911–921
Reymond P, Weber H, Damond M, Farmer EE (2000) Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:707–719
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2001) A new member of the Arabidposis WRKY transcription factor family, AtWRKY6 is associated with both senescence- and defence-related processes. Plant J 28:123–133
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2002) Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense. Genes Dev 16:1139–1149
Ryu SB, Wang X (1996) Activation of phospholipase D and the possible mechanism of activation in wound-induced lipid hydrolysis in castor bean leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta 1303:243–250
Seal SN, Schmidt A, Marcus A (1983) Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A is the component that interacts with ATP in protein chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6562–6565
Schaffer R, Landgraf J, Acerbi M, Simon V, Larson M, Wisman E (2001) Microarray analysis of diurnal and circadian-regulated genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:113–123
Schenk PM, Kazan K, Wilson I, Anderson JP, Richmond T, Somerville SC, Manners JM (2000) Coordinate plant defense responses in Arabidopsis revealed by microarray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(21):11655–11660
Seki M, Narusaka M, Abe H, Kasuga M, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carcini P, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2001) Monitoring the expression pattern of 1300 Arabidopsis genes under drought and cold stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant Cell 13:61–72
Takahashi N, Kuroda H, Kuromori T, Hirayama T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Shimada H, Matsui M (2004) Expression and interaction analysis of Arabidopsis Skp1-related genes. Plant Cell Physiol 45:83–91
The Gene Ontology Consortium (2004) The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D258–D261
Tomkins JP, Mahalingam R, Smith H, Goicoechea JL, Knap HT, Wing RA (1999) A bacterial artificial chromosome library for soybean PI 437654 and identification of clones associated with cyst nematode resistance. Plant Mol Biol 41:25–32
Tusher V, Tibshirani R, Chu C (2001) Significance analysis of microarrays applied to ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5116–5121
Vaghchhipawala Z, Bassuner R, Clayton K, Lewers K, Shoemaker R, Mackenzie S (2001) Modulations in gene expression and mapping of genes associated with cyst nematode infection of soybean. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:42–54
Vaghchhipawala ZE, Schlueter JA, Shoemaker RC, Mackenzie SA (2004) Soybean FGAM synthase promoters direct ectopic nematode feeding site activity. Genome 47:404–413
Van der Eycken W, de Almeida Engler J, Inze D, Montagu M, Gheysen G (1996) A molecular study of root-knot nematode-induced feeding sites. Plant J 9:45–54
Vodkin LO, Khanna A, Shealy R, Clough SJ, Gonzalez DO, Philip R, Zabala G, Thibaud-Nissen F, Sidarous M, Stromvik MV, Shoop E, Schmidt C, Retzel E, Erpelding J, Shoemaker RC, Rodriguez-Huete AM, Polacco JC, Coryell V, Keim P, Gong G, Liu L, Pardinas J, Schweitzer P (2004) Microarrays for global expression constructed with a low redundancy set of 27,500 sequenced cDNAs representing an array of developmental stages and physiological conditions of the soybean plant. BMC Genomics 5:73–91
Wuarin J, Buck V, Nurse P, Millar JB (2002) Stable association of mitotic cyclin B/Cdc2 to replication origins prevents endoreduplication. Cell 111:419–431
Wrather JA, Stienstra WC, Koenning SR (2001) Soybean disease loss estimates for the United States from 1996 to 1998. Can J Plant Pathol 23:122–131
Yang YH, Dudoit S, Luu P, Lin DM, Peng V, Ngai J, Speed TP (2002) Normalization of cDNA microarray data: a robust composite method addressing single and multiple slide systematic variation. Nucleic Acid Res 30(4):e15
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Kris Pilitt and Ann Deiter for their technical support. The authors would also like to thank Nathan Uhlmann, Antoni J. Rafalski, Julie M. Vogel, Feng Han, Carl Simmons, and Guihua Lu from Dupont Inc. for their amplification and identification of the Dupont clones mentioned in this study. All data, raw and normalized, are stored in the Soybean Genomics and Microarray Database (Alkharouf and Matthews 2004) and are available through the web site [http://www.bldg6.arsusda.gov/benlab/]. This work was supported by the United Soybean Board under grant 3214 and USDA CSREES National Research Initiative grant 99-35302-8189. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the United States Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkharouf, N.W., Klink, V.P., Chouikha, I.B. et al. Timecourse microarray analyses reveal global changes in gene expression of susceptible Glycine max (soybean) roots during infection by Heterodera glycines (soybean cyst nematode). Planta 224, 838–852 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0270-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0270-8