Abstract
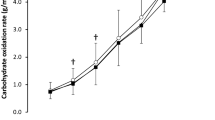
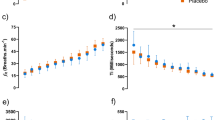
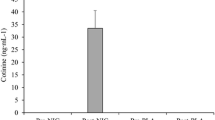
This study investigated the effects of acute ingestion of caffeine (C), ephedrine (E) and their combination (C+E) on time to exhaustion during high-intensity exercise. Using a repeated-measures, double-blind design, eight male subjects exercised on a cycle ergometer at a power output that led to exhaustion after about 12.6 min during a placebo (P) control trial. They did this 1.5 h after ingesting either C (5 mg · kg−1), E (1 mg · kg−1), C+E, or P. Trials were separated by 1 week. Venous blood was sampled before and during exercise. The mean (SD) times to exhaustion were 12.6 (3.1) (P), 14.4 (4.1) (C), 15.0 (5.7) (E) and 17.5 (5.8) (C+E) min. Only the C+E treatment significantly increased time to exhaustion compared to P. Oxygen consumption (V˙O2), carbon dioxide production (V˙CO2), minute ventilation (V˙ E) and the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) were similar during exercise for all trials. Heart rate during exercise was significantly increased for the C+E and C trials compared to P. Subjective ratings of perceived exertion during exercise were significantly lower after C+E compared to P. All treatments significantly increased lactate levels. Free fatty acid (FFA) levels were significantly increased by C ingestion. Glycerol levels were increased by C+E and C ingestion. Glucose levels were also higher with the drug treatments compared to P. Increased monamine availability after C+E treatment was suggested by measurements of catecholamines and dopamine. In conclusion, the combination of C+E significantly prolonged exercise time to exhaustion compared to P, while neither C nor E treatments alone significantly changed time to exhaustion. The improved performance was attributed to increased central nervous system stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 23 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bell, D., Jacobs, I. & Zamecnik, J. Effects of caffeine, ephedrine and their combination on time to exhaustion during high-intensity exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 77, 427–433 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050355