Abstract
Purpose
Many of the potential performance-enhancing properties of ischemic preconditioning suggest that the oxygen cost for a given endurance exercise workload will be reduced, thereby improving the economy of locomotion. The aim of this study was to identify whether ischemic preconditioning improves exercise economy in recreational runners.
Methods
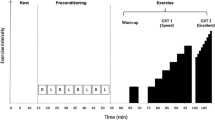
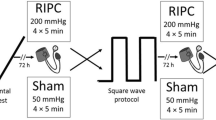
A randomized sham-controlled crossover study was employed in which 18 adults (age 27 ± 7 years; BMI 24.6 ± 3 kg/m2) completed two, incremental submaximal (65–85% VO2max) treadmill running protocols (3 × 5 min stages from 7.2–14.5 km/h) coupled with indirect calorimetry to assess running economy following ischemic preconditioning (3 × 5 min bilateral upper thigh ischemia) and sham control. Running economy was expressed as mlO2/kg/km and as the energy in kilocalories required to cover 1 km of horizontal distance (kcal/kg/km).
Results
Ischemic preconditioning did not influence steady-state heart rate, oxygen consumption, minute ventilation, respiratory exchange ratio, energy expenditure, and blood lactate. Likewise, running economy was similar (P = 0.647) between the sham (from 201.6 ± 17.7 to 204.0 ± 16.1 mlO2/kg/km) and ischemic preconditioning trials (from 202.8 ± 16.2 to 203.1 ± 15.6 mlO2/kg/km). There was no influence (P = 0.21) of ischemic preconditioning on running economy expressed as the caloric unit cost (from 0.96 ± 0.12 to 1.01 ± 0.11 kcal/kg/km) compared with sham (from 1.00 ± 0.10 to 1.00 ± 0.08 kcal/kg/km).
Conclusions
The properties of ischemic preconditioning thought to affect exercise performance at vigorous to severe exercise intensities, which generate more extensive physiological challenge, are ineffective at submaximal workloads and, therefore, do not change running economy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- RER:
-
Respiratory exchange ratio
- RHR:
-
Resting heart rate
- kcal:
-
Kilocalories
- V E :
-
Minute ventilation
- VO2max :
-
Maximal oxygen uptake
- VO2 :
-
Oxygen uptake
- VT:
-
Ventilatory threshold
References
Abe D, Yanagawa K, Yamanobe K, Tamura K (1998) Assessment of middle-distance running performance in sub-elite young runners using energy cost of running. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 77:320–325. doi:10.1007/s004210050340
Alleman RJ, Tsang AM, Ryan TE, Patteson DJ, McClung JM, Spangenburg EE, Shaikh SR, Neufer PD, Brown DA (2016) Exercise-induced protection against reperfusion arrhythmia involves stabilization of mitochondrial energetics. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 310:H1360–H1370. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00858.2015
American College of Sports Medicine (2014) Ninth edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Anderson T (1996) Biomechanics and running economy. Sports Med 22:76–89
Bailey TG, Birk GK, Cable NT, Atkinson G, Green DJ, Jones H, Thijssen DH (2012a) Remote ischemic preconditioning prevents reduction in brachial artery flow-mediated dilation after strenuous exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 303:H533–H538. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00272.2012
Bailey TG, Jones H, Gregson W, Atkinson G, Cable NT, Thijssen DH (2012b) Effect of ischemic preconditioning on lactate accumulation and running performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44:2084–2089. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318262cb17
Barbosa TC, Machado AC, Braz ID, Fernandes IA, Vianna LC, Nobrega AC, Silva BM (2015) Remote ischemic preconditioning delays fatigue development during handgrip exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25:356–364. doi:10.1111/sms.12229
Barnes KR, Kilding AE (2015) Running economy: measurement, norms, and determining factors. Sports Med Open 1:8. doi:10.1186/s40798-015-0007-y
Barros LF (2013) Metabolic signaling by lactate in the brain. Trends Neurosci 36:396–404. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2013.04.002
Brooks GA (2009) Cell–cell and intracellular lactate shuttles. J Physiol 587:5591–5600. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2009.178350
Cherry-Allen KM, Gidday JM, Lee J-M, Hershey T, Lang CE (2015) Remote limb ischemic conditioning enhances motor learning in healthy humans. J Neurophysiol 113:3708–3719. doi:10.1152/jn.01028.2014
Clevidence MW, Mowery RE, Kushnick MR (2012) The effects of ischemic preconditioning on aerobic and anaerobic variables associated with submaximal cycling performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:3649–3654. doi:10.1007/s00421-012-2345-5
Cocking S, Landman T, Benson M, Lord R, Jones H, Gaze D, Thijssen DH, George K (2016) The impact of remote ischemic preconditioning on cardiac biomarker and functional response to endurance exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. doi:10.1111/sms.12724
Conley DL, Krahenbuhl GS (1980) Running economy and distance running performance of highly trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 12:357–360
Craib MW, Mitchell VA, Fields KB, Cooper TR, Hopewell R, Morgan DW (1996) The association between flexibility and running economy in sub-elite male distance runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:737–743
Crisafulli A, Tangianu F, Tocco F, Concu A, Mameli O, Mulliri G, Caria MA (2011) Ischemic preconditioning of the muscle improves maximal exercise performance but not maximal oxygen uptake in humans. J Appl Physiol 111:530–536. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00266.2011
Crisafulli A, Mancardi D, Marongiu E, Rastaldo R, Penna C, Pagliaro P (2015) Preconditioning cardioprotection and exercise performance: a radical point of view. Sport Sci Health 11:137–151. doi:10.1007/s11332-015-0225-1
Cruz RS, de Aguiar RA, Turnes T, Pereira KL, Caputo S (2015) Effects of ischemic preconditioning on maximal constant-load cycling performance. J Appl Physiol 119:961–967. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00498.2015
Cruz RS, de Aguiar RA, Turnes T, Salvador AF, Caputo F (2016) Effects of ischemic preconditioning on short-duration cycling performance. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 41:825–831. doi:10.1139/apnm-2015-0646
de Groot PC, Thijssen DH, Sanchez M, Ellenkamp R, Hopman MT (2010) Ischemic preconditioning improves maximal performance in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 108:141–146. doi:10.1007/s00421-009-1195-2
Fletcher JR, Esau SP, MacIntosh BR (2009) Economy of running: beyond the measurement of oxygen uptake. J Appl Physiol 107:1918–1922. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00307.2009
Frasier CR, Moore RL, Brown DA (2011) Exercise-induced cardiac preconditioning: how exercise protects your achy-breaky heart. J Appl Physiol 111:905–915. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00004.2011
Glenn TC, Martin NA, Horning MA, McArthur DL, Hovda DA, Vespa P, Brooks GA (2015) Lactate: brain fuel in human traumatic brain injury: a comparison with normal healthy control subjects. J Neurotrauma 32:820–832. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3483
Hart S, Drevets K, Alford M, Salacinski A, Hunt BE (2013) A method-comparison study regarding the validity and reliability of the Lactate Plus analyzer. BMJ Open. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001899
Hausenloy DJ, Tsang A, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM (2005) Ischemic preconditioning protects by activating prosurvival kinases at reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H971–H976. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00374.2004
Heusch G, Botker HE, Przyklenk K, Redington A, Yellon D (2015) Remote ischemic conditioning. J Am Coll Cardiol 65:177–195. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2014.10.031
Incognito AV, Burr JF, Millar PJ (2016) The effects of ischemic preconditioning on human exercise performance. Sports Med 46:531–544. doi:10.1007/s40279-015-0433-5
James CA, Willmott AG, Richardson AJ, Watt PW, Maxwell NS (2016) Ischaemic preconditioning does not alter the determinants of endurance running performance in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol. doi:10.1007/s00421-016-3430-y
Jean-St-Michel E, Manlhiot C, Li J, Tropak M, Michelsen MM, Schmidt MR, McCrindle BW, Wells GD, Redington AN (2011) Remote preconditioning improves maximal performance in highly trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1280–1286. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318206845d
Kharbanda RK, Peters M, Walton B, Kattenhorn M, Mullen M, Klein N, Vallance P, Deanfield J, MacAllister R (2001) Ischemic preconditioning prevents endothelial injury and systemic neutrophil activation during ischemia-reperfusion in humans in vivo. Circulation 103:1624–1630
Kido K, Suga T, Tanaka D, Honjo T, Homma T, Fujita S, Hamaoka T, Isaka T (2015) Ischemic preconditioning accelerates muscle deoxygenation dynamics and enhances exercise endurance during the work-to-work test. Physiol Rep. doi:10.14814/phy2.12395
Kono Y, Fukuda S, Hanatani A, Nakanishi K, Otsuka K, Taguchi H, Shimada K (2014) Remote ischemic conditioning improves coronary microcirculation in healthy subjects and patients with heart failure. Drug Des Devel Ther 8:1175–1181. doi:10.2147/dddt.s68715
Loukogeorgakis SP, Panagiotidou AT, Broadhead MW, Donald A, Deanfield JE, MacAllister RJ (2005) Remote ischemic preconditioning provides early and late protection against endothelial ischemia-reperfusion injury in humans: role of the autonomic nervous system. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:450–456. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.04.044
Marocolo M, da Mota GR, Simim MA, Appell Coriolano HJ (2016) Myths and facts about the effects of ischemic preconditioning on performance. Int J Sports Med 37:87–96. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1564253
McCafferty K, Forbes S, Thiemermann C, Yaqoob MM (2014) The challenge of translating ischemic conditioning from animal models to humans: the role of comorbidities. Dis Model Mech 7:1321–1333. doi:10.1242/dmm.016741
Miller BF, Fattor JA, Jacobs KA, Horning MA, Suh SH, Navazio F, Brooks GA (2002) Metabolic and cardiorespiratory responses to “the lactate clamp”. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E889–E898. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00266.2002
Mulliri G, Sainas G, Magnani S, Palazzolo G, Milia N, Orrù A, Roberto S, Marongiu E, Milia R, Crisafulli A (2016) Ischemic preconditioning reduces hemodynamic response during metaboreflex activation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 310:R777–R787. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00429.2015
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Mustafa I, Leverve XM (2002) Metabolic and hemodynamic effects of hypertonic solutions: sodium-lactate versus sodium chloride infusion in postoperative patients. Shock 18:306–310
Pang CY, Yang RZ, Zhong A, Xu N, Boyd B, Forrest CR (1995) Acute ischaemic preconditioning protects against skeletal muscle infarction in the pig. Cardiovasc Res 29:782–788
Patterson SD, Bezodis NE, Glaister M, Pattison JR (2015) The effect of ischemic preconditioning on repeated sprint cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 47:1652–1658. doi:10.1249/mss.0000000000000576
Rassaf T, Totzeck M, Hendgen-Cotta UB, Shiva S, Heusch G, Kelm M (2014) Circulating nitrite contributes to cardioprotection by remote ischemic preconditioning. Circ Res 114:1601–1610. doi:10.1161/circresaha.114.303822
Robergs RA, Dwyer D, Astorino T (2010) Recommendations for improved data processing from expired gas analysis indirect calorimetry. Sports Med 40:95–111. doi:10.2165/11319670-000000000-00000
Salvador AF, De Aguiar RA, Lisboa FD, Pereira KL, Cruz RS, Caputo F (2016) Ischemic preconditioning and exercise performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 11:4–14. doi:10.1123/ijspp.2015-0204
Sanada S, Komuro I, Kitakaze M (2011) Pathophysiology of myocardial reperfusion injury: preconditioning, postconditioning, and translational aspects of protective measures. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1723–H1741. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00553.2011
Saunders PU, Pyne DB, Telford RD, Hawley JA (2004) Factors affecting running economy in trained distance runners. Sports Med 34:465–485
Seeger JP, Timmers S, Ploegmakers DJ, Cable NT, Hopman MT, Thijssen DH (2016) Is delayed ischemic preconditioning as effective on running performance during a 5 km time trial as acute IPC? J Sci Med Sport. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2016.03.010
Sen E, Basu A, Willing LB, Uliasz TF, Myrkalo JL, Vannucci SJ, Hewett SJ, Levison SW (2011) Pre-conditioning induces the precocious differentiation of neonatal astrocytes to enhance their neuroprotective properties. ASN Neuro. doi:10.1042/an20100029
Sharma V, Marsh R, Cunniffe B, Cardinale M, Yellon DM, Davidson SM (2015) From protecting the heart to improving athletic performance—the benefits of local and remote ischaemic preconditioning. Cardiovasc Drug Ther 29:573–588. doi:10.1007/s10557-015-6621-6
Shimizu M, Konstantinov IE, Kharbanda RK, Cheung MH, Redington AN (2007) Effects of intermittent lower limb ischaemia on coronary blood flow and coronary resistance in pigs. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 190:103–109. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01667.x
Tanaka D, Suga T, Tanaka T, Kido K, Honjo T, Fujita S, Hamaoka T, Isaka T (2016) Ischemic preconditioning enhances muscle endurance during sustained isometric exercise. Int J Sports Med. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1565141
Tocco F, Marongiu E, Ghiani G, Sanna I, Palazzolo G, Olla S, Pusceddu M, Sanna P, Corona F, Concu A, Crisafulli A (2015) Muscle ischemic preconditioning does not improve performance during self-paced exercise. Int J Sports Med 36:9–15. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1384546
Turrell HE, Thaitirarot C, Crumbie H, Rodrigo G (2014) Remote ischemic preconditioning of cardiomyocytes inhibits the mitochondrial permeability transition pore independently of reduced calcium-loading or sarcKATP channel activation. Physiol Rep. doi:10.14814/phy2.12231
Yellon DM, Downey JM (2003) Preconditioning the myocardium: from cellular physiology to clinical cardiology. Physiol Rev 83:1113–1151. doi:10.1152/physrev.00009.2003
Zhou K, Yang B, Zhou X-M, Tan C-M, Zhao Y, Huang C, Liao X-B, Xiao HB (2007) Effects of remote ischemic preconditioning on the flow pattern of the left anterior descending coronary artery in normal subjects. Int J Cardiol 122:250–251. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.11.079
Zhu Y, Wu J, Yuan SY (2013) MCT1 and MCT4 expression during myocardial ischemic-reperfusion injury in the isolated rat heart. Cell Physiol Biochem 32:663–674. doi:10.1159/000354470
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all subjects who participated in the study and the Department of Health & Nutritional Sciences at South Dakota State University for the use of laboratory space and supplies necessary to conduct the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-René Lacour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, G., Binger, M., Evans, C. et al. No influence of ischemic preconditioning on running economy. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 225–235 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3522-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3522-8