Abstract
Purpose
To determine the target intensity for fast walking during interval walking training (IWT) in water for middle-aged and older people to enhance physical fitness.
Methods
Thirty-one women [59±5 (SD) years old] were randomly divided into two groups: IWT on land (LG, N = 15) and in water (WG, N = 16). All subjects were instructed to perform ≥6 sets of fast and slow walking for 3 min each in a day, ≥4 days week−1, for 8 weeks, at an intensity 35 % higher than the oxygen consumption rate at the gas exchange threshold (\(\dot{V}\)O2GET), with a subjective feeling of 16–18 points of the Borg scale during fast walking in each condition. Before and after IWT, we measured \(\dot{V}\)O2GET, peak aerobic capacity (\(\dot{V}\)O2peak) by graded walking and cycling tests on land and isometric knee extension (F EXT) and flexion (F FLX) forces.
Results
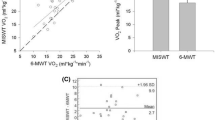
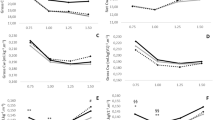
Before IWT, the \(\dot{V}\)O2GET for walking in water was 14 % higher and the heart rate (HR) at a given \(\dot{V}\)O2 was ~10 beats min−1 lower (P=0.001) than on land. During IWT, subjects in both groups performed IWT for ~4 days week−1 (P > 0.9) with a 14 % higher fast walking intensity in WG than in LG (P < 0.05). After IWT, the \(\dot{V}\)O2peak and \(\dot{V}\)O2GET for cycling, F EXT and F FLX increased more in WG than in LG (all, P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Walking in water elevated \(\dot{V}\)O2GET and decreased HR at a given exercise intensity in middle-aged and older women, which enabled them to perform exercise at a higher metabolic rate than on land due to improved subjective feelings, which, for these subjects, resulted in greater gains in physical fitness.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- F EXT :
-
Knee extension force
- F FLX :
-
Knee flexion force
- GET:
-
Gas exchange threshold
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HRGET :
-
HR at GET
- HRpeak :
-
HR at \(\dot{V}\)O2peak
- IWT:
-
Interval walking training
- LG:
-
Land group
- RPE:
-
Rating of perceived exertion
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- \(\dot{V}\)CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide production rate
- VM:
-
Vector magnitude of tri-axial accelerations
- \(\dot{V}\)O2 :
-
Oxygen consumption rate
- \(\dot{V}\)O2GET :
-
\(\dot{V}\)O2 at GET
- \(\dot{V}\)O2peak :
-
Peak oxygen consumption rate
- WG:
-
Water group
References
American College of Sports Medicine (2010) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 8th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, pp 152–182
Bartels EM, Lund H, Hagen KB, Dagfinrud H, Christensen R, Danneskiold-Samsøe B (2007) Aquatic exercise for the treatment of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4):CD005523
Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ (1986) A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 60(6):2020–2027
Bocalini DS, Serra AJ, Murad N, Levy RF (2008) Water- versus land-based exercise effects on physical fitness in older women. Geriatr Gerontol Int 8(4):265–271
Christie JL, Sheldahl LM, Tristani FE, Wann LS, Sagar KB, Levandoski SG, Ptacin MJ, Sobocinski KA, Morris RD (1990) Cardiovascular regulation during head-out water immersion exercise. J Appl Physiol 69(2):657–664
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers, Hillsdale, pp 1–17
Connelly TP, Sheldahl LM, Tristani FE, Levandoski SG, Kalkhoff RK, Hoffman MD, Kalbfleisch JH (1990) Effect of increased central blood volume with water immersion on plasma catecholamines during exercise. J Appl Physiol 69(2):651–656
Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA, Hirsch R, Helmick CG, Jordan JM, Kington RS, Lane NE, Nevitt MC, Zhang Y, Sowers M, McAlindon T, Spector TD, Poole AR, Yanovski SZ, Ateshian G, Sharma L, Buckwalter JA, Brandt KD, Fries JF (2000) Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann Intern Med 133(8):635–646
Hall J, Grant J, Blake D, Taylor G, Garbutt G (2004) Cardiorespiratory responses to aquatic treadmill walking in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Physiother Res Int 9(2):59–73
Harrison R, Hillman M, Bulstrode S (1992) Loading of the lower limb when walking partially immersed: implications for clinical practice. Physiotherapy 78(3):164–166
Hunter AM, St Clair Gibson A, Lambert M, Dennis S, Mullany H, O’Malley MJ, Vaughan CL, Kay D, Noakes TD (2003) EMG amplitude in maximal and submaximal exercise is dependent on signal capture rate. Int J Sports Med 24(2):83–89
Ide MR, Laurindo IMM, Rodrigues-Junior AL, Tanaka C (2008) Effect of aquatic respiratory exercise-based program in patients with fibromyalgia. Int J Rheum Dis 11(2):131–140
Iwashita S, Takeno Y, Okazaki K, Itoh J, Kamijo Y, Masuki S, Yanagidaira Y, Nose H (2003) Triaxial accelerometry to evaluate walking efficiency in older subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(10):1766–1772
Kamioka H, Tsutani K, Okuizumi H, Mutoh Y, Ohta M, Handa S, Okada S, Kitayuguchi J, Kamada M, Shiozawa N, Honda T (2010) Effectiveness of aquatic exercise and balneotherapy: a summary of systematic reviews based on randomized controlled trials of water immersion therapies. J Epidemiol 20(1):2–12
Karstoft K, Winding K, Knudsen SH, Nielsen JS, Thomsen C, Pedersen BK, Solomon TP (2013) The effects of free-living interval-walking training on glycemic control, body composition, and physical fitness in type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes Care 36(2):228–236
Karstoft K, Winding K, Knudsen SH, James NG, Sheel MM, Olesen J, Holst JJ, Pedersen BK, Solomon TP (2014) Mechanisms behind the superior effects of interval vs continuous training on glycaemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetologia 57(10):2081–2093
Lalande S, Okazaki K, Yamazaki T, Nose H, Joyner MJ, Johnson BD (2010) Effects of interval walking on physical fitness in middle-aged individuals. J Prim Care Community Health 1(2):104–110
Lim K, Rhi S (2014) The effects of landed and aquatic treadmill walking at moderate intensity on heart rate, energy expenditure and catecholamine. J Exerc Nutr Biochem 18(2):197–203
Masuki S, Mori M, Tabara Y, Miki T, Sakurai A, Morikawa M, Miyagawa K, Higuchi K, Nose H (2010) Vasopressin V1a receptor polymorphism and interval walking training effects in middle-aged and older people. Hypertension 55(3):747–754
Masuki S, Mori M, Tabara Y, Sakurai A, Hashimoto S, Morikawa M, Miyagawa K, Sumiyoshi E, Miki T, Higuchi K, Nose H (2015) The factors affecting adherence to a long-term interval walking training program in middle-aged and older people. J Appl Physiol 118(5):595–603
Morikawa M, Okazaki K, Masuki S, Kamijo Y, Yamazaki T, Gen-no H, Nose H (2011) Physical fitness and indices of lifestyle-related diseases before and after interval walking training in middle-aged and older males and females. Br J Sports Med 45(3):216–224
Morishima Y, Mizushima T, Yamauchi K, Morikawa M, Masuki S, Nose H (2014) Effects of home-based interval walking training on thigh muscle strength and aerobic capacity in female total hip arthroplasty patients: a randomized, controlled pilot study. PLoS One 9(9):e108690
Muraki S, Oka H, Akune T, Mabuchi A, En-yo Y, Yoshida M, Saika S, Suzuki T, Yoshida H, Ishibashi H, Yamamoto S, Nakamura K, Kawaguchi H, Yoshimura N (2009) Prevalence of radiographic knee osteoarthritis and its association with knee pain in the elderly of Japanese population-based cohorts: the ROAD study. Osteoarthr Cartil 17(9):1137–1143
Nakajima K, Takeoka M, Mori M, Hashimoto S, Sakurai A, Nose H, Higuchi K, Itano N, Shiohara M, Oh T, Taniguchi S (2010) Exercise effects on methylation of ASC gene. Int J Sports Med 31(9):671–675
Nemoto K, Gen-no H, Masuki S, Okazaki K, Nose H (2007) Effects of high-intensity interval walking training on physical fitness and blood pressure in middle-aged and older people. Mayo Clin Proc 82(7):803–811
Nose H, Morikawa M, Yamazaki T, Nemoto K, Okazaki K, Masuki S, Kamijo Y, Gen-No H (2009) Beyond epidemiology: field studies and the physiology laboratory as the whole world. J Physiol 587(Pt 23):5569–5575
Park KS, Choi JK, Park YS (1999) Cardiovascular regulation during water immersion. Appl Human Sci 18(6):233–241
Sanders ME, Takeshima N, Rogers ME, Colado JC, Borreani S (2013) Impact of the S.W.E.A.T.™ water-exercise method on activities of daily living for older women. J Sports Sci Med 12(4):707–715
Silva LE, Valim V, Pessanha AP, Oliveira LM, Myamoto S, Jones A, Natour J (2008) Hydrotherapy versus conventional land-based exercise for the management of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized clinical trial. Phys Ther 88(1):12–21
Slemenda C, Heilman DK, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Mazzuca SA, Braunstein EM, Byrd D (1998) Reduced quadriceps strength relative to body weight: a risk factor for knee osteoarthritis in women? Arthritis Rheum 41(11):1951–1959
Takeshima N, Rogers ME, Watanabe E, Brechue WF, Okada A, Yamada T, Islam MM, Hayano J (2002) Water-based exercise improves health-related aspects of fitness in older women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34(3):544–551
Tsourlou T, Benik A, Dipla K, Zafeiridis A, Kellis S (2006) The effects of a twenty-four-week aquatic training program on muscular strength performance in healthy elderly women. J Strength Cond Res 20(4):811–818
Yamazaki T, Gen-No H, Kamijo Y, Okazaki K, Masuki S, Nose H (2009) A new device to estimate VO2 during incline walking by accelerometry and barometry. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(12):2213–2219
Zhang Y, Hashimoto S, Fujii C, Hida S, Ito K, Matsumura T, Sakaizawa T, Morikawa M, Masuki S, Nose H, Higuchi K, Nakajima K, Taniguchi S (2015) NFkB2 gene as a noble candidate epigenetically responding to interval walking training. Int J Sports Med 36(9):769–775
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (Comprehensive Research on Ageing and Health) and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (24240089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by David C. Poole.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Handa, S., Masuki, S., Ohshio, T. et al. Target intensity and interval walking training in water to enhance physical fitness in middle-aged and older women: a randomised controlled study. Eur J Appl Physiol 116, 203–215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3267-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3267-9