Abstract
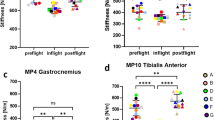
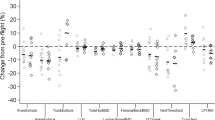
It is generally held that space travelers experience muscle dysfunction and atrophy during exposure to microgravity. However, observations are scarce and reports somewhat inconsistent with regard to the time course, specificity and magnitude of such changes. Hence, we examined four male astronauts (group mean ~43 years, 86 kg and 183 cm) before and after a 17-day spaceflight (Space Transport System-78). Knee extensor muscle function was measured during maximal bilateral voluntary isometric and iso-inertial concentric, and eccentric actions. Cross-sectional area (CSA) of the knee extensor and flexor, and gluteal muscle groups was assessed by means of magnetic resonance imaging. The decrease in strength (P<0.05) across different muscle actions after spaceflight amounted to 10%. Eight ambulatory men, examined on two occasions 20 days apart, showed unchanged (P>0.05) muscle strength. CSA of the knee extensor and gluteal muscles, each decreased (P<0.05) by 8%. Knee flexor muscle CSA showed no significant (P>0.05) change. The magnitude of these changes concord with earlier results from ground-based studies of similar duration. The results of this study, however, do contrast with the findings of no decrease in maximal voluntary ankle plantar flexor force previously reported in the same crew.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams GR, Hather BM, Dudley GA (1994) Effect of short-term unweighting on human skeletal muscle strength and size. Aviat Space Environ Med 65:1116–1121
Akima H, Kawakami Y, Kubo K, Sekiguchi C, Ohshima H, Miyamoto A, Fukunaga T (2000) Effect of short-duration spaceflight on thigh and leg muscle volume. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1743–1747
Alkner BA, Tesch PA (2004) Knee extensor and plantar flexor muscle size and function following 90 days of bed rest with or without resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol (in press). DOI 10.1007/s00421-004-1172-8
Antonutto G, Capelli C, Girardis M, Zamparo P, di Prampero PE (1999) Effects of microgravity on maximal power of lower limbs during very short efforts in humans. J Appl Physiol 86:85–92
Bamman MM, Hunter GR, Stevens BR, Guilliams ME, Greenisen MC (1997) Resistance exercise prevents plantar flexor deconditioning during bed rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:1462–1468
Berg HE, Tesch PA (1994) A gravity-independent ergometer to be used for resistance training in space. Aviat Space Environ Med 65:752–756
Berg HE, Tesch PA (1996) Changes in muscle function in response to 10 days of lower limb unloading in humans. Acta Physiol Scand 157:63–70
Berg HE, Dudley GA, Häggmark T, Ohlsén H, Tesch PA (1991) Effects of lower limb unloading on skeletal muscle mass and function in humans. J Appl Physiol 70:1882–1885
Berg HE, Larsson L, Tesch PA (1997) Lower limb skeletal muscle function after 6 weeks of bed rest. J Appl Physiol 82:182–188
Convertino VA (1990) Physiological adaptations to weightlessness: effects on exercise and work performance. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 18:119–166
Dudley GA, Duvoisin MR, Convertino VA, Buchanan P (1989) Alterations of the in vivo torque–velocity relationship of human skeletal muscle following 30 days exposure to simulated microgravity. Aviat Space Environ Med 60:659–663
Dudley GA, Duvoisin MR, Adams GR, Meyer RA, Belew AH, Buchanan P (1992) Adaptations to unilateral lower limb suspension in humans. Aviat Space Environ Med 63:678–683
Ferrando AA, Tipton KD, Bamman MM, Wolfe RR (1997) Resistance exercise maintains skeletal muscle protein synthesis during bed rest. J Appl Physiol 82:807–810
Gogia P, Schneider VS, LeBlanc AD, Krebs J, Kasson C, Pientok C (1988) Bed rest effect on extremity muscle torque in healthy men. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 69:1030–1032
Hather BM, Adams GR, Tesch PA, Dudley GA (1992) Skeletal muscle responses to lower limb suspension in humans. J Appl Physiol 72:1493–1498
Hayes JC, McBrine JJ, Roper ML, Stricklin MD, Siconolfi SF, Greenisen MC (1992) Effects of space flight on skeletal muscle performance. FASEB J 65:A1770
Koryak YU (2001) Electrically evoked and voluntary properties of the human triceps surae muscle: effects of long-term spaceflights. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Bulg 26:21–27
Kozlovskaya IB, Barmin VA, Stepantsov VI, Kharitonov NM (1990) Results of studies of motor functions in long-term space flights. Physiologist 33:S1–3
Kraemer WJ, Patton JF, Gordon SE, Harman EA, Deschenes MR, Reynolds K, Newton RU, Triplett NT, Dziados JE (1995) Compatibility of high-intensity strength and endurance training on hormonal and skeletal muscle adaptations. J Appl Physiol 78:976–989
LeBlanc A, Gogia P, Schneider V, Krebs J, Schonfeld E, Evans H (1988) Calf muscle area and strength changes after five weeks of horizontal bed rest. Am J Sports Med 16:624–629
LeBlanc A, Rowe R, Schneider V, Evans H, Hedrick T (1995) Regional muscle loss after short duration spaceflight. Aviat Space Environ Med 66:1151–1154
LeBlanc A, Lin C, Shackelford L, Sinitsyn V, Evans H, Belichenko O, Schenkman B, Kozlovskaya I, Oganov V, Bakulin A, Hedrick T, Feeback D (2000) Muscle volume, MRI relaxation times (T2), and body composition after spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 89:2158–2164
LeBlanc AD, Schneider VS, Evans HJ, Pientok C, Rowe R, Spector E (1992) Regional changes in muscle mass following 17 weeks of bed rest. J Appl Physiol 73:2172–2178
Narici M, Kayser B, Barattini P, Cerretelli P (2003) Effects of 17-day spaceflight on electrically evoked torque and cross-sectional area of the human triceps surae. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:275–282
Nicogossian AE, Sawin AI, Grigoriev AI (1994) Countermeasures to space deconditioning. In: Nicogossian AE, Huntoon and Pool SL (eds) Space physiology and medicine. Lea & Febiger, Malvern, Pa., pp 447–467
Schulze K, Gallagher P, Trappe S (2002) Resistance training preserves skeletal muscle function during unloading in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:303–313
Stein TP, Leskiw MJ, Schluter MD, Hoyt RW, Lane HW, Gretebeck RE, LeBlanc AD (1999) Energy expenditure and balance during spaceflight on the space shuttle. Am J Physiol 276:R1739–1748
Tesch PA, Trieschmann JT, Ekberg A (2004) Hypertrophy of chronically unloaded muscle subjected to resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol 96:1451–1458
Trappe S, Trappe T, Gallagher P, Harber M, Alkner B, Tesch P (2004) Human single muscle fibre function with 84 day bed-rest and resistance exercise. J Physiol 557:501–513
Trappe SW, Trappe TA, Lee GA, Widrick JJ, Costill DL, Fitts RH (2001) Comparison of a space shuttle flight (STS-78) and bed rest on human muscle function. J Appl Physiol 91:57–64
Widrick JJ, Knuth ST, Norenberg KM, Romatowski JG, Bain JL, Riley DA, Karhanek M, Trappe SW, Trappe TA, Costill DL, Fitts RH (1999) Effect of a 17 day spaceflight on contractile properties of human soleus muscle fibres. J Physiol (London) 516:915–930
Widrick JJ, Romatowski JG, Norenberg KM, Knuth ST, Bain JL, Riley DA, Trappe SW, Trappe TA, Costill DL, Fitts RH (2001) Functional properties of slow and fast gastrocnemius muscle fibers after a 17-day spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 90:2203–2211
Acknowledgements
We thank the STS-78 crew and the volunteers for their participation in this study. Space Shuttle Columbia was lost with its crew of seven during re-entry from a mission on 1 February 2003. This paper is dedicated to the astronauts who lost their lives on the last Colombia flight. This study was supported by grants from the Swedish National Space Board, the European Space Agency and National Astronautics and Space Administration, contract NAS 9-18952. The technical assistance by Mr. Sigge Hedberg and Mr. Ole Olsen is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tesch, P.A., Berg, H.E., Bring, D. et al. Effects of 17-day spaceflight on knee extensor muscle function and size. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 463–468 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1236-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1236-9