Abstract
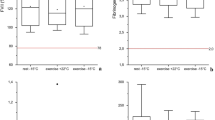
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of a post-exercise active cool-down on von Willebrand factor and fibrinolysis. Ten subjects performed two maximal oxygen uptake (V̇O2max) tests followed by a 10-min passive (PC) or an active (AC) cool-down. Blood samples were obtained pre-exercise, post-exercise, post-PC/AC, and 1 h post-exercise and analyzed for von Willebrand factor antigen (vWf:Ag), tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) antigen and activity and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) activity. Data were analyzed using repeated measures analysis of variance. No significant differences were found between V̇O2max tests for treadmill time, V̇O2max, respiratory exchange ratio, maximal heart rate, or maximal blood lactate concentration. vWf:Ag was significantly elevated (P <0.05) following PC [198.4 (18.3)% normal] versus AC [174.5 (15.6)% normal] and remained elevated 1-h post-exercise [179.4 (16.4)% normal for PC vs 158.6 (13.8)% normal for AC]. There were no differences between tests for tPA or PAI-1 activity, although tPA antigen was significantly elevated following PC versus AC (P <0.05). Following the cool-down, hematocrit was higher (P <0.05) for the PC test [48.90 (0.36)] compared with AC [47.43 (0.51)]. An AC reduces post-exercise vWf:Ag and tPA antigen without affecting tPA or PAI-1 activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew M, Carter C, O’Brodovich H, Heigenhauser G (1986) Increases in factor VIII complex and fibrinolytic activity are dependent on exercise intensity. J Appl Physiol 60:1917–1922
Angleton P, Chandler WL, Schmer G (1989) Diurnal variation of tissue-type plasminogen activator and its rapid inhibitor (PAI-1). Circulation 79:101–106
Bartsch P, Haeberli A, Straub PW (1990) Blood coagulation after long distance running: antithrombin III prevents fibrin formation. Thromb Haemost 63:430–434
Beaumont W Van, Greenleaf JE, Juhos L (1972) Disproportional changes in hematocrit, plasma volume, and proteins during exercise and bed rest. J Appl Physiol 33:55–61
Burg PJ van den, Hospers JE, van Vliet M, Mosterd WL, Bouma BN, Huisveld IA (1997) Effect of endurance training and seasonal fluctuation on coagulation and fibrinolysis in young sedentary men. J Appl Physiol 82: 613–620
Chandler WL, Veith RC, Fellingham GW, Levy WC, Schwartz RS, Cerqueira MD, Kahn SE, Larson VG, Cain KC, Beard JC, et al (1992) Fibrinolytic response during exercise and epinephrine infusion in the same subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol 19:1412–1420
Ciampricotti R, el-Gamal M, Relik T, Taverne R, Panis J, de Swart J, van Gelder B, Relik-van Wely L (1990) Clinical characteristics and coronary angiographic findings of patients with unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction, and survivors of sudden ischemic death occurring during and after sport. Am Heart J 120:1267–1278
Cohen RJ, Epstein SE, Cohen LS, Dennis LH (1968) Alterations of fibrinolysis and blood coagulation induced by exercise, and the role of beta-adrenergic-receptor stimulation. Lancet 2:1264–1266
Davis GL, Abildgaard CF, Bernauer EM, Britton M (1976) Fibrinolytic and hemostatic changes during and after maximal exercise in males. J Appl Physiol 40:287–292
Dimsdale JE, Hartley LH, Guiney T, Ruskin JN, Greenblatt D (1984) Postexercise peril. Plasma catecholamines and exercise. JAMA 251:630–632
Duncan JJ, Farr JE, Upton SJ, Hagan RD, Oglesby ME, Blair SN (1985) The effects of aerobic exercise on plasma catecholamines and blood pressure in patients with mild essential hypertension. JAMA 254:2609–2613
Franklin BA, Whaley MH, Howley ET (2000) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
Fujii Y, Mammen EF, Farag A, Muz J, Salciccioli GG, Weingarden ST (1992) Thrombosis in spinal cord injury. Thromb Res 68:357–368
Giri S, Thompson PD, Kiernan FJ, Clive J, Fram DB, Mitchel JF, Hirst JA, McKay RG, Waters DD (1999) Clinical and angiographic characteristics of exertion-related acute myocardial infarction. JAMA 282:1731–1736
Hansen JB, Wilsgard L, Olsen JO, Osterud B (1990) Formation and persistence of procoagulant and fibrinolytic activities in circulation after strenuous physical exercise. Thromb Haemost 64:385–389
Hegde SS, Goldfarb AH, Hegde S (2001) Clotting and fibrinolytic activity change during the 1 h after a submaximal run. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:887–892
Hilberg T, Glaser D, Reckhart C, Prasa D, Sturzebecher J, Gabriel HH (2003) Blood coagulation and fibrinolysis after long-duration treadmill exercise controlled by individual anaerobic threshold. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:639–642
Kanel R von, Dimsdale JE, Adler KA, Dillon E, Perez CJ, Mills PJ (2003) Effects of nonspecific β-adrenergic stimulation and blockade on blood coagulation in hypertension. J Appl Physiol 94:1455–1459
Laurell CB (1966) Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem 15:45–52
Lin X, El-Sayed MS, Waterhouse J, Reilly T (1999) Activation and disturbance of blood haemostasis following strenuous physical exercise. Int J Sports Med 20:149–153
Mehta J, Mehta P, Lawson D, Saldeen T (1987) Plasma tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor levels in coronary artery disease: correlation with age and serum triglyceride concentrations. J Am Coll Cardiol 9:263–268
Mittleman MA, Maclure M, Tofler GH, Sherwood JB, Goldberg RJ, Muller JE (1993) Triggering of acute myocardial infarction by heavy physical exertion. Protection against triggering by regular exertion. Determinants of Myocardial Infarction Onset Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 329:1677–1683
Mustonen P, Lepantalo M, Lassila R (1998) Physical exertion induces thrombin formation and fibrin degradation in patients with peripheral atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:244–249
Prowse CV, Cash JD (1984) Physiologic and pharmacologic enhancement of fibrinolysis. Semin Thromb Hemost 10:51–60
Rennie JA, Bennett B, Ogston D (1977) Effect of local exercise and vessel occlusion on fibrinolytic activity. J Clin Pathol 30:350–352
Saenko EL, Yakhyaev AV, Mikhailenko I, Strickland DK, Sarafanov AG (1999) Role of the low density lipoprotein-related protein receptor in mediation of factor VIII catabolism. J Biol Chem 274:37685–37692
Scurr JH, Smith PD, Machin S (2001) Deep vein thrombosis in airline passengers—the incidence of deep vein thrombosis and the efficacy of elastic compression stockings. Cardiovasc Surg 9:159–161
Smith DT, Hoetzer GL, Greiner JJ, Stauffer BL, DeSouza CA (2003) Effects of ageing and regular aerobic exercise on endothelial fibrinolytic capacity in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 546:289–298
Sweeney JD, Hoernig LA (1992) Intraplatelet von Willebrand factor and ABO blood group. Thromb Res 68:393–398
Weiss C, Seitel G, Bartsch P (1998) Coagulation and fibrinolysis after moderate and very heavy exercise in healthy male subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:246–251
Winther K, Hillegass W, Tofler GH, Jimenez A, Brezinski DA, Schafer AI, Loscalzo J, Williams GH, Muller JE (1992) Effects on platelet aggregation and fibrinolytic activity during upright posture and exercise in healthy men. Am J Cardiol 70:1051–1055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paton, C.M., Nagelkirk, P.R., Coughlin, A.M. et al. Changes in von Willebrand factor and fibrinolysis following a post-exercise cool-down. Eur J Appl Physiol 92, 328–333 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1098-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1098-1