Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether the apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) 1349 T>G and -656 T>G polymorphisms were associated with the risk of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) in a Chinese population.
Methods
The two APE1 polymorphisms were analyzed among 613 NIHL workers and 613 normal hearing workers using the minor groove binder TaqMan probe assay.
Results
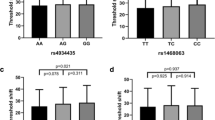
We found that the APE1 -656 TT genotype was associated with a increased risk of NIHL [adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.46, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.05–2.06]. This increased risk was more pronounced in the stratification analysis. Furthermore, we found that subjects with two risk genotypes (hOGG1 Cys/Cys, APE1 -656 TT) had a significantly increased risk of NIHL (adjusted OR 1.91, 95 % CI 1.27–2.88).
Conclusion
Our study identified that the APE1 -656 T>G polymorphism may contribute to the susceptibility of NIHL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basner M, Babisch W, Davis A et al (2014) Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 383(9925):1325–1332
Curhan SG, Eavey R, Shargorodsky J, Curhan GC (2011) Prospective study of alcohol use and hearing loss in men. Ear Hear 32(1):46–52
Daniel E (2007) Noise and hearing loss: a review. J Sch Health 77(5):225–231
Fortini P, Pascucci B, Parlanti E, D’Errico M, Simonelli V, Dogliotti E (2003) The base excision repair: mechanisms and its relevance for cancer susceptibility. Biochimie 85(11):1053–1071
Fortunato G, Marciano E, Zarrilli F et al (2004) Paraoxonase and superoxide dismutase gene polymorphisms and noise-induced hearing loss. Clin Chem 50(11):2012–2018
Fuente A, Hickson L (2011) Noise-induced hearing loss in Asia. Int J Audiol 50(Suppl 1):S3–S10
Gu D, Wang M, Zhang Z, Chen J (2009) The DNA repair gene APE1 T1349G polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 27 case-control studies. Mutagenesis 24(6):507–512
Hadi MZ, Coleman MA, Fidelis K, Mohrenweiser HW, Wilson DM 3rd (2000) Functional characterization of Ape1 variants identified in the human population. Nucleic Acids Res 28(20):3871–3879
Henderson D, Bielefeld EC, Harris KC, Hu BH (2006) The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear 27(1):1–19
Hoeijmakers JH (2001) Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature 411(6835):366–374
Holme RH, Steel KP (2004) Progressive hearing loss and increased susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss in mice carrying a Cdh23 but not a Myo7a mutation. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 5(1):66–79
Itoh A, Nakashima T, Arao H et al (2001) Smoking and drinking habits as risk factors for hearing loss in the elderly: epidemiological study of subjects undergoing routine health checks in Aichi, Japan. Public Health 115(3):192–196
Jacono AA, Hu B, Kopke RD, Henderson D, Van De Water TR, Steinman HM (1998) Changes in cochlear antioxidant enzyme activity after sound conditioning and noise exposure in the chinchilla. Hear Res 117(1-2):31–38
Karlsmose B, Lauritzen T, Engberg M, Parving A (2000) A five-year longitudinal study of hearing in a Danish rural population aged 31–50 years. Br J Audiol 34(1):47–55
Karpa MJ, Gopinath B, Beath K et al (2010) Associations between hearing impairment and mortality risk in older persons: the Blue Mountains Hearing Study. Ann Epidemiol 20(6):452–459
Konings A, Van Laer L, Pawelczyk M et al (2007) Association between variations in CAT and noise-induced hearing loss in two independent noise-exposed populations. Hum Mol Genet 16(15):1872–1883
Konings A, Van Laer L, Michel S et al (2009a) Variations in HSP70 genes associated with noise-induced hearing loss in two independent populations. Eur J Hum Genet 17(3):329–335
Konings A, Van Laer L, Van Camp G (2009b) Genetic studies on noise-induced hearing loss: a review. Ear Hear 30(2):151–159
Konings A, Van Laer L, Wiktorek-Smagur A et al (2009c) Candidate gene association study for noise-induced hearing loss in two independent noise-exposed populations. Ann Hum Genet 73(2):215–224
Kozel PJ, Davis RR, Krieg EF, Shull GE, Erway LC (2002) Deficiency in plasma membrane calcium ATPase isoform 2 increases susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss in mice. Hear Res 164(1–2):231–239
Krokan HE, Nilsen H, Skorpen F, Otterlei M, Slupphaug G (2000) Base excision repair of DNA in mammalian cells. FEBS Lett 476(1–2):73–77
Li XT, Li X, Hu FF et al (2013) Association between paraoxonase 2 gene polymorphisms and noise-induced hearing loss in the Chinese population. J Occup Health 55(2):56–65
Lo YL, Jou YS, Hsiao CF et al (2009) A polymorphism in the APE1 gene promoter is associated with lung cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark. Prev 18(1):223–229
Lu J, Zhang S, Chen D et al (2009) Functional characterization of a promoter polymorphism in APE1/Ref-1 that contributes to reduced lung cancer susceptibility. FASEB J 23(10):3459–3469
Matsumoto Y (2001) Molecular mechanism of PCNA-dependent base excision repair. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 68:129–138
Ohlemiller KK, McFadden SL, Ding DL et al (1999) Targeted deletion of the cytosolic Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase gene (Sod1) increases susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss. Audiol Neurootol 4(5):237–246
Ohlemiller KK, McFadden SL, Ding DL, Lear PM, Ho YS (2000) Targeted mutation of the gene for cellular glutathione peroxidase (Gpx1) increases noise-induced hearing loss in mice. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 1(3):243–254
Pawelczyk M, Van Laer L, Fransen E et al (2009) Analysis of gene polymorphisms associated with K ion circulation in the inner ear of patients susceptible and resistant to noise-induced hearing loss. Ann Hum Genet 73(Pt 4):411–421
Rabinowitz PM, Pierce Wise J Sr, Hur Mobo B, Antonucci PG, Powell C, Slade M (2002) Antioxidant status and hearing function in noise-exposed workers. Hear Res 173(1–2):164–171
Shen H, Huo X, Liu K et al (2012) Genetic variation in GSTM1 is associated with susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. J Occup Environ Med 54(9):1157–1162
Shen H, Cao J, Hong Z et al (2014) A functional Ser326Cys polymorphism in hOGG1 is associated with noise-induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. PLoS One 9(3):e89662
Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Zamyslowska-Szmytke E, Szymczak W et al (2004) Effects of coexposure to noise and mixture of organic solvents on hearing in dockyard workers. J Occup Environ Med 46(1):30–38
Stucken EZ, Hong RS (2014) Noise-induced hearing loss: an occupational medicine perspective. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 22(5):388–393
Thakur S, Sarkar B, Cholia RP, Gautam N, Dhiman M, Mantha AK (2014) APE1/Ref-1 as an emerging therapeutic target for various human diseases: phytochemical modulation of its functions. Exp Mol Med 46:e106
Totonchy MB, Tamura D, Pantell MS et al (2013) Auditory analysis of xeroderma pigmentosum 1971–2012: hearing function, sun sensitivity and DNA repair predict neurological degeneration. Brain 136(Pt 1):194–208
Van Laer L, Carlsson PI, Ottschytsch N et al (2006) The contribution of genes involved in potassium-recycling in the inner ear to noise-induced hearing loss. Hum Mutat 27(8):786–795
Vineis P, Manuguerra M, Kavvoura FK et al (2009) A field synopsis on low-penetrance variants in DNA repair genes and cancer susceptibility. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(1):24–36
Wang M, Chu H, Wang S, Wang W, Han S, Zhang Z (2013) Genetic variant in APE1 gene promoter contributes to cervical cancer risk. Am J Obstet Gynecol 209(4):360.e1–360.e7
Wilson DM 3rd, Bohr VA (2007) The mechanics of base excision repair, and its relationship to aging and disease. DNA Repair (Amst) 6(4):544–559
Yamane A, Kohno T, Ito K et al (2004) Differential ability of polymorphic OGG1 proteins to suppress mutagenesis induced by 8-hydroxyguanine in human cell in vivo. Carcinogenesis 25(9):1689–1694
Yang M, Tan H, Yang Q et al (2006) Association of hsp70 polymorphisms with risk of noise-induced hearing loss in Chinese automobile workers. Cell Stress Chaperones 11(3):233–239
Zhang Z, Shi Q, Sturgis EM, Spitz MR, Wei Q (2005) Polymorphisms and haplotypes of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a case–control analysis. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15(8):557–564
Zhou B, Shan H, Su Y et al (2011) The association of APE1 -656T>G and 1349 T>G polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 37 case-control studies. BMC Cancer 11:521
Acknowledgments
This study was mainly supported by Jiangsu Province’s Outstanding Medical Academic Leader program (LJ201130) and Projects of Jiangsu Society Development (BS2005661), and was partly supported by the Kunshan Municipal Society Development (KS1354).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Huanxi Shen, Jianrui Dou, and Lei Han have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Dou, J., Han, L. et al. Genetic variation in APE1 gene promoter is associated with noise-induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 89, 621–628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-015-1100-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-015-1100-8