Abstract
Objective
Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) was recently introduced as the third generation mobile communication standard in Europe. This was done without any information on biological effects and genotoxic properties of these particular high-frequency electromagnetic fields. This is discomforting, because genotoxic effects of the second generation standard Global System for Mobile Communication have been reported after exposure of human cells in vitro.
Methods
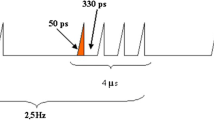
Human cultured fibroblasts of three different donors and three different short-term human lymphocyte cultures were exposed to 1,950 MHz UMTS below the specific absorption rate (SAR) safety limit of 2 W/kg. The alkaline comet assay and the micronucleus assay were used to ascertain dose and time-dependent genotoxic effects. Five hundred cells per slide were visually evaluated in the comet assay and comet tail factor (CTF) was calculated. In the micronucleus assay 1,000 binucleated cells were evaluated per assay. The origin of the micronuclei was determined by fluorescence labeled anticentromere antibodies. All evaluations were performed under blinded conditions.
Results
UMTS exposure increased the CTF and induced centromere-negative micronuclei (MN) in human cultured fibroblasts in a dose and time-dependent way. Incubation for 24 h at a SAR of 0.05 W/kg generated a statistically significant rise in both CTF and MN (P = 0.02). At a SAR of 0.1 W/kg the CTF was significantly increased after 8 h of incubation (P = 0.02), the number of MN after 12 h (P = 0.02). No UMTS effect was obtained with lymphocytes, either unstimulated or stimulated with Phytohemagglutinin.
Conclusion
UMTS exposure may cause genetic alterations in some but not in all human cells in vitro.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames BN, Durston WE, Yamasaki E, Lee FD (1973) Carcinogens are mutagens: a simple test system combining liver homogenates for activation and bacteria for detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 70:2281–2285
Anderson D, Yu T, Phillips B, Schmezer P (1994) The effect of various antioxidants and other modifying agents on oxygen-radical-generated DNA damage in human lymphocytes in the Comet assay. Mutat Res 307:261–271
Czyz J, Guan K, Zeng Q, Nikolova T, Meister A, Schönborn F, Kuster N, Wobus A (2004) High frequency electromagnetic fields (GSM signals) affect gene expression levels in tumor suppressor p53-deficient embryonic stem cells. Bioelectromagnetics 25:296–307
Diem E, Ivancsits S, Rüdiger HW (2002) Basal levels of DNA strand breaks in human leukocytes determined by comet assay. J Toxicol Environ Health A 65:641–648
Diem E, Schwarz C, Adlkofer F, Jahn O, Rüdiger HW (2005) Non-thermal DNA breakage by mobile phone radiation (1800 MHz) in human fibroblasts and transformed GFSH-R17 rat granulosa cells in vitro. Mutat Res 583:178–183
Eastmond DA, Tucker JD (1989) Identification of aneuploidy-inducing agents using cytokinesis-blocked human lymphocytes and an antikinetochore antibody. Environ Mol Mutagen 13:34–43
Farooqi Z, Darroudi F, Natarajan AT (1993) Use of fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of aneugens in cytokinesis-blocked mouse splenocytes. Mutagenesis 8:329–334
Fenech M (1993) The cytokinesis-block micronucleus technique: a detailed description of the method and its application to genotoxicity studies in human populations. Mutat Res 285:35–44
Fenech M, Morley A (1985) Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res 203:339–345
Hardell LO; Carlberg M, Hansson Mild K (2006) Pooled analysis of two case–control studies on use of cellular and cordless telephones and the risk for malignant brain tumours diagnosed in 1997–2003. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 79:630–639
Hardell LO, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F, Mild KH, Morgan LL (2007) Long-term use of cellular phones and brain tumours—increased risk associated with use >10 years. Occup Environ Med 64:626–632
Höytö A, Juutilainen J, Naarala J (2007) Ornitine decarboxylase activity is affected in primary astrocytes but not in secondary cell lines exposed to 872 MHz RF radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 83:367–374
ICNIRP (International Commission for Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection), Standing Committee on Epidemiology: Ahlbom A, Green A, Kheifets L, Savitz D, Swerdlow A (2004) Epidemiology of health effects of radiofrequency exposure. Environ Health Perspect 112:1741–1754
IEGMP (2000) Mobil phones and health. Report of the independent expert group on mobile phones, Chairman: Sir William Stewart, National Radiation Protection Board, London
IEGEMF (2007) Recent research on EMF and health risks. Fourth annual report from SSI’s independent expert group on electromagnetic fields. Statens Stralskyddsinstitut, Stockholm
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Rüdiger HW, Jahn O (2002a) Induction of DNA strand breaks by intermittent exposure to extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic fields in human diploid fibroblasts. Mutat Res 519:1–13
Ivancsits S, Pilger A, Diem E, Schaffer A, Rüdiger HW (2002b) Vanadate induces DNA strand breaks in cultured human fibroblasts at doses relevant to occupational exposure. Mutat Res 519:25–35
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Jahn O, Rüdiger HW (2003) Intermittent extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields cause DNA damage in a dose-dependent way. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 76:431–436
Ivancsits S, Pilger A, Diem E, Jahn O, Rüdiger HW (2005) Cell type specific genotoxic effects of intermittent extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. Mutat Res 583:184–188
Krewski D, Glickman BW, Habash RWY, Habbick B, Lotz WG, Mandeville R, Prato FS, Salem T, Weaver DF (2007) Recent advances in research on radiofrequency fields and health: 2001–2003. J Toxicol Environ Health B 10:287–318
Kundi M, Mild K, Hardell LO, Mattsson MO (2004) Mobile telephones and cancer—a review of epidemiological evidence. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 7:351–384
Lai H, Singh N (1996) Single- and double strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 69:513–521
Lai H, Singh N (2004) Magnetic-field-induced DNA strand breaks in brain cells of the rat. Environ Health Perspect 112:687–694
Lahkola A, Auvinen A, Raitanen J, Shoemaker MJ, Christensen HC, Feychting M, Johansen C, Klaeboe L, Lönn S, Swerdlow AJ, Tynes T, Salminen T (2007) Mobile phone use and risk of glioma in 5 north European countries. Int J Cancer 120(8):1769–1775
Lasne C, Gu Z, Venegas W, Chouroulinkov I (1984) The in vitro micronucleus assay for detection of cytogenetic effects induced by mutagen-carcinogens: comparison with the in vitro sister-chromatid exchange assay. Mutat Res 130:273–282
Lee S, Johnson D, Dunbar K, Dong H, Ge X, Kim Y, Wing C, Jayathilaka N, Emmanuel N, Zhou C, Gerber H, Tseng C, Wang S (2005) 2.45 GHz radiofrequency fields alter gene expression in cultured human cells. FEBS Lett 579:4829–4836
Leszczynski D, Joenväärä S, Reivinen J, Kuokka R (2002) Non-thermal activation of the hsp27/p38MAPK stress pathway by mobile phone radiation in human endothelial cells: molecular mechanism for cancer- and blood-brain barrier-related effects. Differentiation 70:120–129
Meltz M (2003) Radiofrequency exposure and mammalian cell toxicity, genotoxicity, and transformation. Bioelectromagnetics 24:196–213
Ndoumbè Mbonjo Mbonjo H, Streckert J, Bitz A, Hansen V, Glasmachers A, Gencol S, Rozic D (2004) Generic UMTS test signal for RF biolelectromagnetic studies. Bioelectromagnetics 25:415–425
Olive PL, Banath JP (1995) Sizing highly fragmented DNA in individual apoptotic cells using the comet assay and a DNA crosslinking agent. Exp Cell Res 221:19–26
Östling O, Johanson K (1984) Microelectrophoretic study of radiation-induced DNA damages in individual mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Com 123:291–298
Pancini S, Ruggiero M, Sardi I, Aterini S, Gulisano F, Gulisano M (2002) Exposure to global system for mobile communication (GSM) cellular phone radiofrequency alters gene expression, proliferation, and morphology of human skin fibroblasts. Oncol Res 13:19–24
Paulray R, Behari J (2006) Single strand DNA breaks inn rat brain cells exposed to microwave radiation. Mutat Res 596:76–80
REFLEX Final Report (2004) European Union Project QLK4-CT-1999-01574, Risk evaluation of potential environmental hazards from low frequency electromagnetic field exposure using sensitive in vitro methods. Final Report. http://www.verum-foundation.de
Repacholi M (1998) Low-Level exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields: health effects and research needs. Bioelectromagnetics 19:1–19
Schoemaker MJ, Swerdlow AJ, Ahlbom A, Auvinen A, Blaasaas KG, Cardis E, Christensen HC, Feychting M, Hepworth SJ, Johansen C, Klaeboe L, Lonn S, McKinney PA, Muir K, Raitanen J, Salminen T, Thomsen J, Tynes T (2005) Mobile phone use and risk of acoustic neuroma: results of the interphone case–control study in five North European countries. Br J Cancer 93:842–848
Schonborn F, Pokovic K, Burkhard M, Kuster N (2001) Basis for optimization of in vitro exposure apparatus for health hazard evaluations of mobile communications. Bioelectromagnetics 22:547–559
Schuderer J (2005) EMF risk assessment: “in vitro” research and sleep studies. In: Series in microelectronics. Hartung-Gorre Verlag, Konstanz
Schuderer J, Kuster N (2003) Effect of the meniscus at the solid/liquid interface of the SAR distribution in Petri dishes and flasks. Bioelectromagnetics 24:103–108
Schütz J, Böhler E, Berg G, Schlehofer B, Hettinger I, Schlaefer K, Wahrendorf J, Kunna-Grass K, Blettner M (2006) Cellular phones, cordless phones, and the risk of glioma and meningioma (Interphone Study Group, Germany) Am J Epidemiol 163(6):512–520
Singh N, Lai H (1998) 60 Hz magnetic field exposure induces DNA crosslinks in rat brain cells. Mutat Res 400:313–320
Singh N, McCoy M, Tice R, Schneider E (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Singh N, Tice R, Stephens R, Schneider E (1991) A microgel electrophoresis technique for direct quantitation of DNA damage and repair in individual fibroblasts cultured on microscope slides. Mutat Res 252:289–296
Speit G, Schütz P, Hoffmann H (2007) Genotoxic effects of exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMF) in cultured mammalian cells are not independently reproducible. Mutat Res 626:42–47
Vijayalaxmi, Obe G (2004) Controversial cytogenetic observations in mammalian somatic cells exposed to radiofrequency radiation. Radiat Res 162:481–496
Whitehead TD, Moros EG, Brownstein BH, Roto Roti JL (2006) Gene expression does not change significantly in C3H 10T(1/2) cells after exposure to 847.74 CDMA or 835.62 FDMA radiofrequency radiation. Radiat Res 165:626–635
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the Austrian Workers Compensation Board, Vienna, Austria, the Verum Foundation, Munich, Germany, and the Austrian Science Fund FWF (project number P18984-B09). The authors gratefully acknowledge the value assistance of Marietta Weninger and Petra Hartbauer and thank Dr Elisabeth Ponocny-Seliger for helpful statistical advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, C., Kratochvil, E., Pilger, A. et al. Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (UMTS, 1,950 MHz) induce genotoxic effects in vitro in human fibroblasts but not in lymphocytes. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 81, 755–767 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0305-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0305-5