Abstract
Purpose
Exophthalmometry is clinically important for diagnoses, follow-up, and treatment decision-making. Through the years, several drawbacks and sources of error have been described when using Hertel and other exophthalmometers.
Methods
We describe a simple method of non-touch slit-lamp exophthalmometry. Comparing the results between Hertel and slit-lamp exophthalmometry on 60 patients with proptosis showed no statistically significant differences in the two methods.
Results
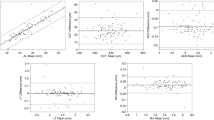
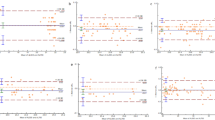
A total of 60 consecutive patients with proptosis were included. Thirty-six cases (60 %) were women. Their mean age was 55.6 ± 16.4 (median 57.5, range 20–87) years. Only 5 % of the measurements had more than 2 mm difference between the two techniques. There were no significant differences in the measurements between the two methods. Intra-correlation coefficient is 0.96 for right side and 0.956 for lest side. The Bland–Altman plot revealed good agreement.
Conclusions
Slit-lamp exophthalmometry offers a simple, easily available, and reliable non-touch technique that does not require an exophthalmometer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nkenke E, Maier T, Benz M, Wiltfang J, Holbach LM, Kramer M, Hausler G, Neukam FW (2004) Hertel exophthalmometry versus computed tomography and optical 3D imaging for the determination of the globe position in zygomatic fractures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33:125–133
O’Donnell NP, Virdi M, Kemp EG (1999) Hertel exophthalmometry: the most appropriate measuring technique. Br J Ophthalmol 83:1096B
Musch DC, Frueh BR, Landis JR (1985) The reliability of Hertel exophthalmometry. Observer variation between physician and lay readers. Ophthalmology 92:1177–1180
Frueh BR, Garber F, Grill R, Musch DC (1985) Positional effects on exophthalmometer readings in Graves’ eye disease. Arch Ophthalmol 103:1355–1356
Davanger M (1970) Principles and sources of error in exophthalmometry. A new exophthalmometer. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 48:625–633
Vardizer Y, Berendschot TT, Mourits MP (2005) Effect of exophthalmometer design on its accuracy. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 21:427–430
Nkenke E, Benz M, Maier T, Wiltfang J, Holbach LM, Kramer M, Hausler G, Neukam FW (2003) Relative en- and exophthalmometry in zygomatic fractures comparing optical non-contact, non-ionizing 3D imaging to the Hertel instrument and computed tomography. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 31:362–368
Cole HP 3rd, Couvillion JT, Fink AJ, Haik BG, Kastl PR (1997) Exophthalmometry: a comparative study of the Naugle and Hertel instruments. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 13:189–194
Sleep TJ, Manners RM (2002) Interinstrument variability in Hertel-type exophthalmometers. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 18:254–257
Hessemer T, Kolling GH (1994) A new method for measuring exophthalmos. The slit lamp exophthalmometer. Ophthalmologe 91:36–40
Conflicting relationships
No conflicting relationship exists for any author.
Competing interests
The authors have no financial interest in any of the materials used in this study.
Funding
This study was not supported by outside funding.
Contributorship
All authors contributed to the writing and editing of this manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Dr Arie Nemet had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almog, Y., Rosen, E. & Nemet, A.Y. Slit-lamp exophthalmometry, a novel technique. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252, 1161–1164 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2620-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2620-8