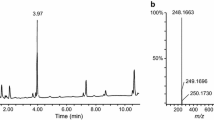
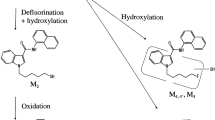
Abstract
High-resolution mass spectrometry and accurate mass measurement by liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry (LC/Q-TOFMS) was applied to postmortem plasma and urine specimens from an autopsy of a fatal case involving synthetic cannabinoid use, resulting in the detection of three synthetic cannabinoids: MAM-2201, AM-1220, and AM-2232. We searched for their metabolites existing in postmortem plasma or urine by LC/Q-TOFMS and were able to detect N-dealkylated metabolites, defluorinated and further oxidized metabolites of MAM-2201, and some hydroxylated metabolites. Postmortem plasma concentrations of the parent drugs, N-dealkylated metabolites, and fluorinated and further oxidized metabolites of MAM-2201 were measured, and quantitation results revealed site differences between heart and femoral postmortem plasma concentrations of parent drugs and some metabolites, suggesting postmortem redistribution of the synthetic cannabinoids and their metabolites. Quantitation results suggest that defluorination is a major metabolic pathway for MAM-2201, and N-dealkylation is a common but minor pathway for the naphthoylindole-type synthetic cannabinoids in human.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 December 2015
Erratum to: Int J Legal Med (2015) 129:1233–1245
References
Tai S, Fantegrossi W (2014) Synthetic cannabinoids: pharmacology, behavioral effects, and abuse potential. Current Addict Rep 1(2):129–136. doi:10.1007/s40429-014-0014-y
ElSohly MA, Gul W, Wanas AS, Radwan MM (2014) Synthetic cannabinoids: analysis and metabolites. Life Sciences 97(1):78–90. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2013.12.212
Kikura-Hanajiri R, Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Goda Y (2013) Changes in the prevalence of synthetic cannabinoids and cathinone derivatives in Japan until early 2012. Forensic Toxicol 31(1):44–53. doi:10.1007/s11419-012-0165-2
Ji N, Takahashi M, Uemura N, Seto T, Fukaya H, Suzuki J, Yoshida M, Kusano M, Nakayama H, Zaitsu K, Ishii A, Moriyasu T, Nakae D (2015) Identification of N, N-bis(1-pentylindol-3-yl-carboxy)naphthylamine (BiPICANA) found in an herbal blend product in the Tokyo metropolitan area and its cannabimimetic effects evaluated by in vitro [35S]GTPγS binding assays. Forensic Toxicol 33(1):84–92. doi:10.1007/s11419-014-0253-6
Castaneto MS, Gorelick DA, Desrosiers NA, Hartman RL, Pirard S, Huestis MA (2014) Synthetic cannabinoids: epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 144:12–41. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.08.005
Huffman JW, Zengin G, Wu M-J, Lu J, Hynd G, Bushell K, Thompson ALS, Bushell S, Tartal C, Hurst DP, Reggio PH, Selley DE, Cassidy MP, Wiley JL, Martin BR (2005) Structure–activity relationships for 1-alkyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indoles at the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors: steric and electronic effects of naphthoyl substituents. New highly selective CB2 receptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem 13(1):89–112. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2004.09.050
Kneisel S, Auwärter V (2012) Analysis of 30 synthetic cannabinoids in serum by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry after liquid-liquid extraction. J Mass Spectrom 47(7):825–835. doi:10.1002/jms.3020
Saito T, Namera A, Miura N, Ohta S, Miyazaki S, Osawa M, Inokuchi S (2013) A fatal case of MAM-2201 poisoning. Forensic Toxicol 31(2):333–337. doi:10.1007/s11419-013-0190-9
Patton AL, Chimalakonda KC, Moran CL, McCain KR, Radominska-Pandya A, James LP, Kokes C, Moran JH (2013) K2 toxicity: fatal case of psychiatric complications following AM2201 exposure. J Forensic Sci 58(6):1676–1680. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.12216
Hermanns-Clausen M, Kneisel S, Hutter M, Szabo B, Auwärter V (2013) Acute intoxication by synthetic cannabinoids – Four case reports. Drug Test Anal 5(9-10):790–794. doi:10.1002/dta.1483
Hermanns-Clausen M, Kneisel S, Szabo B, Auwärter V (2013) Acute toxicity due to the confirmed consumption of synthetic cannabinoids: clinical and laboratory findings. Addiction 108(3):534–544. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.04078.x
K-i T, Funada M (2014) Cytotoxicity of synthetic cannabinoids on primary neuronal cells of the forebrain: the involvement of cannabinoid CB1 receptors and apoptotic cell death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 274(1):17–23. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.10.028
Hebert-Chatelain E, Reguero L, Puente N, Lutz B, Chaouloff F, Rossignol R, Piazza P-V, Benard G, Grandes P, Marsicano G (2014) Cannabinoid control of brain bioenergetics: exploring the subcellular localization of the CB1 receptor. Mol Metab 3(4):495–504. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2014.03.007
Benard G, Massa F, Puente N, Lourenco J, Bellocchio L, Soria-Gomez E, Matias I, Delamarre A, Metna-Laurent M, Cannich A, Hebert-Chatelain E, Mulle C, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Martin-Fontecha M, Klugmann M, Guggenhuber S, Lutz B, Gertsch J, Chaouloff F, Lopez-Rodriguez ML, Grandes P, Rossignol R, Marsicano G (2012) Mitochondrial CB1 receptors regulate neuronal energy metabolism. Nature Neuroscience 15 (4):558-564. doi:http://www.nature.com/neuro/journal/v15/n4/abs/nn.3053.html#supplementary-information
Zaitsu K, Hayashi Y, Suzuki K, Nakayama H, Hattori N, Takahara R, Kusano M, Tsuchihashi H, Ishi A Metabolome disruption of the rat cerebrum induced by the acute toxic effects of the synthetic cannabinoid MAM-2201. Life Sciences. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.05.013
Fantegrossi WE, Moran JH, Radominska-Pandya A, Prather PL (2014) Distinct pharmacology and metabolism of K2 synthetic cannabinoids compared to Δ9-THC: mechanism underlying greater toxicity? Life Sciences 97(1):45–54. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2013.09.017
Huffman JW, Mabon R, Wu M-J, Lu J, Hart R, Hurst DP, Reggio PH, Wiley JL, Martin BR (2003) 3-Indolyl-1-naphthylmethanes: new cannabimimetic indoles provide evidence for aromatic stacking interactions with the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Bioorg Med Chem 11(4):539–549. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00451-0
Esaki H, Ohtaki R, Maegawa T, Monguchi Y, Sajiki H (2007) Novel Pd/C-catalyzed redox reactions between aliphatic secondary alcohols and ketones under hydrogenation conditions: application to H − D exchange reaction and the mechanistic study. J Org Chem 72(6):2143–2150. doi:10.1021/jo062582u
Zaitsu K, Katagi M, Kamata HT, Kamata T, Shima N, Miki A, Tsuchihashi H, Mori Y (2009) Determination of the metabolites of the new designer drugs bk-MBDB and bk-MDEA in human urine. Forensic Sci Int 188(1–3):131–139. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2009.04.001
Zaitsu K, Katagi M, Kamata T, Kamata H, Shima N, Tsuchihashi H, Hayashi T, Kuroki H, Matoba R (2008) Determination of a newly encountered designer drug “p-methoxyethylamphetamine” and its metabolites in human urine and blood. Forensic Sci Int 177(1):77–84. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2007.11.001
Hopfgartner G, Tonoli D, Varesio E (2012) High-resolution mass spectrometry for integrated qualitative and quantitative analysis of pharmaceuticals in biological matrices. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(8):2587–2596. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5641-8
Pélissier-Alicot A-L, Gaulier J-M, Champsaur P, Marquet P (2003) Mechanisms underlying postmortem redistribution of drugs: a review. J Anal Toxicol 27(8):533–544. doi:10.1093/jat/27.8.533
Harris CR, Brown A (2013) Synthetic cannabinoid intoxication: a case series and review. J Emerg Med 44(2):360–366. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2012.07.061
Young AC, Schwarz E, Medina G, Obafemi A, Feng S-Y, Kane C, Kleinschmidt K (2012) Cardiotoxicity associated with the synthetic cannabinoid, K9, with laboratory confirmation. Am J Emerg Med 30(7):1320.e1325–1320.e1327. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2011.05.013
Jang M, Shin I, Yang W, Chang H, Yoo HH, Lee J, Kim E (2014) Determination of major metabolites of MAM-2201 and JWH-122 in in vitro and in vivo studies to distinguish their intake. Forensic Sci Int 244:85–91. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2014.08.008
Sobolevsky T, Prasolov I, Rodchenkov G (2012) Detection of urinary metabolites of AM-2201 and UR-144, two novel synthetic cannabinoids. Drug Test Anal 4(10):745–753. doi:10.1002/dta.1418
Hutter M, Moosmann B, Kneisel S, Auwärter V (2013) Characteristics of the designer drug and synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist AM-2201 regarding its chemistry and metabolism. J Mass Spectrom 48(7):885–894. doi:10.1002/jms.3229
Jang M, Yang W, Shin I, Choi H, Chang H, Kim E (2014) Determination of AM-2201 metabolites in urine and comparison with JWH-018 abuse. Int J Legal Med 128(2):285–294. doi:10.1007/s00414-013-0884-x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 30700546.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitsu, K., Nakayama, H., Yamanaka, M. et al. High-resolution mass spectrometric determination of the synthetic cannabinoids MAM-2201, AM-2201, AM-2232, and their metabolites in postmortem plasma and urine by LC/Q-TOFMS. Int J Legal Med 129, 1233–1245 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-015-1257-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-015-1257-4