Abstract
Introduction
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy is a newly emerging radiotherapy treatment method that, compared with conventionally fractionated radiation therapy (CFRT), allows an ablative dose of radiation to be delivered to a confined area around a tumor. The aim of the present study was to investigate the changes of various cytokines that may be involved in ablative radiation-induced lung injury in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
In the in vivo study, ablative-dose radiation was delivered to a small volume of the left lung of C3H/HeJCr mice using a small-animal irradiator. The levels of 24 cytokines in the peripheral blood were tested at several time points after irradiation. For the in vitro study, three mouse cell types (type II pneumocytes, alveolar macrophages, and fibroblasts) known to play important roles in radiation-induced pneumonitis and lung fibrosis were analyzed using a co-culture system.
Results
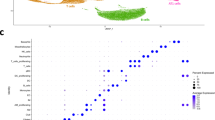
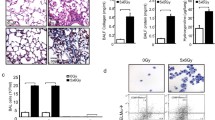
In the in vivo study, we found obvious patterns of serum cytokine changes depending on the volume of tissue irradiated (2-mm vs. 3.5-mm collimator). Only the levels of 3 cytokines increased with the 2-mm collimator at the acute phase (1–2 weeks after irradiation), while the majority of cytokines were elevated with the 3.5-mm collimator. In the in vitro co-culture system, after the cells were given an ablative dose of irradiation, the levels of five cytokines (GM-CSF, G-CSF, IL-6, MCP-1, and KC) increased significantly in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusions
The cytokine levels in our radiation-induced lung injury model showed specific changes, both in vivo and in vitro. These results imply that biological studies related to ablative-dose small-volume irradiation should be investigated using the corresponding experimental models rather than on those simulating large-volume CFRT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Videtic GM, Stephans KL (2010) The role of stereotactic body radiotherapy in the management of non-small cell lung cancer: an emerging standard for the medically inoperable patient? Curr Oncol Rep 12(4):235–241
Timmerman R, Bastasch M, Saha D, Abdulrahman R, Hittson W, Story M (2007) Optimizing dose and fractionation for stereotactic body radiation therapy. Normal tissue and tumor control effects with large dose per fraction. Front Radiat Ther Oncol 40:352–365
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C, Papiez L, Tudor K, DeLuca J, Ewing M, Abdulrahman R, DesRosiers C, Williams M, Fletcher J (2006) Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(30):4833–4839
Timmerman RD, Story M (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy: a treatment in need of basic biological research. Cancer J 12(1):19–20
Lo SS, Sahgal A, Kunos AC, Teh SB, Yao M, Machtay M, Mayr AN, Huang Z, Chang LE (2012) Reported Toxicities Associated with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. In: Lo SS, Teh BS, Lu JJ, Schefter TE (eds) Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Springer, Berlin, pp 373–392
Story MD, Nirodi C, Park C (2012) Radiobiology of stereotactic body radiation therapy/stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. In: Lo SS, Teh BS, Lu JJ, Schefter TE (eds) Stereotactic body radiation therapy. Springer, Berlin, pp 123–136
Hadziahmetovic M, Loo BW, Timmerman RD, Mayr NA, Wang JZ, Huang Z, Grecula JC, Lo SS (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy (stereotactic ablative radiotherapy) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer–updates of radiobiology, techniques, and clinical outcomes. Discov Med 9(48):411–417
Cho J, Kodym R, Seliounine S, Richardson JA, Solberg TD, Story MD (2010) High dose-per-fraction irradiation of limited lung volumes using an image-guided, highly focused irradiator: simulating stereotactic body radiotherapy regimens in a small-animal model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77(3):895–902
Pidikiti R, Stojadinovic S, Speiser M, Song KH, Hager F, Saha D, Solberg TD (2011) Dosimetric characterization of an image-guided stereotactic small animal irradiator. Phys Med Biol 56(8):2585–2599
Song KH, Pidikiti R, Stojadinovic S, Speiser M, Seliounine S, Saha D, Solberg TD (2010) An x-ray image guidance system for small animal stereotactic irradiation. Phys Med Biol 55(23):7345–7362
Chen Y, Williams J, Ding I, Hernady E, Liu W, Smudzin T, Finkelstein JN, Rubin P, Okunieff P (2002) Radiation pneumonitis and early circulatory cytokine markers. Semin Radiat Oncol 12(1 Suppl 1):26–33
Mehta V (2005) Radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis in non-small-cell lung cancer: pulmonary function, prediction, and prevention. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63(1):5–24
Fleckenstein K, Gauter-Fleckenstein B, Jackson IL, Rabbani Z, Anscher M, Vujaskovic Z (2007) Using biological markers to predict risk of radiation injury. Semin Radiat Oncol 17(2):89–98
Ao X, Zhao L, Davis MA, Lubman DM, Lawrence TS, Kong FM (2009) Radiation produces differential changes in cytokine profiles in radiation lung fibrosis sensitive and resistant mice. J Hematol Oncol 2:6
Xie CH, Zhang MS, Zhou YF, Han G, Cao Z, Zhou FX, Zhang G, Luo ZG, Wu JP, Liu H, Chen J, Zhang WJ (2006) Chinese medicine Angelica sinensis suppresses radiation-induced expression of TNF-alpha and TGF-beta1 in mice. Oncol Rep 15(6):1429–1436
Gorshkova I, Zhou T, Mathew B, Jacobson JR, Takekoshi D, Bhattacharya P, Smith B, Aydogan B, Weichselbaum RR, Natarajan V, Garcia JG, Berdyshev EV (2012) Inhibition of serine palmitoyltransferase delays the onset of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis through the negative regulation of sphingosine kinase-1 expression. J Lipid Res 53(8):1553–1568
Rube CE, Wilfert F, Palm J, Konig J, Burdak-Rothkamm S, Liu L, Schuck A, Willich N, Rube C (2004) Irradiation induces a biphasic expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the lung. Strahlenther Onkol 180(7):442–448
Matej R, Housa D, Pouckova P, Zadinova M, Olejar T (2007) Radiation-induced production of PAR-1 and TGF-beta 1 mRNA in lung of C57Bl6 and C3H murine strains and influence of pharmacoprophylaxis by ACE inhibitors. Pathol Res Pract 203(2):107–114
Rubin P, Johnston CJ, Williams JP, McDonald S, Finkelstein JN (1995) A perpetual cascade of cytokines postirradiation leads to pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 33(1):99–109
Johnston CJ, Hernady E, Reed C, Thurston SW, Finkelstein JN, Williams JP (2010) Early alterations in cytokine expression in adult compared to developing lung in mice after radiation exposure. Radiat Res 173(4):522–535
Johnston CJ, Manning C, Hernady E, Reed C, Thurston SW, Finkelstein JN, Williams JP (2011) Effect of total body irradiation on late lung effects: hidden dangers. Int J Radiat Biol 87(8):902–913
Hong ZY, Lee HJ, Choi WH, Lee YJ, Eun SH, Lee JI, Park K, Lee JM, Cho J (2014) A preclinical rodent model of acute radiation-induced lung injury after ablative focal irradiation reflecting clinical stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiat Res 182(1):83–91
Hong ZY, Eun SH, Park K, Choi WH, Lee JI, Lee EJ, Lee JM, Story MD, Cho J (2014) Development of a small animal model to simulate clinical stereotactic body radiotherapy-induced central and peripheral lung injuries. J Radiat Res 55(4):648–657
Anscher MS, Kong FM, Andrews K, Clough R, Marks LB, Bentel G, Jirtle RL (1998) Plasma transforming growth factor beta1 as a predictor of radiation pneumonitis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 41(5):1029–1035
Anscher MS, Peters WP, Reisenbichler H, Petros WP, Jirtle RL (1993) Transforming growth factor beta as a predictor of liver and lung fibrosis after autologous bone marrow transplantation for advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 328(22):1592–1598
Johnston CJ, Piedboeuf B, Baggs R, Rubin P, Finkelstein JN (1995) Differences in correlation of mRNA gene expression in mice sensitive and resistant to radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Radiat Res 142(2):197–203
Lukacs NW, Hogaboam C, Chensue SW, Blease K, Kunkel SL (2001) Type 1/type 2 cytokine paradigm and the progression of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 120(1 Suppl):5S–8S
Shao DD, Suresh R, Vakil V, Gomer RH, Pilling D (2008) Pivotal Advance: Th-1 cytokines inhibit, and Th-2 cytokines promote fibrocyte differentiation. J Leukoc Biol 83(6):1323–1333
Herzog EL, Bucala R (2010) Fibrocytes in health and disease. Exp Hematol 38(7):548–556
Sakamoto H, Zhao LH, Jain F, Kradin R (2002) IL-12p40(−/−) mice treated with intratracheal bleomycin exhibit decreased pulmonary inflammation and increased fibrosis. Exp Mol Pathol 72(1):1–9
Keane MP, Belperio JA, Burdick MD, Strieter RM (2001) IL-12 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 281(1):L92–L97
Sun L, Louie MC, Vannella KM, Wilke CA, LeVine AM, Moore BB, Shanley TP (2011) New concepts of IL-10-induced lung fibrosis: fibrocyte recruitment and M2 activation in a CCL2/CCR2 axis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 300(3):L341–L353
Westermann W, Schobl R, Rieber EP, Frank KH (1999) Th2 cells as effectors in postirradiation pulmonary damage preceding fibrosis in the rat. Int J Radiat Biol 75(5):629–638
Gharaee-Kermani M, Nozaki Y, Hatano K, Phan SH (2001) Lung interleukin-4 gene expression in a murine model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cytokine 15(3):138–147
Fajardo LF, Berthrong M (1978) Radiation injury in surgical pathology: part I. Am J Surg Pathol 2(2):159–199
Moore BB, Kolodsick JE, Thannickal VJ, Cooke K, Moore TA, Hogaboam C, Wilke CA, Toews GB (2005) CCR2-mediated recruitment of fibrocytes to the alveolar space after fibrotic injury. Am J Pathol 166(3):675–684
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Hong K, Lutz MA, Murray LA, Xue YY, Belperio JA, Keane MP, Strieter RM (2004) Circulating fibrocytes traffic to the lungs in response to CXCL12 and mediate fibrosis. J Clin Invest 114(3):438–446
Brach MA, Gruss HJ, Kaisho T, Asano Y, Hirano T, Herrmann F (1993) Ionizing radiation induces expression of interleukin 6 by human fibroblasts involving activation of nuclear factor-kappa B. J Biol Chem 268(12):8466–8472
Suga M, Iyonaga K, Ichiyasu H, Saita N, Yamasaki H, Ando M (1999) Clinical significance of MCP-1 levels in BALF and serum in patients with interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J 14(2):376–382
Molls RR, Savransky V, Liu M, Bevans S, Mehta T, Tuder RM, King LS, Rabb H (2006) Keratinocyte-derived chemokine is an early biomarker of ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290(5):1187–1193
Li WQ, Li YM, Guo J, Liu YM, Yang XQ, Ge HJ, Xu Y, Liu HM, He J, Yu HY (2010) Hepatocytic precursor (stem-like) WB-F344 cells reduce tumorigenicity of hepatoma CBRH-7919 cells via TGF-beta/Smad pathway. Oncol Rep 23(6):1601–1607
Milliat F, Francois A, Isoir M, Deutsch E, Tamarat R, Tarlet G, Atfi A, Validire P, Bourhis J, Sabourin JC, Benderitter M (2006) Influence of endothelial cells on vascular smooth muscle cells phenotype after irradiation: implication in radiation-induced vascular damages. Am J Pathol 169(4):1484–1495
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nuclear Research and Development Program (NRF-2011-0031695)(JC) and the Radiation Technology R&D program (NRF-2013M2A2A7042978) (JC) through the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning; by a faculty research grant from the Yonsei University College of Medicine for 2014 (6-2014-0031)(JC); and by a grant from the Varian Corporation (MDS).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The authors dedicate this article to the late Dr. Reinhard Kodym.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, ZY., Song, K.H., Yoon, JH. et al. An Experimental Model-Based Exploration of Cytokines in Ablative Radiation-Induced Lung Injury In Vivo and In Vitro. Lung 193, 409–419 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-015-9705-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-015-9705-y