Abstract
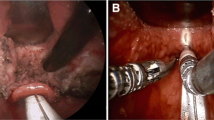
Retroglossal obstruction is one of the etiologies causing obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and can be addressed by removing some tissues of the tongue base. However, because of its deep-seated location, its surgical removal is still challenging. Although coblation technique has been introduced, its efficacy and morbidity need further evaluation, particularly in Asians. This study aimed to assess its safety and effectiveness and to identify outcome prognosticators. Forty-seven OSA patients who underwent coblation lingual tonsil removal were included. Retroglossal obstruction was confirmed by drug-induced sleep videofluoroscopy. Attended full-night polysomnography was performed twice; before and 6 months after surgery in 27 patients. The tongue base was fully exposed with three deep-seated traction sutures, visualized with a 30° or 70° endoscope, and ablated using a coblator. Surgical success was defined with postoperative apnea hypopnea index (AHI) <20 and reduction >50 %. Postoperative morbidities were evaluated. Demographic and polysomnographic parameters between success and failure groups were compared. None of the patients had immediate postoperative hemorrhage. Postoperatively, one patient had delayed hemorrhage and one patient severe respiratory difficulty. Taste loss, tongue dysmotility, dental injury or severe oropharyngeal stricture were absent. A mean AHI decreased from 37.7 ± 18.6 to 18.7 ± 14.8/h (P < 0.001). The success rate was 55.6 %. Their mean minimal oxygen saturation was significantly lower (P = 0.004) in the failure group. Coblation lingual tonsil removal technique showed minimal morbidity and favorable outcome in Koreans. The surgical outcome might be associated with the severity of single respiratory events.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suh GD (2013) Evaluation of open midline glossectomy in the multilevel surgical management of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 148:166–171
Fujita S, Woodson BT, Clark JL, Wittig R (1991) Laser midline glossectomy as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 101:805–809
Friedman M, Soans R, Gurpinar B, Lin HC, Joseph N (2008) Evaluation of submucosal minimally invasive lingual excision technique for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 139:378–384 discussion 385
Lin HS, Rowley JA, Badr MS et al (2013) Transoral robotic surgery for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 123:1811–1816
Bock JM, Trask DK (2008) Coblation-assisted lingual tonsillectomy for dysphagia secondary to tongue base hypertrophy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 117:506–509
Rotenberg B, Tan S (2011) Endoscopic-assisted radiofrequency lingual tonsillectomy. Laryngoscope 121:994–996
Leitzbach SU, Bodlaj R, Maurer JT, Hormann K, Stuck BA (2014) Safety of cold ablation (coblation) in the treatment of tonsillar hypertrophy of the tongue base. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:1635–1639
Lee CH, Hong SL, Rhee CS, Kim SW, Kim JW (2012) Analysis of upper airway obstruction by sleep videofluoroscopy in obstructive sleep apnea: a large population-based study. Laryngoscope 122:237–241
Sher AE, Schechtman KB, Piccirillo JF (1996) The efficacy of surgical modifications of the upper airway in adults with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 19:156–177
Robinson S, Ettema SL, Brusky L, Woodson BT (2006) Lingual tonsillectomy using bipolar radiofrequency plasma excision. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:328–330
Babademez MA, Ciftci B, Acar B et al (2010) Low-temperature bipolar radiofrequency ablation (coblation) of the tongue base for supine-position-associated obstructive sleep apnea. ORLJ Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 72:51–55
Lin HC, Friedman M, Chang HW, Yalamanchali S (2014) Z-palatopharyngoplasty combined with endoscopic coblator open tongue base resection for severe obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 150:1078–1085
Vicini C, Dallan I, Canzi P et al (2012) Transoral robotic surgery of the tongue base in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome: anatomic considerations and clinical experience. Head Neck 34:15–22
Lin HC, Friedman M, Chang HW, Gurpinar B (2008) The efficacy of multilevel surgery of the upper airway in adults with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 118:902–908
Mediano O, Barcelo A, de la Pena M, Gozal D, Agusti A, Barbe F (2007) Daytime sleepiness and polysomnographic variables in sleep apnoea patients. Eur Respir J 30:110–113
Kulkas A, Tiihonen P, Julkunen P, Mervaala E, Toyras J (2013) Novel parameters indicate significant differences in severity of obstructive sleep apnea with patients having similar apnea-hypopnea index. Med Biol Eng Comput 51:697–708
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wee, J.H., Tan, K., Lee, WH. et al. Evaluation of coblation lingual tonsil removal technique for obstructive sleep apnea in Asians: preliminary results of surgical morbidity and prognosticators. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 2327–2333 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3330-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3330-x