Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effects of a moderate physical training (T) on the blood and splenic lymphocytes subsets and the rate of apoptosis in adult offspring submitted to perinatal low-protein (LP) diet.
Methods
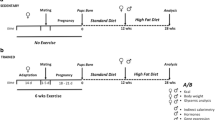
Male Wistar rats were divided according to their mother’s diet: control (C, 17 % casein) and undernourished (LP, 8 % casein). At the 60th day, pups were submitted to moderate physical training (8 weeks, 5 days week−1, 60 min day−1, at 70 % of VO2max). After T period, pups received an injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). B, NK, and TCD3+ lymphocytes subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry. Spleen lymphocytes apoptosis was evaluated by DNA fragmentation, phosphatidylserine externalization (PSE), and mitochondrial transmembrane depolarization (MTD) using a flow cytometer. Plasma TNF-α concentrations were analyzed by ELISA.
Results
LP + LPS pups showed a higher percentage of blood B, CD4+, and NK and a reduction in TCD3+, CD8+ than C pups. The percentage of NK and CD3+ was restored in LP + T + LPS pups. In the spleen, T normalized the percentage of NK in LP + LPS pups. LP + LPS pups showed a higher percentage of cells with PSE and MTD than C + LPS pups that was attenuated by T. The concentration of TNF-α was higher in LP + LPS than C + LPS, but it was attenuated in LP + T + LPS pups.
Conclusion
Moderate physical training was able to revert the effects of perinatal LP diet on circulation lymphocytes subsets and attenuated splenic lymphocytes apoptosis and plasma TNF-α concentrations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemente AP, Santos CD, Martins VJ, Benedito-Silva AA, Albuquerque MP, Sawaya AL (2011) Mild stunting is associated with higher body fat: study of a low-income population. J Pediatr (Rio J) 87:138–144
Clemente AP, Santos CD, Silva AA, Martins VJ, Marchesano AC, Fernandes MB, Albuquerque MP, Sawaya AL (2012) Mild stunting is associated with higher blood pressure in overweight adolescents. Arq Bras Cardiol 98:6–12
Martins VJ, Toledo Florencio TM, Grillo LP, do Carmo PFM, Martins PA, Clemente AP, Santos CD, de Fatima AVM, Sawaya AL (2011) Long-lasting effects of undernutrition. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:1817–1846
Principi N, Bianchini S, Baggi E, Esposito S (2013) Implications of maternal vitamin D deficiency for the fetus, the neonate and the young infant. Eur J Nutr 52:859–867
Langley-Evans SC, Carrington LJ (2006) Diet and the developing immune system. Lupus 15:746–752
Molina V, Medici M, Taranto MP, Font de Valdez G (2008) Effects of maternal vitamin B12 deficiency from end of gestation to weaning on the growth and haematological and immunological parameters in mouse dams and offspring. Arch Ani Nut 62:162–168
Morgan G (1997) What, if any, is the effect of malnutrition on immunological competence? Lancet 349:1693–1695
Ferreira ESWT, Galvao BA, Ferraz-Pereira KN, de-Castro CB, Manhaes-de-Castro R (2009) Perinatal malnutrition programs sustained alterations in nitric oxide released by activated macrophages in response to fluoxetine in adult rats. NeuroImmunoModulation 16:219–227
Ortiz R, Cortes L, Cortes E, Medina H (2009) Malnutrition alters the rates of apoptosis in splenocytes and thymocyte subpopulations of rats. Clin Exp Immunol 155:96–106
Jones KD, Berkley JA, Warner JO (2010) Perinatal nutrition and immunity to infection. Pediatric allergy and immunology official publication of the European Society of Pediatric Allergy and Immunology 21:564–576
McDade TW, Beck MA, Kuzawa CW, Adair LS (2001) Prenatal undernutrition and postnatal growth are associated with adolescent thymic function. J Nutr 131:1225–1231
Cortes E, Gonzalez C, Betancourt M, Ortiz R (2001) Assessment of DNA damage in spleen, bone marrow, and peripheral blood from malnourished rats by single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Terat, Carci, and Mutage 21:231–247
Moita L, Lustosa MF, Silva AT, Pires-de-Melo IH, de Melo RJ, de Castro RM, Filho NT, Ferraz JC, Leandro CG (2011) Moderate physical training attenuates the effects of perinatal undernutrition on the morphometry of the splenic lymphoid follicles in endotoxemic adult rats. NeuroImmunoModulation 18:103–110
Cortes-Barberena E, Gonzalez-Marquez H, Gomez-Olivares JL, Ortiz-Muniz R (2008) Effects of moderate and severe malnutrition in rats on splenic T lymphocyte subsets and activation assessed by flow cytometry. Clin Exp Immunol 152:585–592
McMurray DN (1984) Cell-mediated immunity in nutritional deficiency. Progr Food & Nut Sci 8:193–228
Friedenreich CM, Neilson HK, Woolcott CG, McTiernan A, Wang Q, Ballard-Barbash R, Jones CA, Stanczyk FZ, Brant RF, Yasui Y, Irwin ML, Campbell KL, McNeely ML, Karvinen KH, Courneya KS (2011) Changes in insulin resistance indicators, IGFs, and adipokines in a year-long trial of aerobic exercise in postmenopausal women. Endocr Relat Cancer 18:357–369
van de Weert-van Leeuwen PB, de Vrankrijker AM, Fentz J, Ciofu O, Wojtaszewski JF, Arets HG, Hulzebos HJ, van der Ent CK, Beekman JM, Johansen HK (2013) Effect of long-term voluntary exercise wheel running on susceptibility to bacterial pulmonary infections in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 8:e82869
Leandro CG, de Lima TM, Alba-Loureiro TC, do Nascimento E, Manhaes de Castro R, de Castro CM, Pithon-Curi TC, Curi R (2007) Stress-induced downregulation of macrophage phagocytic function is attenuated by exercise training in rats. NeuroImmunoModulation 14:4–7
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, Nieman DC, Swain DP (2011) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1334–1359
Levada-Pires AC, Lambertucci RH, Mohamad M, Hirabara SM, Curi R, Pithon-Curi TC (2007) Exercise training raises expression of the cytosolic components of NADPH oxidase in rat neutrophils. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:153–160
Shimizu K, Kimura F, Akimoto T, Akama T, Tanabe K, Nishijima T, Kuno S, Kono I (2008) Effect of moderate exercise training on T-helper cell subpopulations in elderly people. Exerc Immunol Rev 14:24–37
Leandro CG, Martins de Lima T, Folador A, Alba-Loreiro T, Nascimento E, Manhaes de Castro R, de Castro CM, Pithon-Curi T, Curi R (2006) Physical training attenuates the stress-induced changes in rat T-lymphocyte function. NeuroImmunoModulation 13:105–113
Bayne K (1996) Revised Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals available. American Physiological Society. Physiologist 39:199–208
Leandro CG, Levada AC, Hirabara SM, Manhaes-de-Castro R, De-Castro CB, Curi R, Pithon-Curi TC (2007) A program of moderate physical training for Wistar rats based on maximal oxygen consumption. J Strength Cond Res 21:751–756
Carnevale R, Iuliano L, Nocella C, Bartimoccia S, Trape S, Russo R, Gentile MC, Cangemi R, Loffredo L, Pignatelli P, Violi F (2013) Relationship between platelet and urinary 8-Iso-PGF2alpha levels in subjects with different degrees of NOX2 regulation. J Am Heart Assoc 2:e000198
Ringheim GE, Lee L, Laws-Ricker L, Delohery T, Liu L, Zhang D, Colletti N, Soos TJ, Schroeder K, Fanelli B, Tian N, Arendt CW, Iglesias-Bregna D, Petty M, Ji Z, Qian G, Gaur R, Weinstock D, Cavallo J, Telsinskas J, McMonagle-Strucko K (2013) Teriflunomide attenuates immunopathological changes in the dark agouti rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Front Neurol 4:169
Navarro F, Bacurau AV, Almeida SS, Barros CC, Moraes MR, Pesquero JL, Ribeiro SM, Araujo RC, Costa Rosa LF, Bacurau RF (2010) Exercise prevents the effects of experimental arthritis on the metabolism and function of immune cells. Cell Biochem Funct 28:266–273
Badr G, Mohany M (2011) Maternal perinatal undernutrition attenuates T-cell function in adult male rat offspring. Cell Physiol Biochem 27:381–390
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Lagranha CJ, Senna SM, de Lima TM, Silva E, Doi SQ, Curi R, Pithon-Curi TC (2004) Beneficial effect of glutamine on exercise-induced apoptosis of rat neutrophils. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:210–217
Hirabara SM, Curi R, Maechler P (2010) Saturated fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 222:187–194
Borges Lda S, Bortolon JR, Santos VC, de Moura NR, Dermargos A, Cury-Boaventura MF, Gorjao R, Pithon-Curi TC, Hatanaka E (2014) Chronic inflammation and neutrophil activation as possible causes of joint diseases in ballet dancers. Mediat Inflamm 2014:846021
Moore DC, Elsas PX, Maximiano ES, Elsas MI (2006) Impact of diet on the immunological microenvironment of the pregnant uterus and its relationship to allergic disease in the offspring—a review of the recent literature. Rev Paul Med 124:298–303
Barros KM, Manhaes-De-Castro R, Lopes-De-Souza S, Matos RJ, Deiro TC, Cabral-Filho JE, Canon F (2006) A regional model (Northeastern Brazil) of induced mal-nutrition delays ontogeny of reflexes and locomotor activity in rats. Nutr Neurosci 9:99–104
Lopes de Souza S, Orozco-Solis R, Grit I, Manhaes de Castro R, Bolanos-Jimenez F (2008) Perinatal protein restriction reduces the inhibitory action of serotonin on food intake. Eur J Neurosci 27:1400–1408
Toscano AE, Manhaes-de-Castro R, Canon F (2008) Effect of a low-protein diet during pregnancy on skeletal muscle mechanical properties of offspring rats. Nutrition 24:270–278
Ozanne SE, Hales CN (2004) Lifespan: catch-up growth and obesity in male mice. Nature 427:411–412
de Melo Montenegro IH, Moita L, Dos Reis FK, de Oliveira E, Lisboa PC, de Moura EG, Manhaes-de-Castro R, Leandro CG (2012) Effects of a moderate physical training on the leptin synthesis by adipose tissue of adult rats submitted to a perinatal low-protein diet. Horm Metab Res 44:414–418
Leandro CG, da Silva Ribeiro W, Dos Santos JA, Bento-Santos A, Lima-Coelho CH, Falcao-Tebas F, Lagranha CJ, Lopes-de-Souza S, Manhaes-de-Castro R, Toscano AE (2012) Moderate physical training attenuates muscle-specific effects on fibre type composition in adult rats submitted to a perinatal maternal low-protein diet. Eur J Nutr 51:807–815
Ghattas H, Darboe BM, Wallace DL, Griffin GE, Prentice AM, Macallan DC (2005) Measuring lymphocyte kinetics in tropical field settings. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 99:675–685
Prestes-Carneiro LE, Laraya RD, Silva PR, Moliterno RA, Felipe I, Mathias PC (2006) Long-term effect of early protein malnutrition on growth curve, hematological parameters and macrophage function of rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 52:414–420
Landgraf MA, Tostes Rde C, Borelli P, Zorn TM, Nigro D, Carvalho MH, Fortes ZB (2007) Mechanisms involved in the reduced leukocyte migration in intrauterine undernourishment. Nutrition 23:145–156
Landgraf MA, Martinez LL, Rastelli VM, Franco Mdo C, Soto-Suazo M, Tostes Rde C, Carvalho MH, Nigro D, Fortes ZB (2005) Intrauterine undernutrition in rats interferes with leukocyte migration, decreasing adhesion molecule expression in leukocytes and endothelial cells. J Nutr 135:1480–1485
de Moura EG, Lisboa PC, Passos MC (2008) Neonatal programming of neuroimmunomodulation—role of adipocytokines and neuropeptides. NeuroImmunoModulation 15:176–188
Navarrete M, Nunez H, Ruiz S, Soto-Moyano R, Valladares L, White A, Perez H (2007) Prenatal undernutrition decreases the sensitivity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in rat, as revealed by subcutaneous and intra-paraventricular dexamethasone challenges. Neurosci Lett 419:99–103
Thompson EB (1999) Mechanisms of T-cell apoptosis induced by glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10:353–358
Hoffman-Goetz L, Spagnuolo PA (2007) Freewheel exercise training modifies pro- and anti-apoptotic protein expression in mouse splenic lymphocytes. Int J Sports Med 28:787–791
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Level or Education Personnel (CAPES), and State of Pernambuco Science and Technology Support Foundation (FACEPE).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senna, S.M., Torres, M.K., Lopes, D.A.P. et al. Moderate physical training attenuates perinatal low-protein-induced spleen lymphocyte apoptosis in endotoxemic adult offspring rats. Eur J Nutr 55, 1113–1122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0925-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0925-y