Abstract
Purpose
Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has not been standardized due to technical difficulties and requires extensive training for reliability. Ex vivo animal model is convenient, but has no blood flow. The objective of this study is to evaluate the characteristics of various ex vivo animal models including a blood flow model for colorectal ESD training and the usefulness of practicing endoscopic hemostasis and closure using an animal model.
Methods
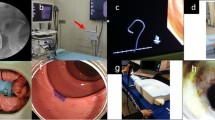
Harvested porcine cecum, rectum, and stomach and bovine cecum and rectum were analyzed regarding ease of mucosal injection, degree of submucosal elevation, and status of the proper muscle layer. Ex vivo animal model with blood flow was made using the bovine cecum. The vessel around the cecum was detached, and red ink was injected. Endoscopic hemostasis for perioperative hemorrhage and endoscopic closure for perforation were performed in this model.
Results
Mucosal injection was easily performed in the bovine cecum and rectum. Submucosal elevation was low in the bovine cecum, while the proper muscle layer was not tight in the porcine rectum and bovine cecum. Endoscopic hemostasis were accomplished in six (60 %) out of ten procedures of the ex vivo blood flow model. In two non-experts, the completion rates of endoscopic closure were 40 and 60 % in the first five procedures. These rates became 100 % in the last five procedures.
Conclusions
We have evaluated the characteristics of various ex vivo animal models and shown the possibility of training for endoscopic hemostasis and endoscopic closure in the ex vivo animal model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kudo S, Hirota S, Nakajima T et al (1994) Colorectal tumours and pit pattern. J Clin Pathol 47:880–885
Tobaru T, Mitsuyama K, Tsuruta O et al (2008) Sub-classification of type VI pit patterns in colorectal tumors: relation to the depth of tumor invasion. Int J Oncol 33:503–508
Yoshida N, Naito Y, Kugai M et al (2011) Efficacy of magnifying endoscopy with flexible spectral imaging color enhancement in the diagnosis of colorectal tumors. J Gastroenterol 46:65–72
Tanaka S, Haruma K, Oka S et al (2001) Clinicopathological features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm. Gastrointest Endosc 54:62–66
Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T et al (2010) Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc 24:343–352
Yoshida N, Naito Y, Yagi Y et al (2012) Importance of histological evaluation in endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 3:44–59
Yoshida N, Naito Y, Kugai M et al (2011) Efficacy of hyaluronic acid in endoscopic mucosal resection for colorectal tumors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:286–291
Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I et al (2007) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc 66:100–107
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T et al (2007) Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: a case series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 66:966–973
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N et al (2007) Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms in 200 consecutive cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:678–683
Yoshida N, Naito Y, Sakai K et al (2010) Outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors in elderly people. Int J Colorectal Dis 25:455–461
Takeuchi Y, Uedo N, Ishihara R et al (2010) Efficacy of an endo-knife with a water-jet function (flushknife) for endoscopic submucosal dissection of superficial colorectal neoplasms. Am J Gastroenterol 105:314–322
Toyonaga T, Man-I M, Morita Y et al (2009) The new resources of treatment for early stage colorectal tumors: EMR with small incision and simplified endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 21(Suppl 1):S31–S37
Yoshida N, Yagi N, Naito Y et al (2010) Safe procedure in endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors focused on preventing complications. World J Gastroenterol 16:1688–1695
Tanimoto MA, Torres-Villalobos G, Fujita R et al (2010) Endoscopic submucosal dissection in dogs in a World Gastroenterology Organisation training center. World J Gastroenterol 16:1759–1764
Parra-Blanco A, Arnau MR, Nicolás-Pérez D et al (2010) Endoscopic submucosal dissection training with pig models in a Western country. World J Gastroenterol 16:2895–2900
Hon SS, Ng SS, Lee JF et al (2010) In vitro porcine training model for colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection: an inexpensive and safe way to acquire a complex endoscopic technique. Surg Endosc 24:2439–2443
Hirasaki S, Kozu T, Yamamoto H et al (2009) Usefulness and safety of 0.4 % sodium hyaluronate solution as a submucosal fluid “cushion” for endoscopic resection of colorectal mucosal neoplasms: a prospective multi-center open-label trial. BMC Gastroenterol 9:1
Akahoshi K, Motomura Y, Kubokawa M et al (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of a rectal carcinoid tumor using grasping type scissors forceps. World J Gastroenterol 15:2162–2165
Schurr MO, Hartmann C, Ho CN et al (2008) An over-the-scope clip (OTSC) system for closure of iatrogenic colon perforations: results of an experimental survival study in pigs. Endoscopy 40:584–588
Vazquez-Sequeiros E, de Miquel DB, Olcina JR et al (2009) Training model for teaching endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric tumors. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 101:546–552
Yamamoto H (2007) Technology insight: endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal neoplasms. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:511–520
Gotoda T, Friedland S, Hamanaka H et al (2005) A learning curve for advanced endoscopic resection. Gastrointest Endosc 62:866–867
Choi IJ, Kim CG, Chang HJ et al (2005) The learning curve for EMR with circumferential mucosal incision in treating intramucosal gastric neoplasm. Gastrointest Endosc 62:860–865
Hotta K, Oyama T, Shinohara T et al (2010) Learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of large colorectal tumors. Dig Endosc 22:302–306
Yamamoto S, Uedo N, Ishihara R et al (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer performed by supervised residents: assessment of feasibility and learning curve. Endoscopy 41:923–928
Yoshida N, Wakabayashi N, Kanemasa K et al (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors: technical difficulties and rate of perforation. Endoscopy 41:758–761
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y et al (2010) A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72:1217–1225
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N et al (2006) Successful nonsurgical management of perforation complicating endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy 38:1001–1006
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Noriya Uedo, Dr. Toshio Uraoka, Dr. Ken Ohata, Dr. Shinji Tanaka, Dr. Kiyoaki Homma, Dr. Hirohisa Machida, Dr. Yoshinori Morita, and Dr. Naohisa Yahagi for providing helpful advice for developing the ex vivo animal model with blood flow.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, N., Yagi, N., Inada, Y. et al. Possibility of ex vivo animal training model for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Int J Colorectal Dis 28, 49–56 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1531-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1531-6