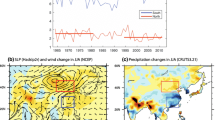
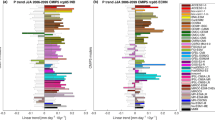
Abstract
The East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) circulation and summer rainfall over East China have experienced large decadal changes during the latter half of the 20th century. To investigate the potential causes behind these changes, a series of simulations using the national center for atmospheric research (NCAR) community atmospheric model version 3 (CAM3) and the geophysical fluid dynamics laboratory (GFDL) atmospheric model version 2.1 (AM2.1) are analyzed. These simulations are forced separately with different historical forcing, namely tropical sea surface temperature (SSTs), global SSTs, greenhouse gases plus aerosols, and a combination of global SSTs and greenhouse gases plus aerosols. This study focuses on the relative roles of these individual forcings in causing the observed monsoon and rainfall changes over East Asia during 1950–2000. The simulations from both models show that the SST forcing, primarily from the Tropics, is able to induce most of the observed weakening of the EASM circulation, while the greenhouse gas plus (direct) aerosol forcing increases the land-sea thermal contrast and thus enhances the EASM circulation. The results suggest that the recent warming in the Tropics, especially the warming associated with the tropical interdecadal variability centered over the central and eastern Pacific, is a primary cause for the weakening of the EASM since the late 1970s. However, a realistic simulation of the relatively small-scale rainfall change pattern over East China remains a challenge for the global models.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bueh C, Cubasch U, Hagemann S (2003) Impacts of global warming on changes in the East Asian monsoon and the related river discharge in a global time-slice experiment. Clim Res 24:47–57. doi:10.3354/cr024047
Chang C, Zhang Y, Li T (2000) Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: roles of the subtropical ridge. J Clim 13:4310–4325. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<4310:IAIVOT>2.0.CO;2
Chen M, Xie P, Janowiak J, Arkin P (2002) Global land precipitation: a 50-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations. J Hydrometeorol 3:249–266. doi:10.1175/1525-7541(2002)003<0249:GLPAYM>2.0.CO;2
Collins W et al (2006) The formulation and atmospheric simulation of the community atmosphere model version 3 (CAM3). J Clim 19:2144–2161. doi:10.1175/JCLI3760.1
Dai A, Wigley T, Boville B, Kiehl J, Buja L (2001) Climates of the twentieth and twenty-first centuries simulated by the NCAR climate system model. J Clim 14:485–519. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<0485:COTTAT>2.0.CO;2
Deser C, Phillips A, Hurrell J (2004) Pacific interdecadal climate variability: linkages between the tropics and the North Pacific during boreal winter since 1900. J Clim 17:3109–3124. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<3109:PICVLB>2.0.CO;2
Deser C, Phillips A (2006) Simulation of the 1976/77 climate transition over the North Pacific: sensitivity to tropical forcing. J Clim 19:6170–6180. doi:10.1175/JCLI3963.1
GFDL Global Atmospheric Model Development Team (2004) The new GFDL global atmosphere and land model AM2-LM2: evaluation with prescribed SST simulations. J Clim 17:4641–4673. doi:10.1175/JCLI-3223.1
Gong D, Ho C (2002) Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s. Geophys Res Lett 29(10):1436. doi:10.1029/2001GL014523
Guan B, Nigam S (2008) Pacific sea surface temperatures in the twentieth century: an evolution-centric analysis of variability and trend. J Clim 21:2790–2809. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI2076.1
Guo Q, Cai J, Shao X, Sha W (2003) Interdecadal variability of East-Asian summer monsoon and its impact on the climate of China. Acta Geogr Sin 58:569–576 in Chinese
Han J, Wang H (2007) Interdecadal variability of the East Asian summer monsoon in an AGCM. Adv Atmos Sci 24:808–818. doi:10.1007/s00376-007-0808-0
Hu Z (1997) Interdecadal variability of summer climate over East Asia and its association with 500 hPa height and global sea surface temperature. J Geophys Res 102(D16):19403–19412. doi:10.1029/97JD01052
Hu Z, Latif M, Roeckner E, Bengtsson L (2000) Intensified Asian summer monsoon and its variability in a coupled model forced by increasing greenhouse gas concentrations. Geophys Res Lett 27(17):2681–2684. doi:10.1029/2000GL011550
Hu Z, Yang S, Wu R (2003) Long-term climate variations in China and global warming signals. J Geophys Res 108(D19):4614. doi:10.1029/2003JD003651
Huang Y, Dickinson R, Chameides W (2006) Impact of aerosol indirect effect on surface temperature over East Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(12):4371–4376. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504428103
Hurrell J, Hack J, Shea D, Caron J, Rosinski J (2008) A new sea surface temperature and sea ice boundary data set for the Community Atmosphere Model. J Clim 21(19):5145–5153. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2292.1
Kalnay E et al (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
Kang I, Jin K, Wang B, Lau K, Shukla J, Krishnamurthy V, Schubert S, Wailser D, Stern W, Kitoh A, Meehl G, Kanamitsu M, Galin V, Satyan V, Park C, Liu Y (2002) Intercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs. Clim Dyn 19:383–395. doi:10.1007/s00382-002-0245-9
Lau K, Weng H (2001) Coherent modes of global SST and summer rainfall over China: an assessment of the regional impacts of the 1997 98 El Niño. J Clim 14:1294–1308. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<1294:CMOGSA>2.0.CO;2
Li J, Yu R, Zhou T, Wang B (2005) Why is there an early spring cooling shift downstream of the Tibetan Plateau. J Clim 18(22):4660–4668. doi:10.1175/JCLI3568.1
Li H, Zhou T, Yu R (2008) Analysis of July–August daily precipitation characteristics variation in Eastern China during 1958–2000. Chin J Atmos Sci 32:358–371 in Chinese
Ma Z, Fu C (2007) Evidences of drying trend in the global during the later half of 20th century and their relationship with large-scale climate background. Sci China D 37:222–233 in Chinese
Menon S, Hansen J, Nazarenko L, Luo Y (2002) Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 297:2250–2253. doi:10.1126/science.1075159
Nitta T, Hu Z (1996) Summer climate variability in China and its association with 500 hPa height and tropical convection. J Metab Soc Jpn 74:425–445
Qian Y, Giorgi F (1999) Interactive coupling of regional climate and sulfate aerosol models over eastern Asia. J Geophys Res 104(D6):6477–6499. doi:10.1029/98JD02347
Qian Y, Leung L, Ghan S, Giorgi F (2003) Regional climate effects of aerosols over China: modeling and observation. Tellus B Chem Phys Meterol 55:914–934. doi:10.1046/j.1435-6935.2003.00070.x
Trenberth K, Hurrell J (1994) Decadal atmosphere-ocean variations in the Pacific. Clim Dyn 9:303–319. doi:10.1007/BF00204745
Uppala S et al (2005) The ERA-40 re-analysis. QJR Metab Soc 131:2961–3012. doi:10.1256/qj.04.176
Wang H (2001) The weakening of Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970s. Adv Atmos Sci 18:376–386. doi:10.1007/BF02919316
Wang B, Ding Q (2006) Changes in global monsoon precipitation over the past 56 years. Geophys Res Lett 33:L06711. doi:10.1029/2005GL025347
Wang B, Fan Z (1999) Choice of south Asian summer monsoon indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80:629–638. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<0629:COSASM>2.0.CO;2
Wang B, Wu R, Fu X (2000) Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: how does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Clim 13:1517–1536. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2
Wang B, Ding Q, Fu X, Kang I, Jin K, Shukla J, Doblas-Reyes F (2005) Fundamental challenges in simulation and prediction of summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 32:L15711. doi:10.1029/2005GL022734
Webster P, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems. QJR Metab Soc 118:877–926. doi:10.1002/qj.49711850705
Weng H, Lau K, Xue Y (1999) Multi-scale summer rainfall variability over China and its long-term link to global sea surface temperature variability. J Metab Soc Jpn 77:845–857
Wu R, Wang B (2002) A contrast of the East Asian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship between 1962–77 and 1978–93. J Clim 15:3266–3279. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<3266:ACOTEA>2.0.CO;2
Wu R, Hu Z, Kirtman B (2003) Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J Clim 16(22):3742–3758. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3742:EOERAI>2.0.CO;2
Xin X, Yu R, Zhou T, Wang B (2006) Drought in late spring of South China in recent decades. J Clim 19(13):3197–3206. doi:10.1175/JCLI3794.1
Xu M, Chang C, Fu C, Qi Y, Robock A, Robinson D, Zhang H (2006) Steady decline of East Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J Geophys Res 111:D24111. doi:10.1029/2006JD007337
Xu Q (2001) Abrupt change of the mid-summer climate in central east China by the influence of atmospheric pollution. Atmos Environ 35:5029–5040. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00315-6
Yang F, Lau K (2004) Trend and variability of China precipitation in spring and summer: linkage to sea-surface temperatures. Int J Climatol 24:1625–1644. doi:10.1002/joc.1094
Yang X, Xie Q, Zhu Y, Sun X, Guo Y (2005) Decadal-to-interdecadal variability of precipitation in North China and associated atmospheric and oceanic anomaly patterns. Chin J Geophys 48:789–797 in Chinese
Yatagai A, Yasunari T (1994) Trends and decadal-scale fluctuations of surface air temperature and precipitation over China and Mongolia during the recent 40 year period (1951–1990). J Metab Soc Jpn 72:937–957
Yu R, Zhou T (2004) Impacts of winter NAO on March cooling trends over subtropical Eurasia continent in the recent half century. Geophys Res Lett 31:L12204. doi:10.1029/2004GL019814
Yu R, Wang B, Zhou T (2004) Tropospheric cooling and summer monsoon weakening trend over East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 31:L22212. doi:10.1029/2004GL021270
Yu R, Zhou T (2007) Seasonality and three-dimensional structure of the interdecadal change in East Asian monsoon. J Clim 20:5344–5355. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1559.1
Zeng G, Sun Z, Wang W, Lin Z, Ni D (2007) Interdecadal variation of East Asian summer monsoon simulated by NCAR CAM3 driven by global SSTs. Clim Environ Res 12:211–224 in Chinese
Zhang Y, Wallace J, Battisti D (1997) ENSO-like interdecadal variability: 1900–93. J Clim 10:1004–1020. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<1004:ELIV>2.0.CO;2
Zhang Y, Kuang X, Guo W, Zhou T (2006) Seasonal evolution of the upper-tropospheric westerly jet core over East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 33:L11708. doi:10.1029/2006GL026377
Zhou L, Huang R (2003) Research on the characteristics of interdecadal variability of summer climate in China and its possible cause. Clim Environ Res 8:274–290 in Chinese
Zhou T, Li Z (2002) Simulation of the East Asian summer monsoon by using a variable resolution atmospheric GCM. Clim Dyn 19:167–180. doi:10.1007/s00382-001-0214-8
Zhou T, Yu R (2005) Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with typical anomalous summer rainfall patterns in China. J Geophys Res 110:D08104. doi:10.1029/2004JD005413
Zhou T, Yu R, Zhang J, Drange H, Cassou C, Deser C, Hodson D, Sanchez-Gomez E, Li J, Keenlyside N, Xin X, Okumura Y (2008a) Why the Western Pacific subtropical high has extended westward since the late 1970s. J Clim, in revision
Zhou T, Zhang L, Li H (2008b) Changes in global land monsoon area and total rainfall accumulation over the last half century. Geophys Res Lett 35:L16707. doi:10.1029/2008GL034881
Zhou T, Yu R, Li H, Wang B (2008c) Ocean forcing to changes in global monsoon precipitation over the recent half century. J Clim 21:3833–3852. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2067.1
Zhou T, Wu B, Scaife AA, Brönnimann S et al (2008d) The CLIVAR C20C project: which components of the Asian–Australian monsoon circulation variations are forced and reproducible? Clim Dyn (in Revision)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an NSF SGER Grant #OCE-0740011 through the CLIVAR DRICOMP project, NSFC of China under grant Nos. 40523001, 90711004, 40625014, and National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB403603). The National Center for Atmospheric Research is sponsored by the U.S. National Science Foundation. We thank Adam Phillips for making the CAM3 simulations available. We acknowledge Fangrong Zhang and Tom Delwoth for conducting the experiments with AM2.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Dai, A., Zhou, T. et al. Responses of East Asian summer monsoon to historical SST and atmospheric forcing during 1950–2000. Clim Dyn 34, 501–514 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0482-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0482-7