Abstract
Aims and Objectives
The significance of beaten copper appearance (BCA) on skull radiographs in children following surgery for isolated sagittal craniosynostosis has not been studied. This study was designed to look for any correlation between BCA and symptoms suggestive of intracranial hypertension in this group of patients.
Materials and Methods
Forty-eight consecutive children, who were operated for isolated sagittal synostosis from1987 to 2000 and had postoperative skull radiographs, were included. Patients were divided into: (a) BCA group (n = 20), consisting of children who had beaten copper appearance on skull radiographs at last follow up, and (b) Non-BCA group (n = 28), consisting of children who did not have this finding. Records were reviewed to look for symptoms suggestive of intracranial hypertension, such as headache, head banging, and irritability.
Results
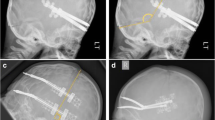
Median age at surgery was 4.8 months for BCA group and 4 months for the non-BCA group. Follow up ranged from 4 to 156 months with a mean of 36.2 months. Total of 28.6% (n = 6) of the children with follow up radiographs done at ≤18 months of age had BCA. The incidence of BCA increased to 83.3% in children with skull radiographs performed after 48 months of age. In 18 (90%) children, the BCA was ‘diffuse’ with 5 (25%) children having the maximum possible score of 8. In the BCA group, 45% (n = 9) had symptoms compared to 10.7% (n = 3) in the control group (p = 0.0068).
Conclusions
This study suggests a significant number of children with BCA on radiographs develop symptoms suggestive of raised ICP following surgical treatment in infancy and prolonged follow up may be warranted in this group of patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camfield PR, Camfield CS (1986) Neurological aspects of craniosynostosis. In: Cohen MM (ed) Craniosynostosis: diagnosis, evaluation, and management. Raven, New York, pp 215–226
Campbell JW, Albright AL, Losken HW, Biglan AW (1995) Intracranial hypertension after cranial vault decompression for craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 22:270–273
Cohen SR, Dauser RC, Newman MH, Muraszko K (1993) Surgical techniques of cranial vault expansion for increases in intracranial pressure in older children. J Craniofac Surg 4:167–176 (discussion 174–166)
Cohen SR, Persing JA (1998) Intracranial pressure in single-suture craniosynostosis. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 35:194–196
Davidoff L (1936) Convulational digitations seen in roentgenograms of immature human skulls. Bull Neurol Inst N Y 5:61–71
Du Boulay G (1956) The significance of digital impressions in children’s skulls. Acta Radiol 46:112–122
Greene CS Jr (1998) Pancraniosynostosis after surgery for single sutural craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:127–132
Guimaraes-Ferreira J, Gewalli F, David L, Olsson R, Friede H, Lauritzen CG (2001) Clinical outcome of the modified pi-plasty procedure for sagittal synostosis. J Craniofac Surg 12:218–224 (discussion 225–216)
Macaulay D (1951) Digital markings in radiographs of the skull in children. Br J Radiol 24:647–652
Minns R (1991) Problems of intracranial pressure in childhood. In: Minns R (ed) Clinics in developmental Medicine. MacKieth, London
Munro D (1928) Cerebrospinal fluid pressure in the newborn. JAMA 90:1688–1690
Pollack IF, Losken HW, Biglan AW (1996) Incidence of increased intracranial pressure after early surgical treatment of syndromic craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:202–209
Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Marchac D, Hirsch JF (1982) Intracranial pressure in craniostenosis. J Neurosurg 57:370–377
Siddiqi SN, Posnick JC, Buncic R, Humphreys RP, Hoffman HJ, Drake JM, Rutka JT (1995) The detection and management of intracranial hypertension after initial suture release and decompression for craniofacial dysostosis syndromes. Neurosurgery 36:703–708 (discussion 708–709)
Tamburrini G, Di Rocco C, Velardi F, Santini P (2004) Prolonged intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring in non-traumatic pediatric neurosurgical diseases. Med Sci Monit 10:MT53–MT63
Thompson DN, Malcolm GP, Jones BM, Harkness WJ, Hayward RD (1995) Intracranial pressure in single-suture craniosynostosis. Pediatr Neurosurg 22:235–240
Tuite GF, Evanson J, Chong WK, Thompson DN, Harkness WF, Jones BM, Hayward RD (1996) The beaten copper cranium: a correlation between intracranial pressure, cranial radiographs, and computed tomographic scans in children with craniosynostosis. Neurosurgery 39:691–699
Welch K (1980) The intracranial pressure in infants. J Neurosurg 52:693–699
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, D., Steinbok, P. & Cochrane, D.D. Significance of beaten copper appearance on skull radiographs in children with isolated sagittal synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst 23, 1467–1470 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0430-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-007-0430-6