Abstract
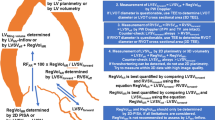
Percutaneous balloon-mitral-valvotomy (PBMV) is an alternative to surgery in selected patients with mitral valve (MV) stenosis (MS). Applying echocardiography, suitability for PBMV is assessed by detailed morphological description. Echo-scores alone are suboptimal to describe MV morphology, because single parameters, important for a decision concerning PBMV, are not distinguishable out of a score number. The aim was to design a tool (coding-system), which combines a number for a stenotic MV like scores (for statistical options) and decodable, generally applied parameters describing the MS morphology. The reproducibility of the MS morphology using the coding-system has to be tested in 90 patients. A separate group of 297 patients (pts) with MS, scheduled for PBMV, should be investigated prospectively applying the coding-system and a comparable score. We chose the Wilkins score (WS) as representative of scores. The coding-system is designed as a parameter sequencing set consisting of 6 digits. The first digit indicates a decision code concerning suitability for PBMV. The following 5 digits indicate generally accepted morphological parameters, which are partially also used in the WS. Therefore, the MS morphology can be “read” retrospectively by decoding. 201/297 patients were found suitable for PBMV. Applying the coding-system all 201 suitable patients were correctly distinguished from 96 morphologically unsuitable patients. Astonishingly 48/96 of the rejected patients showed a WS ≤8 whereas 28/201 of the suitable patients demonstrated a WS >8. 25/28 of them showed a successful initial outcome. Applying the generally known threshold of “8” when predicting suitability of a MS, the WS demonstrated an initial success rate of 62 %, sensitivity of 0.87, specificity of 0.45, precision of 0.79, and accuracy of 0.78. Applying the coding-system, the initial success rate was 70.8 %, sensitivity = 0.96, specificity = 1.0, precision = 1.0, and accuracy = 0.97. The coding-system is an advanced diagnostic aid, is statistically applicable, offers a decodable morphological description, includes a decision code regarding suitability for PBMV, and can be used for comparing different groups of patients with MS by calculating “mean morphologies” of groups.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue K (1991) Percutaneous transvenous mitral commissurotomy using the Inoue balloon. Eur Heart J 12:99–108
Post J, Feldman T, Isner J, Herrmann H (1995) Inoue balloon mitral valvotomy in patients with severe valvular and subvalvular deformity. J Am Coll Cardiol 25:1129–1136
Chmielak Z, Klopotowski M, Kruk M, Demkow M, Konka M, Chojnowska L, Hoffman P, Witkowski A, Ruzyllo W (2010) Repeat percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty for patients with mitral valve restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 76:986–992
Nair K, Sivadasanpillai H, Sivasubramonium P, Ramachandran P, Tharakan JA, Titus T, Ajit Kumar VK, Sivasubramonian S, Krishnamoorthy KM, Dora S (2010) Percutaneous valvuloplasty for mitral valve restenosis: postballoon valvotomy patients fare better than postsurgical closed valvotomy patients. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 76:174–180
Hamatani Y, Saito N, Tazaki J, Natsuaki M, Nakai K, Makiyama T, Sasaki Y, Imai M, Watanabe S, Shioi T, Kimura T, Inoue K (2013) Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty for bioprosthetic mitral valve stenosis. Heart Vessels 28:667–671
Fukuda Y, Yoshida T, Inage T, Takeuchi T, Gondo T, Takii E, Imaizumi T (2012) Long-term results of the maze procedure on left ventricular function for persistent atrial fibrillation associated with mitral valve disease. Heart Vessels 27:53–57
Sutaria N, Elder AT, Shaw TR (2000) Long term outcome of percutaneous mitral balloon valvotomy in patients aged 70 and over. Heart 83:433–438
Arora R, Nair M, Kalra GS, Nigam M, Khalilullah M (1993) Immediate and long-term results of balloon and surgical closed mitral valvotomy: a randomized comparative study. Am Heart J 125:1091–1094
Iung B, Cormier B, Ducimetiere P, Porte JM, Nallet O, Michel PL, Acar J, Vahanian A (1996) Functional results 5 years after successful percutaneous mitral commissurotomy in a series of 528 patients and analysis of predictive factors. J Am Coll Cardiol 27:407–414
Abascal VM, Wilkins GT, O’Shea JP, Choong CY, Palacios IF, Thomas JD, Rosas E, Newell JB, Block PC, Weyman AE (1990) Prediction of successful outcome in 130 patients undergoing percutaneous balloon mitral valvotomy. Circulation 82:448–456
Herrmann HC, Lima JA, Feldman T, Chisholm R, Isner J, O’Neill W, Ramaswamy K (1993) Mechanisms and outcome of severe mitral regurgitation after Inoue balloon valvuloplasty. North American Inoue Balloon Investigators. J Am Coll Cardiol 22:783–789
Miche E, Vogt J, Gleichmann U, Mannebach H, Bogunovic N, Mirow N, Minami K, Knobl H (1996) Ultrasound examination of stenotic mitral valves: an in vitro study. Am J Card Imag 10:175–179
Prendergast B, Shaw T, Iung B, Vahanian A, Northridge DB (2002) Contemporary criteria for the selection of patients for percutaneous balloon mitral valvuloplasty. Heart 87:401–404
Iung B, Garbarz E, Michaud P, Helou S, Farah B, Berdah P, Michel PL, Cormier B, Vahanian A (1999) Late results of percutaneous mitral commissurotomy in a series of 1024 patients. Analysis of late clinical deterioration: frequency, anatomic findings, and predictive factors. Circulation 99:3272–3278
Palacios IF, Sanchez PL, Harrell LC, Weyman AE, Block PC (2002) Which patients benefit from percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty? Prevalvuloplasty and postvalvuloplasty variables that predict long-term outcome. Circulation 105:1465–1471
Cannan CR, Nishimura RA, Reeder GS, Ilstrup DR, Larson DR, Holmes DR, Tajik AJ (1997) Echocardiographic assessment of commissural calcium: a simple predictor of outcome after percutaneous mitral balloon valvotomy. J Am Coll Cardiol 29:175–180
Messika-Zeitoun D, Iung B, Brochet E, Himbert D, Serfaty JM, Laissy JP, Vahanian A (2008) Evaluation of mitral stenosis in 2008. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 101:653–663
Puri R, Dundon BK, Khurana S, Worthley MI, Edwards J, Worthley SG (2010) Gross echocardiographic underestimation of mitral valve calcification: a near fatal experience. Int J Cardiol 143:e24–e26
Miche E, Faßbender D, Minami K, Gleichmann U, Mannebach H, Schmidt H, Terwesten HP, Mirow N, Seifert D, Greve H, Bogunovic N, Baller D, Vogt J, Körfer R (1996) Pathomorphological characteristics of resected mitral valves after unsuccessful valvuloplasty. J Cardiovasc Surg 37:475–481
Rossi A, Faggiano P, Amado AE, Cicoira M, Bonapace S, Franceschini L, Dini FL, Ghio S, Agricola E, Temporelli PL, Vassanelli C (2013) Mitral and aortic valve sclerosis/calcification and carotid atherosclerosis: results from 1065 patients. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-013-0433-z
Iung B, Cormier B, Ducimetiere P, Porte JM, Nallet O, Michel PL, Acar J, Vahanian A (1996) Immediate results of percutaneous mitral commissurotomy. A predictive model on a series of 1514 patients. Circulation 94:2124–2130
Miche E, Bogunovic N, Faßbender D, Baller D, Gleichmann U, Mannebach H, Terwesten HP, Schmidt H, Minami K, Mirow N, Vogt J, Körfer R (1996) Predictors of unsuccessful outcome after percutaneous mitral valvulotomy including a new echocardiographic scoring system. J Heart Valve Dis 5:430–435
Sutaria N, Northridge DB, Shaw T (2000) Significance of commissural calcification on outcome of mitral balloon valvotomy. Heart 84:398–402
Fatkin D, Roy P, Morgan J, Feneley M (1993) Percutaneous balloon mitral valvotomy with the inoue single-balloon catheter: commissural morphology as a determinant of outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol 21:390–397
Mezilis NE, Salame MY, Oakley GD (1999) Predicting mitral regurgitation following percutaneous mitral valvotomy with the inoue balloon: comparison of two echocardiographic scoring systems. Clin Cardiol 22:453–458
Wilkins GT, Weyman AE, Abascal VM, Block PC, Palacios IF (1988) Percutaneous balloon dilatation of the mitral valve: an analysis of echocardiographic variables related to outcome and the mechanism of dilatation. Br Heart J 60:299–308
Goldstein SA, Lindsay J Jr (2010) Do we need more echo scores for balloon mitral valvuloplasty? J Am Soc Echocardiogr 23:23–25
Cruz-Gonzalez I, Sanchez-Ledesma M, Sanchez PL, Martin-Moreiras J, Jneid H, Rengifo-Moreno P, Inglessis-Azuaje I, Maree AO, Palacios IF (2009) Predicting success and long-term outcomes of percutaneous mitral valvuloplasty: a multifactorial score. Am J Med 122:581e.11–581e.19
Rifaie O, Esmat I, Abdel-Rahman M, Nammas W (2009) Can a novel echocardiographic score better predict outcome after percutaneous balloon mitral valvuloplasty? Echocardiography 26:119–127
Kaneko H, Suzuki S, Uejima T, Kano H, Matsuno S, Otsuka T, Takai H, Oikawa Y, Yajima J, Koike A, Nagashima K, Kirigaya H, Sagara K, Tanabe H, Sawada H, Aizawa T, Yamashita T (2013) Prevalence and the long-term prognosis of functional mitral regurgitation in Japanese patients with symptomatic heart failure. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-013-0448-5
Padial LR, Freitas N, Sagie A, Newell JB, Weyman AE, Levine RA, Palacios IF (1996) Echocardiography can predict which patient will develop severe mitral regurgitation after percutaneous mitral valvulotomy. J Am Coll Cardiol 27:1225–1231
Kupferwasser I, Mohr-Kahaly S, Menzel T, Spiecker M, Dohmen G, Mayer E, Oelert H, Erbel R, Meyer J (1996) Quantification of mitral valve stenosis by three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography. Int J Card Imaging 12:241–247
Salem-Omar AM, Tanaka H, Abdel Dayem TK, Sadek AS, Raslaan H, Al-Sherbiny A, Yamawaki K, Ryo K, Fukuda Y, Norisada K, Tatsumi K, Onishi T, Matsumoto K, Kawai H, Hirata K (2011) Comparison of mitral valve area by pressure half-time and proximal isovelocity surface area method in patients with mitral stenosis: effect of net atrioventricular compliance. Eur J Echocardiogr 12:283–290
Nakabo A, Goda A, Masaki M, Otsuka M, Yoshida C, Eguchi A, Hirotani S, Lee-Kawabata M, Tsujino T, Masuyama T (2014) The impairment of the parasympathetic modulation is involved in the age-related change in mitral E/A ratio. Heart Vessels 29:343–353
Krishnamoorthy KM, Dash PK (2009) Factors affecting immediate changes in cardiac output following balloon mitral valvulotomy: the role of pulmonary hemodynamics. J Heart Valve Dis 18:128–134
Krittayaphong R, Chotinaiwatarakul C, Kangkagate C (2007) Improvement of quality of life after percutaneous balloon mitral valvulotomy in patients with mitral stenosis: does rhythm matter? J Heart Valve Dis 16:13–18
Feldman T, Carroll JD, Isner JM, Chisholm RJ, Holmes DR, Massumi A, Pichard AD, Herrmann HC, Stertzer SH, O’Neill WW (1992) Effect of valve deformity on results and mitral regurgitation after Inoue balloon commissurotomy. Circulation 85:180–187
Reid CL, Otto CM, Davis KB, Labovitz A, Kisslo KB, McKay CR (1992) Influence of mitral valve morphology on mitral balloon commissurotomy: immediate and six-month results from the NHLBI Balloon Valvuloplasty Registry. Am Heart J 124:657–665
Vahanian A, Baumgartner H, Bax J, Butchart E, Dion R, Filippatos G, Flachskampf F, Hall R, Iung B, Kasprzak J, Nataf P, Tornos P, Torracca L, Wenink A (2007) Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease. The task force on the management of valvular heart disease of the European society of cardiology. Eur Heart J 28:230–268
Kim KH, Kim YJ, Shin DH, Chang SA, Kim HK, Sohn DW, Oh BH, Park YB (2010) Left atrial remodelling in patients with successful percutaneous mitral valvuloplasty: determinants and impact on long-term clinical outcome. Heart 96:1050–1055
Herrmann HC, Ramaswamy K, Isner JM, Feldman TE, Carroll JD, Pichard AD, Bashore TM, Dorros G, Massumi A, Sundram P, Tobis JM, Feldman RC, Ramee S (1992) Factors influencing immediate results, complications, and short-term follow-up status after Inoue balloon mitral valvotomy: a North American multicenter study. Am Heart J 124:160–166
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogunovic, N., Horstkotte, D., Scholtz, W. et al. A differentiated morphological parameter-coding system to describe the suitability of mitral valve stenoses intended for percutaneous valvotomy. Heart Vessels 30, 632–641 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-014-0536-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-014-0536-1