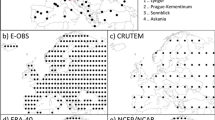
Abstract
The purpose of this review article is to discuss the development and associated estimation of uncertainties in the global and hemispheric surface temperature records. The review begins by detailing the groups that produce surface temperature datasets. After discussing the reasons for similarities and differences between the various products, the main issues that must be addressed when deriving accurate estimates, particularly for hemispheric and global averages, are then considered. These issues are discussed in the order of their importance for temperature records at these spatial scales: biases in SST data, particularly before the 1940s; the exposure of land-based thermometers before the development of louvred screens in the late 19th century; and urbanization effects in some regions in recent decades. The homogeneity of land-based records is also discussed; however, at these large scales it is relatively unimportant. The article concludes by illustrating hemispheric and global temperature records from the four groups that produce series in near-real time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnfield, A. J., 2003: Two decades of urban climate research: a review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Inter. J. Climatol., 23, 1–26.
Böhm, R., P. D. Jones, J. Hiebl, D. Frank, M. Brunetti, and M. Maugeri, 2010: The early instrumental warm-bias: A solution for long Central Europe an temperature series 1760–2007. Climatic Change, 101, 41–67.
Bojinski, S., M. Verstraete, T. C. Peterson, C. Richter, A. Simmons, and M. Zemp, 2014: The concept of essential climate variables in support of climate research, applications, and policy. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 95, 1431–1443.
Brohan, P., J. J. Kennedy, I. Harris, S. F. B. Tett, and P. D. Jones, 2006: Uncertainty estimates in regional and global observed temperature changes: A new data set from 1850. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D12106, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006548.
Brunet, M., and Coauthors, 2011: The minimization of the screen bias from ancient Western Mediterranean air temperature records: an exploratory statistical analysis. Inter. J. Climatol., 31, 1879–1895, doi: 10.1002/joc. 2192.
Callendar, G. S., 1938: The artificial production of carbon dioxide and its influence on temperature. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 64, 223–240, doi: 10.1002/qj.49706427503.
Callendar, G. S., 1961: Temperature fluctuations and trends over the earth. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 87, 1–12, doi: 10.1002/qj.49708737102.
Compo, G. P., and Coauthors, 2011: The twentieth century reanalysis project. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 1–28, doi: 10.1002/qj.776.
Compo, G. P., P. D. Sardesmukh, J. S. Whitaker, P. Brohan, P. D. Jones, and C. McColl, 2013: Independent confirmation of global land warming without the use of station. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, 3170–3174, doi: 10.1002/grl.50425.
Conrad, V., and L. W. Pollak, 1962: Methods in Climatology. Harvard University Press, 459 pp.
Cowtan, K., and R. G. Way, 2014: Coverage bias in the hadcrut4 temperature series and its impact on recent temperature trends. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 140, 1935–1944, doi: 10.1002/qj.2297.
Dee, D. P., and Coauthors, 2011: The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 553–597, doi: 10.1002/ qj.828.
Farmer, G., T. M. L. Wigley, P. D. Jones, and M. Salmon, 1989: Documenting and explaining recent global-mean temperature changes. Final Report to the Natural Environment Research Council, Contract No. GR3/6565, East Anglia University, Norwich, UK. [Available online at http://wwwcruueaac. uk/cru/pubs/pdf/Farmer-1989-NERCpdf.]
Folland, C. K., 2005: Assessing bias corrections in historical sea surface temperature using a climate model. Inter. J. Climatol., 25, 895–911, doi: 10.1002/joc.1171.
Folland, C. K., and D. E. Parker, 1995: Correction of instrumental biases in historical sea surface temperature data. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 121, 319–367.
Foster, G., and S. Rahmstorf, 2011: Global temperature evolution 1979–2010. Environ. Res. Lett., 6, 044022, doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/6/4/044022.
Hansen, J., R. Ruedy, J. Glascoe, and M. Sato, 1999: GISS analysis of surface temperature change. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 30997–31022, doi: 10.1029/1999JD900835.
Hansen, J., M. Sato, R. Ruedy, K. Lo, D. W. Lea, and M. Medina- Elizade, 2006: Global temperature change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 14288–14293.
Hansen, J., R. Ruedy, M. Sato, and K. Lo, 2010: Global surface temperature change. Rev. Geophys., 48, RG4004, doi: 10.1029/2010RG000345.
Hartmann, D. L., and Coauthors, 2013: Observations: Atmosphere and surface. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, T. F. Stocker et al., Eds. Cambridge University Press.
Hawkins, E., and P. D. Jones, 2013: On increasing global temperatures: 75 years after Callendar. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 139, 1961–1963, doi: 10.1002/qj.2178.
Hersbach, H., C. Peubey, A. Simmons, P. Berrisford, P. Poli, and D. Dee, 2015: ERA-20CM: A twentieth-century atmospheric model ensemble. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 141, 2350–2375, doi: 10.1002/qj.2528.
Huang, B. Y., and Coauthors, 2015: Extended reconstructed Sea surface temperature Version 4 (ERSSTv4). Part I: upgrades and intercomparisons. J. Climate, 28, 911–930.
Ishii, M., A. Shouji, S. Sugimoto, and T. Matsumoto, 2005: Objective analyses of Sea-surface temperature and marine meteorological variables for the 20th century using ICOADS and the Kobe collection. Inter. J. Climatol., 25, 865–879.
Jansen, E., and Coauthors, 2007: Palaeoclimate. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, S. Solomon et al., Eds. Cambridge University Press, 433–497.
Jones, P. D., 1994: Hemispheric surface air temperature variations: a reanalysis and an update to 1993. J. Climate, 7, 1794–1802.
Jones, P. D., and D. H. Lister, 2009: The urban heat island in central London and urban-related warming trends in central London since 1900. Weather, 64, 323–327.
Jones, P. D., and D. H. Lister, 2015: Antarctic near-surface air temperatures compared with ERA-Interim values since 1979. International Journal of Climatology, 35, 1354–1366, doi: 10.1002/joc.4061.
Jones, P. D., and T. M. L. Wigley, 2010: Estimation of global temperature trends: What’s important and what isn’t. Climatic Change, 100, 59–69.
Jones, P. D., P. Y. Groisman, M. Coughlan, N. Plummer, W.-C. Wang, and T. R. Karl, 1990: Assessment of urbanization effects in time series of surface air temperature over land. Nature, 347, 169–172.
Jones, P. D., T. J. Osborn, and K. R. Briffa, 1997: Estimating sampling errors in large-scale temperature averages. J. Climate, 10, 2548–2568.
Jones, P. D., K. R. Briffa, and T. J. Osborn, 2003: Changes in the Northern hemisphere annual cycle: Implications for paleoclimatology? J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4588, doi: 10.1029/2003JD 003695.
Jones, P. D., D. H. Lister, and Q. Li, 2008: Urbanization effects in large-scale temperature records, with an emphasis on China. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D16122, doi: 10.1029/2008JD009916.
Jones, P. D., D. H. Lister, T. J. Osborn, C. Harpham, M. Salmon, and C. P. Morice, 2012: Hemispheric and large-scale landsurface air temperature variations: An extensive revision and an update to 2010. J. Geophys. Res., 117, D05127, doi: 10.1029/2011JD017139.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–471.
Karl, T. R., C. N. Williams Jr., P. J. Young, and W. M. Wendland, 1986: A model to estimate the time of observation bias associated with monthly mean maximum, minimum and mean temperatures for the United States. J. Climate Appl. Meteor., 25, 145–160.
Karl, T. R., R. W. Knight, and J. R. Christy, 1994: Global and hemispheric temperature trends: Uncertainties related to inadequate spatial sampling. J. Climate, 7, 1144–1163.
Karl, T. R., and Coauthors, 2015: Possible artifacts of data biases in the recent global surface warming hiatus. Science, 348, 1469–1472.
Kennedy, J. J., 2014: A review of uncertainty in in situ measurements and data sets of Sea surface temperature. Rev. Geophys., 52, 1–32, doi: 10.1002/2013RG000434.
Kennedy, J. J., N. A. Rayner, R. O. Smith, D. E. Parker, and M. Saunby, 2011a: Reassessing biases and other uncertainties in Sea surface temperature observations measured in situ since 1850: 1. Measurement and sampling uncertainties. J. Geophys. Res., 116, doi: 10.1029/2010JD015218.
Kennedy, J. J., N. A. Rayner, R. O. Smith, D. E. Parker, and M. Saunby, 2011b: Reassessing biases and other uncertainties in Sea surface temperature observations measured in situ since 1850: 2. Biases and homogenization. J. Geophys. Res., 116, doi: 10.1029/2010JD015220.
Kent, E. C., J. J. Kennedy, D. I. Berry, and R. O. Smith, 2010: Ef fects of instrumentation changes on sea surface temperature measured in situ. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 1(5), 718–728, doi: 10.1002/wcc.55.
Kent, E. C., N. A. Rayner, D. I. Berry, M. Saunby, B. I. Moat, J. J. Kennedy, and D. E. Parker, 2013: Global analysis of night marine air temperature and its uncertainty since 1880: The HadNMAT2 data set. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 1281–1298, doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50152.
Köppen, W., 1873: Über mehrjährige perioden der witterung, insbesondere über die 11-jährige periode der temperatur. Zeitschrift der ö sterreichischen Gesellschaft für Meteorologie, Bd VIII, 241–248, 257–267.
Le Treut, H., R. Somerville, U. Cubasch, Y. Ding, C. Mauritzen, A. Mokssit, T. Peterson, and M. Prather, 2007: Historical overview of climate change. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, S. Solomon et al., Eds. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 93–127.
Li, Q. X, J. Y. Huang, Z. H. Jiang, L. M. Zhou, P. Chu, and K. X. Hu, 2014: Detection of urbanization signals in extreme winter minimum temperature changes over Northern China. Climatic Change, 122, 595–608.
Liu, W., and Coauthors, 2015: Extended reconstructed Sea surface temperature Version 4 (ERSSTv4): Part II. Parametric and structural uncertainty estimations. J. Climate, 28, 931–951.
Lugina, K. M., P. Y. Groisman, K. Y. Vinnikov, V. V. Koknaeva, and N. A. Speranskaya, 2006: Monthly surface air temperature time series area-averaged over the 30-degree latitudinal belts of the globe, 1881–2005. Trends: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Dept. Energy, Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.A. [Available online at http://cdiacesdornlgov/trends/temp/lugina/luginahtml.]
Masson Delmotte, V. M., and Coauthors, 2013: Information from paleoclimate archives. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, T. F. Stocker et al., Eds. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
Maury, M. F., 1855: Wind and Current Charts. 7th ed., US Navy, Philadelphia.
Menne, M. J., C. N. Williams Jr., and R. S. Vose, 2009: The U.S historical climatology network monthly temperature data, Version 2. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 90, 993–1007.
Moberg, A., H. Alexandersson, H. Bergström, and P. D. Jones, 2003: Were southern Swedish summer temperatures before 1860 as warm as measured? Inter. J. Climatol., 23, 1495–1521.
Morice, C. P., J. J. Kennedy, N. A. Rayner, and P. D. Jones, 2012: Quantifying uncertainties in global and regional temperature change using an ensemble of observational estimates: the HadCRUT4 data set. J. Geophys. Res., 117, D08101, doi: 10.1029/2011JD017187.
Nicholls, N., R. Tapp, K. Burrows, and D. Richards, 1996: Historical thermometer exposures in Australia. Inter. J. Climatol., 16, 705–710.
Parker, D. E., 1994: Effects of changing exposure of thermometers at land stations. Inter. J. Climatol., 14, 1–31.
Parker, D. E., 2004: Climate: large-scale warming is not urban. Nature, 432, 290 pp.
Parker, D. E., 2006: A demonstration that large-scale warming is not urban. J. Climate, 19, 2882–2895.
Parker, D. E., 2010: Urban heat island effects on estimates of observed climate change. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 1(1), 123–133, doi: 10.1002/wcc.21.
Parker, D. E., 2011: Recent land surface air temperature trends assessed using the 20th century reanalysis. J. Geophys. Res., 116, D20125, doi: 10.1029/2011JD016438.
Parker, D. E., P. Jones, T. C. Peterson, and J. Kennedy, 2009: Comment on “Unresolved issues with the assessment of multidecadal global land surface temperature trends” by Roger A. Pielke Sr. et al. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D05104, doi: 10.1029/ 2008JD010450.
Peterson, T. C., and T. W. Owen, 2005: Urban heat island assessment: metadata are important. J. Climate, 18, 2637–2646.
Poli, P., and Coauthors, 2013: The data assimilation system and initial performance evaluation of the ECMWF pilot reanalysis of the 20th-century assimilating surface observations only (ERA-20C). ERA Report Series, 14 pp.
Quayle, R. G., D. R. Easterling, T. R. Karl, and P. Y. Hughes, 1991: Effects of recent thermometer changes in the cooperative station network. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 72, 1718–1723.
Ren, G. Y., Y. Q. Zhou, Z. Y. Chu, J. X. Zhou, A. Y. Zhang, J. Guo, and X. F. Liu, 2008: Urbanization effects on observed surface air temperature trends in North China. J. Climate, 21, 1333–1348.
Rennie, J., and Coauthors, 2014: The international surface temperature initiative global land surface databank: Monthly temperature data release description and methods. Geoscience Data Journal, 1, 75–102, doi: 10.1002/gdj3.8.
Rohde, R., and Coauthors, 2013a: A new estimate of the average earth surface land temperature spanning 1753 to 2011. Geoinfor Geostat: An Overview, 1, doi: 10.4172/2327-4581. 1000101.
Rohde, R., and Coauthors, 2013b: Berkeley earth temperature averaging process. Geoinfor Geostat: An Overview, 1, doi: 10.4172/ gigs.1000103.
Simmons, A. J., K. M. Willett, P. D. Jones, P. W. Thorne, and D. P. Dee, 2010: Low-frequency variations in surface atmospheric humidity, temperature, and precipitation: inferences from reanalyses and monthly gridded observational data sets. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D01110, doi: 10.1029/2009JD012442.
Smith, T. M., R. W., and Reynolds, 2005: A global merged land and sea surface temperature reconstruction based on historical observations (1880–1997). J Climate, 18, 2021–2036.
Smith, T. M., R. W. Reynolds, T. C. Peterson, and J. Lawrimore, 2008: Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged Land-Ocean surface temperature analysis (1880–2006). J. Climate, 21, 2283–2293.
Thompson, D. W. J., J. J. Kennedy, J. M. Wallace, and P. D. Jones, 2008: A large discontinuity in the mid-twentieth century in observed global-mean surface temperature. Nature, 453, 646–649.
Thompson, D. W. J., J. M. Wallace, P. D. Jones, and J. J. Kennedy, 2009: Identifying signatures of natural climate variability in time series of global-mean surface temperature: Methodology and insights. J. Climate, 22, 6120–6141.
Trenberth, K. E., and Coauthors, 2007: Observations: surface and atmospheric climate change. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, S. D. Solomon et al., Eds. Cambridge University Press, 235–336.
Trewin, B., 2010: Exposure, instrumentation, and observing practice effects on land temperature measurements. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 1, 490–506, doi: 10.1002/wcc.46, 2010.
Venema, V. K. C., and Coauthors, 2012: Benchmarking homogenization algorithms for monthly data. Climates of the Past, 8, 89–115.
Vose, R. S., and Coauthors, 2012: NOAA’s merged Land–Ocean surface temperature analysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93, 1677–1685, doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00241.1.
Wang, F., Q. S. Ge, S. W. Wang, Q. X. Li, and P. D. Jones, 2015: A new estimation of urbanization’s contribution to the warming trend in China. J. Climate, 28, 8923–8938, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00427.1.
Wang, J., Z. W. Yan, P. D. Jones, and J. J. Xia, 2013: On “observation minus reanalysis” method: A view from multidecadal variability. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 7450–7458, doi: 10.1002/ jgrd.50574.
Wickham, C., and Coauthors, 2013: Influence of urban heating on the global temperature land average using rural sites identified from MODIS classifications. Geoinfor Geostat: An Overview, 1, doi: 10.4172/2327-4581.1000104.
Wilby, R. L., P. D. Jones, and D. H. Lister, 2011: Decadal variations in the nocturnal heat island of London. Weather, 66, 59–64. Woodruff, S. D., and Coauthors, 2011: ICOADS release 2.5: extensions and enhancements to the surface marine meteorological archive. Inter. J. Climatol., 31, 951–967, doi: 10.1002/joc.2103.
Xu, W. H., Q. X. Li, X. L. Wang, S. Yang, L. J. Cao, and Y. Feng, 2013: Homogenization of Chinese daily surface air temperatures and analysis of trends in the extreme temperature indices. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 9708–9720, doi: 10.1002/jgrd. 50791.
Zhao, P., P. D. Jones, L. J. Cao, Z. W. Yan, S. Y. Zha, Y. N. Zhu, Y. Yu, and G. L. Tang, 2014: Trend of surface air temperature in eastern china and associated large-scale climate variability over the last 100 years. J. Climate. 27, 4693–4703, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00397.1.
Zhou, L. M., R. E. Dickinson, Y. H. Tian, J. Y. Fang, Q. X. Li, R. K. Kaufmann, C. J. Tucker, and R. B. Myneni, 2004: Evidence for a significant urbanization effect on climate in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 9540–9544.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, P. The reliability of global and hemispheric surface temperature records. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 33, 269–282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-015-5194-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-015-5194-4