Abstract
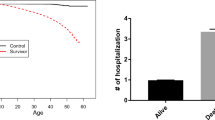
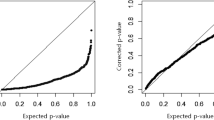
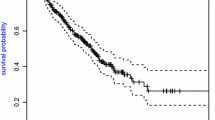
Recurrent event data with an additive marginal rates function have been extensively studied in the literature. The existing statistical inference, however, faces the difficulty with high-dimensional covariates due to “curse of dimensionality”. Examples include gene expression and single nucleotide polymorphism data which have revolutionized our understanding of disease such as cancer recurrence. In this paper, a technique of partial sufficient dimension reduction is applied to an additive rates model for recurrent event data. A two-step procedure is proposed to estimate parameters. First, partial sufficient dimension reduction is used to estimate the basis of the partial central subspace and the structural dimension. Then the second step estimates the baseline and the regression function of covariates based on the estimated partial central subspace using the average surface method. Simulation is performed to confirm and assess the theoretical findings, and an application on a set of chronic granulomatous disease data is demonstrated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen PK, Gill RD (1982) Cox’s regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Ann Stat 10:1100–1120
Andersen PK, Borgan Q, Gill RD, Keiding N (1993) Statistical models based on counting processes. Springer, New York
Bura E, Cook RD (2001) Extending sliced inverse regression: the weighted chisquared test. J Am Stat Assoc 96:996–1003
Cai ZW, Fan JQ (2000) Average regression surface for dependent data. J Multivar Anal 75:112–142
Chen XL, Wang QH (2013) Variable selection in the additive rates model for recurrent event data. Comput Stat Data Anal 57:491–503
Chen XL, Wang QH, Cai JW, Shankar V (2012) Semiparametric additive marginal regression models for multiple type recurrent events. Lifetime Data Anal 18:504–527
Chiaromonte F, Cook RD, Li B (2002) Sufficient dimension reduction in regressions with categorical predictors. Ann Stat 30:475–497
Cook RD (1998) Regression graphics. Wiley, New York
Cook RJ, Lawless JF (1996) Interim monitoring of longitudinal comparative studies with recurrent event response. Biometrics 52:1311–1323
Cook RJ, Lawless J (2007) The statistical analysis of recurrent events. Springer, New York
Cook RD, Weisberg S (1991) Discussion to ”Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction”. J Am Stat Assoc 86:316–324
Cook RJ, Lawless JF, Nadeau JC (1996) Robust tests for treatment comparisons based on recurrent event responses. Biometrics 52:557–571
Fan JQ, Gijbels I (1996) Local polynomial modelling and its applications. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Fan JQ, Yao QW, Tong H (1996) Estimation of conditional densities and sensitivity measures in nonlinear dynamical systems. Biometrika 83:189–206
Fan JQ, Hardle W, Mammen E (1998) Direct estimation of low dimensional components in additive models. Ann Stat 26:943–971
Feng ZH, Wen XR, Yu Z, Zhu LX (2013) On partial sufficient dimension reduction with application to partial linear multi-index models. J Am Stat Assoc 108:237–246
Fleming TR, Harrington DP (1991) Counting processes and survival analysis. Wiley, New York
Gao JT, Liang H (1997) Statistical inference in single-index and partially nonlinear models. Ann Inst Stat Math 49:493–517
Huang CY, Wang MC (2004) Joint modeling and estimation of recurrent event processes and failure time data. J Am Stat Assoc 99:1153–1165
Li KC (1991) Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction. J Am Stat Assoc 86:316–327
Li B, Wang S (2007) On directional regression for dimension reduction. J Am Stat Assoc 102:997–1008
Li B, Cook DR, Chiaromonte F (2002) Dimension reduction for the conditional mean in regressions with categorical predictors. Ann Stat 31:1636–1668
Li L, Li B, Zhu LX (2010) Groupwise dimension reduction. J Am Stat Assoc 105:1188–1201
Lin DY, Wei LJ, Yang I, Ying Z (2000) Semiparametric regression for the mean and rate functions of recurrent events. J R Stat Soc 62:711–730
Liu Y, Wu Y, Cai J, Zhou H (2010) Additive-multiplicative rates model for recurrent events. Lifetime Data Anal 16:353–373
Lu WB, Li LX (2011) Sufficient dimension reduction for censored regressions. Biometrics 67:513–523
Luo XH, Wang MC, Huang CY (2008) A comparison of various rate functions of a recurrent event process in the presence of a terminal event. Stat Methods Med Res 17:207–221
Nevalainen J, Datta S, Oja H (2014) Inference on the marginal distribution of clustered data with informative cluster size. Stat Pap 55:71–92
Pena EA, Slate EH, Gonzalez JR (2007) Semiparametric inference for a general class of models for recurrent event. J Stat Plan Inference 137:1727–1747
Pepe MS, Cai J (1993) Some graphical displays and marginal regression analysis for recurrent failure times and time dependent covariates. J Am Stat Assoc 88:811–820
Prentice RL, Williams BJ, Peterson AV (1981) On the regression analysis of multivariate failure time data. Biometrika 68:373–379
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI, Gascoyne RD, Muller-Hermelink HK, Smeland EB, Staudt LM (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346:1937–1947
Ruppert D, Wand MP (1994) Multivariate weighted least squares regression. Ann Stat 22:1346–1370
Schaubel DE, Zeng DL, Cai JW (2006) A semiparametric additive rates model for recurrent event data. Lifetime Data Anal 12:389–406
Shao Y, Cook RD, Weisberg S (2009) Partial central subspace and sliced average variance estimation. J Stat Plan Inference 139:952–961
Tong XW, Zhu L, Sun JG (2009) Variable selection for recurrent event data via nonconcave penalized estimating function. Lifetime Time Data Anal 15:197–215
Wand MP, Jones MC (1995) Kernel estimation. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Wang MC, Jewell NP, Tsia WY (1986) Asymptotic properties of the product limit estimate under random truncation. Ann Stat 14:1597–1605
Wei LJ, Lin DY, Weissfeld L (1989) Regression analysis of multivariate incomplete failure time data by modeling marginal distributions. J Am Stat Assoc 84:1065–1073
Wen X, Cook RD (2007) Optimal sufficient dimension reduction in regressions with categorical predictors. J Stat Plan Inference 137:1961–1978
Xia YC, Zhang DX, Xu JF (2010) Dimension reduction and semiparametric estimation of survival models. J Am Stat Assoc 105:278–290
Zeng D, Cai J (2010) A semiparametric additive rate model for recurrent events with an informative terminal event. Biometrika 97:699–712
Zhu LX, Miao BQ, Peng H (2006) Sliced Inverse Regression with large dimensional covariates. J Am Stat Assoc 101:630–643
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the NSFC under Grant No. 11271317, Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. LY16A010007, and First Class Discipline of Zhejiang - A (Zhejiang University of Finance and Economics- Statistics).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Zhou, X. Partial sufficient dimension reduction on additive rates model for recurrent event data with high-dimensional covariates. Stat Papers 61, 523–541 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-017-0949-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-017-0949-x