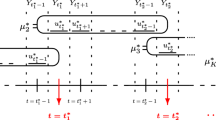
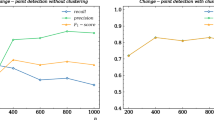
Abstract
Change point problem is one of the hot issues in statistics, econometrics, signal processing and so on. LAD estimator is more robust than OLS estimator, especially when datasets subject to heavy tailed errors or outliers. LASSO is a popular choice for shrinkage estimation. In the paper, we combine the two classical ideas together to put forward a robust detection method via adaptive LAD-LASSO to estimate change points in the mean-shift model. The basic idea is converting the change point estimation problem into variable selection problem with penalty. An enhanced two-step procedure is proposed. Simulation and a real example show that the novel method is really feasible and the fast and effective computation algorithm is easier to realize.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Angelosante D, Giannakis GI (2012) Group lassoing change-points in piecewise-constant AR processes. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 70(1):1–16
Arslan O (2012) Weighted LAD-LASSO method for robust parameter estimation and variable selection in regression. Comput Stat Data Anal 56:1952–1965
Bai J (1995) Least absolute deviation estimation of s shift. Econom Theory 11(3):403–436
Bai J (1998) Estimation of multiple-regime regressions with least absolutes deviation. J Stat Plan Inference 74(1):103–134
Boysen L, Kempe A, Liebscher V, Munk A, Wittich O (2009) Consistencies and rates of convergence of jump penalized least squares estimators. Ann Stat 37(1):157–183
Chan NH, Yau CY, Zhang R (2014) Group LASSO for structural break time series. J Am Stat Assoc 109(506):590–599
Chow GC (1960) Tests of equality between sets of coefficients in two linear regressions. Econometrica 28(3):591–605
Ciuperca G (2011) Penalized least absolute deviations estimation for nonlinear model with change-points. Stat Pap 52(2):371–390
Ciuperca G (2014) Model selection by LASSO methods in a change-point model. Stat Pap 55(4):349–374
Donoho D, Johnstone I (1995) Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage. J Am Stat Assoc 90(432):1200–1224
Efron B, Hastie T, Johnstone I, Tibshirani R (2004) Least angle regression. Ann Stat 32(2):407–451
Fan J, Li R (2001) Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J Am Stat Assoc 96(456):1348–1360
Fan J, Lv J (2008) Sure independence screening for ultrahigh dimensional feature space. J R Stat Soc Ser B 70(5):849–911
Gao X, Huang J (2010a) Asymptotic analysis of high-dimensional LAD regression with lasso. Stat Sin 20:1485–1506
Gao X, Huang J (2010b) A robust penalized method for the analysis of noisy DNA copy number data. BMC Genomics 11(517):1–10
Harchaoui Z, Lévy-Leduc C (2008) Catching change-points with lasso. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 20:161–168
Harchaoui Z, Lévy-Leduc C (2010) Multiple change-point estimation with a total variation penalty. J Am Stat Assoc 105(492):1480–1493
Hawkins DM (1977) Testing a sequence of observations for a shift in location. J Am Stat Assoc 72(357):180–186
Huang T, Wu B, Lizardi P, Zhao H (2005) Detection of DNA copy number alterations using penalized least squares regression. Bioinformatics 21(20):3811–3817
Knight K, Fu WJ (2000) Asymptotics for Lasso-type estimators. Ann Stat 28(5):1356–1378
Lavielle M, Moulines E (2000) Least-squares estimation of an unknown number of shifts in a time series. J Time Ser Anal 21(1):33–59
Little MA, Jones NS (2011a) Generalized methods and solvers for noise removal from piecewise constant signals. I. Background theory. Proc R Soc A 467:3088–3114
Little MA, Jones NS (2011b) Generalized methods and solvers for noise removal from piecewise constant signals. II. New methods. Proc R Soc A 467:3115–3140
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B 58(1):267–288
Wang L (2013) The \(L_1\) penalized LAD estimator for high dimensional linear regression. J Multivar Anal 120:135–151
Wang H, Li G, Jiang G (2007) Robust regression shrinkage and consistent variable selection through the LAD-Lasso. J Bus Econ Stat 25(3):347–355
Xu J, Ying Z (2010) Simultaneous estimation and variable selection in median regression using Lasso-type penalty. Ann Inst Stat Math 62:487–514
Yao Y, Au ST (1989) Least-squares estimation of a step function. Sankhya 51(3):370–381
Zhang C (2010) Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann Stat 38(2):894–942
Zhang B, Geng J, Lai L (2015) Multiple change-points estimation in linear regression models via sparse group Lasso. Signal Process 63(9):2209–2224
Zhao P, Yu B (2006) On model selection consistency of Lasso. J Mach Learn Res 7:2541–2563
Zou H (2006) The adaptive Lasso and its oracle properties. J Am Stat Assoc 101(476):1418–1429
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71271128 and Grant No. 71540038), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province in China (Grant No. ZR2014AL006) and the Talent Research Fund of Taishan University (Grant No. Y-01-2016002). The authors thank the Editor and the three Referees for their very helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Wang, L. Robust change point detection method via adaptive LAD-LASSO. Stat Papers 61, 109–121 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-017-0927-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-017-0927-3