Abstract
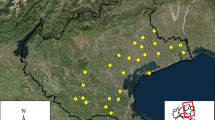
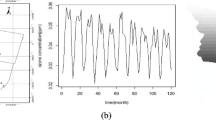
Statistical analysis of natural phenomena with spatial and temporal correlations requires the specification of the correlation structure via a covariance function. A separable spatio-temporal covariance function is usually used for the ease of application. Nonetheless, the separability of the spatio-temporal covariance function can be unrealistic in many settings, where it is required to use a non-separable spatio-temporal covariance function. In this paper, the role of Stieltjes transformation in the construction of non-separable spatio-temporal covariance function is investigated. Then, structural copula function is applied to construct a family of non-separable spatio-temporal covariance function. Afterwards, it is proved that this family of covariance functions does not possess any dimple which exists in some Gneiting’s models. Finally, a modified genetic algorithm is applied to explore the spatio-temporal correlation structure of Ozone data in Tehran, Iran.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1973) Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In: Proceedings of 2nd international symposium on information theory, pp 267–281
Auffarth B (2010) Clustering by a genetic algorithm with biased mutation operator. IEEE, 18–23
Bajpai P, Kumar M (2008) Genetic algorithm: an approach to solve global optimisation problems. Indian J Comput Sci Eng 1(3):199–206
Berg C (2008) Stieltjes–Pick–Bernstein–Schoenberg and their connection to complete monotonicity. In: Mateu J, Porcu E (eds) Positive definite functions from Schoenberg to space–time challenges. Universitat Jaume I, Castellon de la Plana
Cressie N, Huang H (1999) Classes of non-separable, spatio-temporal stationary covariance functions. J Am Stat Assoc 94:1330–1340
De Iaco S, Myers D, Posa D (2001) Space–time analysis using a general product-sum model. Stat Probab Lett 52(1):21–28
De Iaco S, Myers DE, Posa D (2002) Nonseparable space–time covariance models: some parametric families. Math Geol 34:23–42
Feller W (1966) An introduction to probability theory and its applications. Wiley, New York
Fuentes M, Chen L, Davis JM (2007) A class of nonseparable and nonstationary spatial temporal covariance functions. Environmetrics 19:487–507
Gneiting T (2002) Nonseparable, stationary covariance functions for space–time data. J Am Stat Assoc 97:590–600
Gneiting T, Genton M, Guttorp P (2007) Geostatistical space–time models, stationarity, separability and full symmetry. In: Finkenstadt B, Held L, Isham V (eds) Statistical methods for spatio-temporal systems. Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton, pp 151–175
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search. Optimisation, and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Haupt RL, Haupt SE (2004) Practical genetic algorithms, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. The University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Joe H (1997) Multivariate models and dependence concepts. Chapman and Hall, New York
Kent J, Mohammadzadeh M, Mosammam A (2011) The dimple in gneiting’s spatio temporal covariance model. Biometrika 98:489–494
Kolovos A, Christakos G, Hristopulos D, Serre M (2004) Methods for generating non-separable spatio-temporal covariance models with potential environmental applications. Adv Water Resour 27:815–830
Koza JR (1992) Genetic programming: on the programming of computers by means of natural selection. MIT Press, Cambridge
Kumar A, Jani NN (2010) Network design problem using genetic algorithm-an empirical study on mutation operator. Glob J Comput Sci Technol 10:77–82
Lai D (2010) Box–Cox transformation for spatial linear models: a study on lattice data. Stat Pap 51:853–864
Ma C (2002) Spatio-temporal covariance functions generated by mixtures. Math Geol 34:965–975
Ma C (2003) Families of spatio-temporal stationary covariance models. J Stat Plan Inference 116:489–501
Ma C (2005a) Spatio-temporal variograms and covariance models. Adv Appl Probab 37:706–725
Ma C (2005b) Linear combinations of space–time covariance functions and variograms. IEEE Trans Signal Process 53(3):857–864
Marzuki K, Ibrahim MF, Yusof R, Abdul Rahman RZ (2011) Optimisation of Fuzzy model using genetic algorithm for process control application. J Frankl Inst 348(7):1717–1737
Michiels F, De Schepper A (2012) How to improve the fit of archimedean copulas by means of transforms. Stat Pap 53(2):345–355
Miller KS, Samko SG (2001) Completely Monotonic Functions. Integral Transforms and Special Functions. 12(4):389–402
Minaei-Bidgoli B, Punch WF (2003) Algorithms using genetic, for data mining optimisation in an educational web-based system. In: GECCO Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, (2003). Springer, New York, 2252–2263
Montoya J, Diaz-Frances E, Sprott DA (2009) On a criticism of the profile likelihood function. Stat Pap 50:195–202
Nelsen RB (2006) An introduction to copulas, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Paciorek CJ, Lipshitz B, Zhuo W, Prabhat Kaufman, CG, Thomas RC (2013) Parallelizing Gaussian Process Calculations in R. arXiv:1305.4886. http://arxiv.org/abs/1305.4886
Pham DT, Ghanbarzadeh A, Koc E, Otri S, Rahim S, Zaidi M (2005) The bees algorithm. Technical Note Manufacturing Engineering Centre, Cardiff University, UK
Porcu E, Mateu J (2007) Mixture-based modelling for space–time data. Environmetrics 18:285–302
Porcu E, Mateu J, Saura F (2008) New classes of covariance and spectral density functions for spatio-temporal modelling. Stoch Environ Res Risk assess 22:65–79
Porcu E, Mateu J, Christakos G (2009) Quasi-arithmetic means of covariance functions with potential applications to space–time data. J Multivar Anal 100(8):1830–1844
Rodrigues A, Diggle P (2010) A class of convolution-based models for spatio-temporal processes with non-separable covariance structure. Scand J Stat 37(4):553–567
Schmitt LM (2001) Theory of genetic algorithms. Theor Comput Sci 259:1–61
Sklar A (1959) Fonctions de Repartition a n Dimensions et Leurs Marges. Publications de l’Institut de Statistique de l’Universite de Paris 8:229–231
Stein ML (2005a) Space–time covariance functions. J Am Stat Assoc 100:310–321
Stein ML (2005b) Statistical methods for regular monitoring data. J R Stat Soc B 67:667–687
Tezuka M, Munetomo M, Kiyoshi Akama K (2007) Genetic algorithm to optimise fitness function with samplling error and its application to financial optimisation problem. Evolutionary computation in dynamic and uncertain environments, 417–434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omidi, M., Mohammadzadeh, M. A new method to build spatio-temporal covariance functions: analysis of ozone data. Stat Papers 57, 689–703 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-015-0674-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-015-0674-2