Abstract
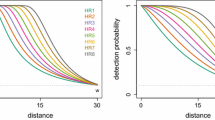
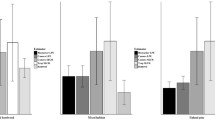
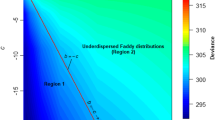
Point transect sampling is a well-known methodology for estimating wildlife population density. In this context, the usual approach is to assume a model for the detection function. Thus, the estimate depends on the shape of the detection function. In particular, the estimation is influenced by the so-called shoulder condition, which guarantees that detection is nearly certain at small distances from the observer. For instance, the half-normal model satisfies this condition, whereas the negative exponential model does not. Testing whether the shoulder condition is consistent with data is a crucial issue. In this paper we propose the uniformly most powerful unbiased test for the shoulder condition in the exponential mixture model of the half-normal and the negative exponential. Critical values of the proposed test are calculated for large samples by means of asymptotic distribution theory and for small samples via Monte Carlo simulations. Finally, a case study is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabesi L (2001) Local parametric density estimation methods in line transect sampling. Metron LIX: 21–37
Borgoni R, Quatto P (2009) On the uniformly most powerful invariant test for the shoulder condition in line transect sampling. Stat Appl VII:15–24
Borgoni R, Cameletti M, Quatto P (2005) Comparing estimators of animal abundance: a simulation study. In: Atti del Convegno della Società Italiana di Statistica “Statistica e Ambiente”. Università degli Studi di Messina, Messina, pp 181–184
Buckland ST (1987) On the variable circular plot method of estimating animal density. Biometrics 43: 363–384
Buckland ST, Anderson DR, Burnham KP, Laake JL, Borchers DL, Thomas L (2001) Introduction to distance sampling. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Buckland ST, Anderson DR, Burnham KP, Laake JL, Borchers DL, Thomas L (2004) Advanced distance sampling. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Eidous OM (2005) On improving kernel estimators using line transect sampling. Commun Stat Theory Methods 34:931–941
Lehmann EL (2001) Elements of large-sample theory. Springer, New York
Lehmann EL, Romano JP (2005) Testing statistical hypotheses. Springer, New York
Mack YP (1998) Testing for the shoulder condition in transect sampling. Commun Stat Theory Methods 27: 423–432
Panjabi A (2003) Monitoring the birds of the Black Observatory, Fort Collins, CO
Zhang S (2001) Generalized likelihood ratio test for the shoulder condition in line transect sampling. Commun Stat Theory Methods 30: 2343–2354
Zhang S (2003). A note on testing the shoulder condition in line transect sampling. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Hawaii international conference on statistics and related topics
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borgoni, R., Quatto, P. Uniformly most powerful unbiased test for shoulder condition in point transect sampling. Stat Papers 53, 1035–1044 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-011-0406-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-011-0406-1
Keywords
- Distance sampling
- Detection function
- Shoulder condition
- Uniformly most powerful unbiased test
- Exponential Family