Abstract
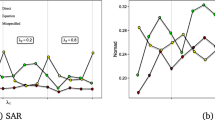
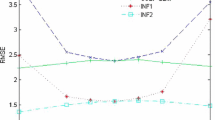
This paper considers a panel data regression model with spatial and serial correlation. We derive the best linear unbiased predictors for a spatial error component model including remainder disturbances that follow an AR(1) process, an AR(2) process, a special AR(4) process for quarterly data or an MA(1) process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anselin, L. (1988) Spatial Econometrics, Kluwer, Dordrecht.
Anselin, L. and Bera, A. (1998) Spatial dependence in linear regression models with an introduction to spatial econometrics correlation: a suggested, in: A. Ullah and D.E.A. Giles, eds., Handbook of Applied Economic Statistics, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Balestra, P. (1980) A note on the exact transformation associated with the first-order moving average process. Journal of Econometrics 14, 381–394.
Baltagi, B.H. (1980) On the seemingly unrelated regressions with error components. Econometrica 48, 1547–1551.
Baltagi, B.H. (1989) Prediction with a two way error component regression model: Problem 88.1.1. Econometric Theory 4, 171.
Baltagi, B.H. (1995) Econometric Analysis of Panel Data. Wiley, New York.
Baltagi, B.H. and Li, Q. (1992) Prediction in the one-way error component model with serial correlation. Journal of Forecasting 11, 561–567.
Baltagi, B.H. and Li, D. (1999) Prediction in the panel data model with spatial correlation, in: L. Anselin and R. Florax, eds., Advances in Spatial Econometrics, Springer, Heidelberg.
Cliff, A.D. and Ord, J.K. (1981) Spatial Processes Models and Application, Pion, London.
Goldberger, A.S. (1962) Best linear unbiased prediction in the generalized linear regression model. Journal of the American Statistical Association 57, 369–375.
Kelejian, H.H. and Robinson, D.P. (1995) Spatial correlation: a suggested alternative to the autoregressive model, in: L. Anselin and R. Florax, eds., New Directions in Spatial Econometrics, Springer, Berlin.
Lempers, F.B. and Kloek, T. (1973) On a simple transformation for second-order autocorrelated disturbances in regression analysis. Statistica Neerlandica 27, 69–75.
Prais, S.J. and Winsten, C.B. (1954) Trends estimator and serial correlation, Cowles Commision Discussion Paper. University of Chicago.
Taub, A.J. (1979) Prediction in the context of the variance components model. Journal of Econometrics 10, 103–108.
Thomas, J.J. and Wallis, K.F. (1971) Seasonal variation in regression analysis, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 134, 67–72.
Wansbeek, T. and Kapteyn, A. (1978) The seperation of individual variation and systematic change in the analysis of panel data. Annales de I’INSEE 30-31, 659–680.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S.H., Jung, B.C. BLUP in the panel regression model with spatially and serially correlated error components. Statistical Papers 43, 551–566 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-002-0123-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-002-0123-x