Abstract
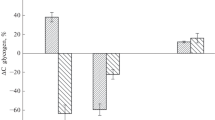
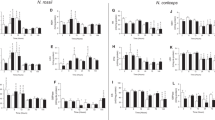
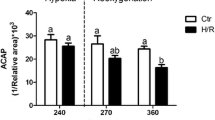
Mobilization of glycogen stores was examined in the anoxic crucian carp (Carassius carassius Linnaeus). Winter-acclimatized fish were exposed to anoxia for 1, 3, or 6 weeks at 2 °C, and changes in the size of glycogen deposits were followed. After 1 week of anoxia, a major part of the glycogen stores was mobilized in liver (79.5 %) and heart (75.6 %), and large decreases occurred in gill (46.7 %) and muscle (45.1 %). Brain was an exception in that its glycogen content remained unchanged. The amount of glycogen degraded during the first anoxic week was sufficient for the anaerobic ethanol production for more than 6 weeks of anoxia. After 3 and 6 weeks of anoxia, there was little further degradation of glycogen in other tissues except the brain where the stores were reduced by 30.1 and 49.9 % after 3 and 6 weeks of anoxia, respectively. One week of normoxic recovery following the 6-week anoxia was associated with a complete replenishment of the brain glycogen and partial recovery of liver, heart, and gill glycogen stores. Notably, the resynthesis of glycogen occurred at the expense of the existing energy reserves of the body in fasting fish. These findings indicate that in crucian carp, glycogen stores are quickly mobilized after the onset of anoxia, with the exception of the brain whose glycogen stores may be saved for putative emergency situations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blazka B (1958) The anaerobic metabolism of fish. Physiol Zool 31:117–128
Bradshaw JC, Kumai Y, Perry SF (2012) The effects of gill remodeling on transepithelial sodium fluxes and the distribution of presumptive sodium-transporting ionocytes in goldfish (Carassius auratus). J Comp Physiol B 182:351–366
Crawshaw LI, Wollmuth LP, O’Connor CS (1989) Intracranial ethanol and ambient anoxia elicit selection of cooler water by goldfish. Am J Physiol 256:R133–R137
DeVries AL (1971) Freezing resistance in fishes. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology. Academic Press, New York London, pp 157–190
Hochachka PW (1985) Assessing metabolic strategies for surviving O2 lack: role of metabolic arrest coupled with channel arrest. Mol Physiol 8:331–350
Holopainen IJ, Hyvärinen H (1985) Ecology and physiology of crucian carp (Carassius carassius (L.)) in small Finnish ponds with anoxic conditions in winter. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 22:2566–2570
Holopainen IJ, Oikari A (1992) Ecophysiological effects of temporary acidification on crucian carp, Carassius carassius (L.): a case history of a forest pond in eastern Finland. Ann Zool Fenn 29:29–38
Holopainen IJ, Hyvärinen H, Piironen J (1986) Anaerobic wintering of crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.)—II. Metabolic products. Comp Biochem Physiol A 83:239–242
Huang MT, Lee CF, Lin RF, Chen RJ (1997) The exchange between proglycogen and macroglycogen and the metabolic role of the protein-rich glycogen in rat skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest 99:501–505
Hyvärinen H, Holopainen IJ, Piironen J (1985) Anaerobic wintering of crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.)—I. Annual dynamics of glycogen reserves in nature. Comp Biochem Physiol A 82:797–803
Johnson LN (1992) Glycogen phosphorylase: control by phosphorylation and allosteric effectors. Faseb J 6:2274–2282
Kelly DA, Storey KB (1988) Organ-spesific control of glycolysis in anoxic turtles. Am J Physiol 255:R774–R779
Lardon I, Nilsson GE, Stecyk JA, Vu TN, Laukens K, Dommisse R, De Boeck G (2013) 1H-NMR study of the metabolome of an unecptionally anoxia tolerant vertebrate the crucian carp (Carassius carassius). Metabolomics 9:311–323
Lo S, Russell JC, Taylor AW (1970) Determination of glycogen in small tissue samples. Am J Physiol 28:234–236
McDougal DB Jr, Holowach J, Howe MC, Jones EM, Thomas CA (1968) The effects of anoxia upon energy sources and selected metabolic intermediates in the brains of fish, frog and turtle. J Neurochem 15:577–588
Merrick AW, Meyer DK (1954) Clycogen fractions of cardiac muscle in the normal and anoxic heart. Am J Physiol 177:441–443
Nikolsky GV (1963) Ecology of fishes. Academic Press, pp 352
Nilsson GE (1990) Long-term anoxia in crucian carp: changes in the levels of amino acid and monoamine neurotransmitters in the brain, catecholamines in chromaffin tissue, and liver glycogen. J Exp Biol 150:295–320
Nilsson GE (2001) Surviving anoxia with the brain turned on. NIPS 16:217–221
Piironen J, Holopainen IJ (1986) A note on seasonality in anoxia tolerance of crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.) in the laboratory. Ann Zool Fenn 23:335–338
Shoubridge EA, Hochachka PW (1981) Ethanol: novel end product of vertebrate anaerobic metabolism. Science 209:308–309
Shoubridge EA, Hochachka PW (1983) The integration and control of metabolism in the anoxic goldfish. Mol Physiol 4:165–195
Sollid J, De Angelis P, Gundersen K, Nilsson GE (2003) Hypoxia induces adaptive and reversible gross morphological changes in crucian carp gills. J Exp Biol 206:3667–3673
Sollid J, Weber RE, Nilsson GE (2005) Temperature alters the respiratory surface area of crucian carp Carassius carassius and goldfish Carassius auratus. J Exp Biol 208:1109–1116
Tiitu V, Vornanen M (2001) Cold adaptation suppresses the contractility of both atrial and ventricular muscle of the crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.) heart. J Fish Biol 59:141–156
Van den Thillart G, Kesbeke F, Waarde A (1980) Anaerobic energy-metabolism of goldfish, Carassius auratus (L.). J Comp Physiol B 136:45–52
Van Der Boon J, Eelkema FA, Van Den Thillart GEEJM, Addink ADF (1992) Influence of anoxia on free amino acid levels in blood, liver and skeletal muscles of the goldfish, Carassius auratus L. Comp Biochem Physiol B 101B:193–198
Van Waarde A (1983) Aerobic and anaerobic ammonia production by fish. Comp Biochem Physiol B 74:675–684
van Waarde A, De Graaff I, van den Thillart G, Erkelens C (1991) Acidosis (measured by nuclear magnetic resonance) and ethanol production in anoxic goldfish acclimated to 5 and 20°C. J Exp Biol 159:387–405
Vornanen M (1994a) Seasonal adaptation of crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.) heart: glycogen stores and lactate dehydrogenase activity. Can J Zool 72:433–442
Vornanen M (1994b) Seasonal and temperature-induced changes in myosin heavy chain composition of the crucian carp hearts. Am J Physiol 267:R1567–R1573
Vornanen M, Haverinen J (2011) Seasonality of glycogen phosphorylase activity in crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.). J Comp Physiol B 181:917–926
Vornanen M, Paajanen V (2006) Seasonal changes in glycogen content and Na+-K+-ATPase activity in the brain of crucian carp. Am J Physiol 291:R1482–R1489
Vornanen M, Stecyk JA, Nilsson GE (2009) Chapter 9 The anoxia-tolerant crucian carp (Carassius Carassius L.). In: Hypoxia, pp. 397–441. Amsterdam, Boston: Elsevier/Academic Press
Vornanen M, Asikainen J, Haverinen J (2011) Body mass dependence of glycogen stores in the anoxia-tolerant crucian carp (Carassius carassius L.). Naturwissenschaften 98:225–232
Walker RM, Johansen PH (1977) Anaerobic metabolism in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Can J Zool 55:1304–1311
Wright PA, Perry SF, Moon TW (1989) Regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis by catecholamines in rainbow trout during environmental hypoxia. J Exp Biol 147:169–188
Acknowledgments
Anita Kervinen is acknowledged for skillful technical assistance in analysis of tissue metabolites and Varpu Häyhä in collection of tissue samples. The project was funded by a grant from the Academy of Finland to MV (Project no. 210400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vornanen, M., Haverinen, J. Glycogen dynamics of crucian carp (Carassius carassius) in prolonged anoxia. J Comp Physiol B 186, 999–1007 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1007-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1007-z