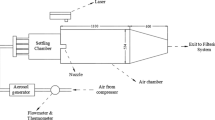
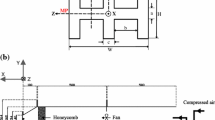
Abstract
This article reports on an experimental investigation of the near-field behavior of interacting jets at low Reynolds numbers (Re = 2125, 3290 and 4555). Two measurement techniques, particle image velocimetry (PIV) and laser Doppler anemometry (LDA), were employed to measure mean velocity and turbulence statistics in the near field of a row of six parallel coplanar round jets with equidistant spacing. The overall results from PIV and LDA measurements show good agreement, although LDA enabled more accurate measurements in the thin shear layers very close to the nozzle exit. The evolution of all six coplanar jets showed initial, merging, and combined regions. While the length of the potential core and the maximum velocity in the merging region are Reynolds number-dependent, the location of the merging points and the minimum velocity between jets were found to be independent of Reynolds number. Side jets at the edges of the coplanar row showed a constant decay rate of maximum velocity after their core region, which is comparable to a single round jet. Jets closer to the center of the row showed reducing velocity decay in the merging region, which led to a higher maximum velocity compared to a single round jet. A comparison with the flow for an in-line array of 6 × 6 round jets showed that the inward bending of streamwise velocity, which exists in the near field of the 6 × 6 jet array, does not occur in the single row of coplanar jets, although both setups have identical nozzle shape, spacing, and Reynolds number.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absil LHJ (1995) Analysis of the laser Doppler measurement technique for application in turbulent flows. Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands
Adrian RJ, Westerweel J (2010) Particle image velocimetry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Albrecht H-E (2003) Laser Doppler and phase Doppler measurement techniques. Springer, Berlin
Anderson EA, Spall RE (2001) Experimental and numerical investigation of two-dimensional parallel jets. J Fluids Eng Trans ASME 123:401–406
Awbi HB (2003) Ventilation of buildings. Spon Press, New York
Ball CG, Fellouah H, Pollard A (2012) The flow field in turbulent round free jets. Prog Aeosp Sci 50:1–26. doi:10.1016/j.paerosci.2011.10.002
Benedict LH, Gould RD (1996) Towards better uncertainty estimates for turbulence statistics. Exp Fluids 22:129–136. doi:10.1007/s003480050030
Boguslawski L, Popiel CO (1979) Flow structure of the free round turbulent jet in the initial region. J Fluid Mech 90:531–539. doi:10.1017/S0022112079002378
Böhm B, Stein O, Kempf A, Dreizler A (2010) In-nozzle measurements of a turbulent opposed jet using PIV. Flow Turbul Combust 85:73–93
Bradshaw P (1973) Effects of streamline curvature on turbulent flow. Advisory Group for Aerospace Research and Development (North Atlantic Treaty Organisation)
Cho Y, Awbi HB, Karimipanah T (2008) Theoretical and experimental investigation of wall confluent jets ventilation and comparison with wall displacement ventilation. Build Environ 43:1091–1100. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2007.02.006
Corrsin S (1944) Investigation of the behavior of parallel two-dimensional air jets. NASA No 4H24
Crow SC, Champagne FH (1971) Orderly structure in jet turbulence. J Fluid Mech 48:547–591. doi:10.1017/S0022112071001745
Deo R (2005) Experimental investigations of the influence of Reynolds number and boundary conditions on a plane air jet. The University of Adelaide, School of Mechanical Engineering
Deo RC, Mi J, Nathan GJ (2007) The influence of nozzle-exit geometric profile on statistical properties of a turbulent plane jet. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 32:545–559. doi:10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2007.06.004
Durve A, Patwardhan AW, Banarjee I, Padmakumar G, Vaidyanathan G (2012) Numerical investigation of mixing in parallel jets. Nucl Eng Des 242:78–90. doi:10.1016/j.nucengdes.2011.10.051
Fellouah H, Ball CG, Pollard A (2009) Reynolds number effects within the development region of a turbulent round free jet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:3943–3954
Fujisawa N, Nakamura K, Srinivas K (2004) Interaction of two parallel plane jets of different velocities. J Vis Jpn 7:135–142
Geers LFG (2004) Multiple impinging jet arrays: an experimental study on flow and heat transfer. Delft University of Technology, Delft
Geers LFG, Tummers MJ, Hanjalić K (2004) Experimental investigation of impinging jet arrays. Exp Fluids 36:946–958. doi:10.1007/s00348-004-0778-2
Geers LFG, Tummers MJ, Hanjalic K (2005) Particle imaging velocimetry-based identification of coherent structures in normally impinging multiple jets. Phys Fluids 17:055105–055113
Geers LFG, Hanjalic K, Tummers MJ (2006) Wall imprint of turbulent structures and heat transfer in multiple impinging jet arrays. J Fluid Mech 546:255–284
Ghahremanian S, Moshfegh B (2014) Evaluation of RANS models in predicting low Reynolds, free, turbulent round jet. J Fluids Eng 136:011201-011201–011201-011213. doi:10.1115/1.4025363
Ghahremanian S, Svensson K, Tummers MJ, Moshfegh B (2014) Near-field mixing of jets issuing from an array of round nozzles. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 47:84–100. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2014.01.007
Harima T, Fujita S, Osaka H (2001) Mixing and diffusion processes of twin circular free jets with various nozzle spacing 5th world conference on experimental heat transfer, fluid mechanics, and thermodynamics, pp 1017–1022
Hill BJ (1972) Measurement of local entrainment rate in the initial region of axisymmetric turbulent air jets. J Fluid Mech 51:773–779. doi:10.1017/S0022112072001351
Janbakhsh S, Moshfegh B (2014) Experimental investigation of a ventilation system based on wall confluent jets. Build Environ 80:18–31
Janbakhsh S, Moshfegh B, Ghahremanian S (2010) A newly designed supply diffuser for industrial premises. Int J Vent 9:59–67
Knystautas R (1962) The turbulent jet from a series of holes in line. MERL report 62-1, McGill University, Canada
Ko NWM, Lau KK (1989) Flow structures in initial region of two interacting parallel plane jets. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 2:431–449. doi:10.1016/0894-1777(89)90006-X
Kwon SJ, Seo IW (2005) Reynolds number effects on the behavior of a non-buoyant round jet. Exp Fluids 38:801–812. doi:10.1007/s00348-005-0976-6
Marsters GF (1979) Measurements in the Flow Field of a Linear Array of Rectangular Nozzles. Journal of Aircraft 17:774–780
Mi J, Nathan GJ, Nobes DS (2001) Mixing Characteristics of Axisymmetric Free Jets From a Contoured Nozzle, an Orifice Plate and a Pipe. Journal of Fluids Engineering- Transactions of the ASME 123:878–883
Mi JC, Feng BP, Deo RC, Nathan GJ (2009) Effect of exit Reynolds number on self-preservation of a plane jet. Wuli Xuebao/Acta Physica Sinica 58:7756–7764
Miller DR, Comings EW (1960) Force-momentum fields in a dual-jet flow. J Fluid Mech 7:237–256. doi:10.1017/S0022112060001468
Morel T (1975) Comprehensive design of axisymmetric wind tunnel contractions. J Fluids Eng 97:225–233
Nasr A, Lai JCS (1997) Two parallel plane jets: mean flow and effects of acoustic excitation. Exp Fluids 22:251–260. doi:10.1007/s003480050044
Nasr A, Lai JCS (2000) The effects of nozzle spacing on the development of two parallel plane jets. Int J Transp Phenom 2:57–70
Obot NT, Graska ML, Trabold TA (1984) The near field behavior of round jets at moderate Reynolds numbers. Can J Chem Eng 62:587–593. doi:10.1002/cjce.5450620503
Okamoto T, Yagita M, Watanabe A, Kawamura K (1985) Interaction of twin turbulent circular jet. Bull JSME 28:617–622
Olsson M, Fuchs L (1996) Large eddy simulation of the proximal region of a spatially developing circular jet. Phys Fluids 8:2125–2137
Pani B, Dash R (1983) Three dimensional single and multiple free jets. J Hydraul Eng 109:254–269. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1983)109:2(254
Quinn WR, Militzer J (1989) Effects of nonparallel exit flow on round turbulent free jets. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 10:139–145. doi:10.1016/0142-727x(89)90008-8
Raffel M, Willer C, Wereley S, Kompenhans J (2007) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer, Berlin
Rajaratnam N (1976) Turbulent jets. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Ricou FP, Spalding DB (1961) Measurements of entrainment by axisymmetrical turbulent jets. J Fluid Mech 11:21–32. doi:10.1017/S0022112061000834
Rieth M, Proch F, Stein OT, Pettit MWA, Kempf AM (2014) Comparison of the Sigma and Smagorinsky LES models for grid generated turbulence and a channel flow. Comput Fluids. doi:10.1016/j.compfluid.2014.04.018
Sami S, Carmody T, Rouse H (1967) Jet diffusion in the region of flow establishment. J Fluid Mech 27:231–252. doi:10.1017/S0022112067000291
Schlichting H, Gersten K (2000) Boundary-layer theory. Springer, New York
Stein O, Böhm B, Dreizler A, Kempf A (2011) Highly-resolved LES and PIV analysis of isothermal turbulent opposed jets for combustion applications. Flow Turbul Combust 87:425–447. doi:10.1007/s10494-010-9310-3
Svensson K, Rohdin P, Moshfegh B, Tummers MJ (2014) Numerical and experimental investigation of the near zone flow field in an array of confluent round jets. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 46:127–146. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2014.01.004
Tanaka E (1970) The interference of two-dimensional parallel jets: 1st report, experiments on dual jet. Bull JSME 13:272–280
Tanaka E (1974) The interference of two-dimensional parallel jets: 2nd report, experiments on the combined flow of dual jet. Bull JSME 17:920–927
Tatsumi K, Tanaka M, Woodfield PL, Nakabe K (2010) Swirl and buoyancy effects on mixing performance of baffle-plate-type miniature confined multijet. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 31:45–56. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2009.09.005
Thielen L, Jonker HJJ, Hanjalić K (2003) Symmetry breaking of flow and heat transfer in multiple impinging jets. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 24:444–453. doi:10.1016/S0142-727X(03)00042-0
Thielen L, Hanjalić K, Jonker H, Manceau R (2005) Predictions of flow and heat transfer in multiple impinging jets with an elliptic-blending second-moment closure. Int J Heat Mass Transf 48:1583–1598. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2004.10.025
Todde V, Spazzini PG, Sandberg M (2009) Experimental analysis of low-Reynolds number free jets: evolution along the jet centerline and Reynolds number effects. Exp Fluids 47:279–294
Villermaux E, Hopfinger EJ (1994) Periodically arranged co-flowing jets. J Fluid Mech 263:63–92
Vouros A, Panidis T (2008) Influence of a secondary, parallel, low Reynolds number, round jet on a turbulent axisymmetric jet. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 32:1455–1467. doi:10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2008.03.007
Yimer I, Becker HA, Grandmaison EW (1996) Development of flow from multiple-jet burners. Can J Chem Eng 74:840–851
Yin Z-q, Zhang H-j, Lin J-z (2007) Experimental study on the flow field characteristics in the mixing region of twin jets. J Hydrodyn Ser B 19:309–313
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support received from the University of Gävle (Sweden), Linköping University (Sweden), Stravent Oy (Finland), and the Swedish Research Council (Grant No. 2008-31145-61023-37). The authors are thankful for the assistance received by personnel at the laboratory of Delft University of Technology, and especially to Mr. Bart Hoek and Mr. Erwin de Beus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghahremanian, S., Svensson, K., Tummers, M.J. et al. Near-field development of a row of round jets at low Reynolds numbers. Exp Fluids 55, 1789 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1789-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-014-1789-2