Abstract
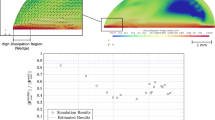
The vertical impact of single, mono disperse water droplets on a dry smooth surface was studied experimentally by means of shadowgraphy. A glass substrate was mounted on a rotating wheel to obtain high impact velocities. The droplets were generated on demand. While the Ohnesorge number was kept constant, Weber number and Reynolds number were varied by adjusting the impact velocity. In all performed experiments, splashing was observed. The distinction of the different measurement series was done by the use of the Weber number. The different Weber numbers were, 3,500, 5,000 and 10,000. Phase-locked images were taken and the temporal evolution of the impact was reconstructed by means of the nondimensional impingement time. The outcome of the measurement was analysed by digital image processing to quantify the distribution of the diameter of the resulting secondary droplets in size and time as well as their velocity, and the total deposited mass fraction remaining on the surface after the impingement. In all cases, the greater part of the impinging primary droplet remained on the substrate.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Nondimensional coefficient (1)
- d :
-
Diameter (m)
- F :
-
Force (N)
- H :
-
Falling height (m)
- m :
-
Mass (kg)
- n :
-
Natural number (1)
- R :
-
Radius of impact (m)
- R a :
-
Surface roughness (m)
- r :
-
Radial position (m)
- s :
-
Arc length (m)
- T a :
-
Approximate period of substitution (s)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- V :
-
Volume (m3)
- v :
-
Velocity (m s−1)
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates (m)
- δ :
-
Depth of field (m)
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Segment angle (rad)
- η :
-
Deposited mass fraction (1)
- \(\zeta\) :
-
Weighting factor (1)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (N s m−2)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- σ :
-
Surface tension (N m−1)
- τ k :
-
Characteristic kinematic time scale (s)
- ω :
-
Angular frequency (s−1)
- * :
-
Quantity explicitly dimensioned
- cent:
-
Centrifugal
- crit:
-
Critical
- cor:
-
Coriolis
- drag:
-
Drag
- dyn:
-
Dynamic
- D:
-
Primary droplet
- f:
-
Frontal
- g:
-
Gas, air
- I :
-
Counter of images
- imp:
-
Impact
- i, j :
-
Indices
- l:
-
Liquid
- l:
-
Lateral
- l,g:
-
Interface liquid—gas
- max:
-
Maximum
- min:
-
Minimum
- nom:
-
Nominal
- m :
-
Individual mode
- q :
-
Interval of impingement time
- r:
-
Rotational
- sub:
-
Substrate
- tot:
-
Total
- K :
-
K-parameter
- Oh :
-
Ohnesorge number
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- We :
-
Weber number
- est:
-
Estimation
- voi:
-
Volume of interest
References
Abraham FF (1970) Functional dependence of drag coefficient of a sphere on Reynolds number. Phys Fluids 13(8):2194–2195
Armster SQ, Delplanque JP, Rein M, Lavernia EJ (2002) Thermo-fluid mechanisms controlling droplet based materials processes. Int Mater Rev 47(6):265–301
Bai C, Gosman AD (1995) Development of methodology for spray impingement simulation. In: SAE International (ed) SAE 1995 World Congress, SAE International, Warrendale and Pa., pp 69–87
Bannister M (2000) Drag and dirt deposition mechanisms of external rear view mirrors and techniques used for optimisation. In: SAE International (ed) SAE 2000 World Congress. SAE International, Warrendale and Pa., pp 97–113
Driscoll MM, Nagel SR (2011) Ultrafast interference imaging of air in splashing dynamics. Phys Rev Lett 107(15):154502
Frohn A, Roth N (2000) Dynamics of droplets. Experimental fluid mechanics. Springer, Berlin
Kim KS, Kim SS (1994) Drop sizing and depth-of-field correction in tv imaging. At Sprays 4(1):65–78
Kuthada T, Widdecke N, Wiedemann J (2002) Advanced investigation methods on vehicle soiling. In: Motor Industry Research Association (ed) 4th MIRA international vehicle aerodynamics conference, Warwick
Mandre S, Mani M, Brenner MP (2009) Precursors to splashing of liquid droplets on a solid surface. Phys Rev Lett 102(13):134502
Mani M, Mandre S, Brenner MP (2010) Events before droplet splashing on a solid surface. J Fluid Mech 647:163–185
Mehdizadeh NZ, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J (2000) Splashing of a small droplet impinging on a solid surface at high velocity. In: Kim JH (ed) Proceedings of the ASME heat transfer division 2000, vol 3. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York and NY, HTD, pp 397–405
Mehdizadeh NZ, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J (2004) Formation of fingers around the edges of a drop hitting a metal plate with high velocity. J Fluid Mech 510:353–373
Mundo C (1996) Zur Sekundärzerstäubung Newtonscher Fluide an Oberflächen. PhD thesis, Universität Erlangen, Erlangen
Mundo C, Sommerfeld M, Tropea C (1994) Experimental studies of the deposition and splashing of small liquid droplets impinging on a flat surface. In: Yule AJ, Dumouchel C (eds) Proceedings of the sixth international conference on liquid atomization and spray systems, vol 1. Begell House, New York, pp 134–141
Mundo C, Sommerfeld M, Tropea C (1995) Droplet-wall collisions: experimental studies of the deformation and breakup process. Int J Multiph Flow 21(2):151–173
Palacios J, Gómez P, Zanzi C, López J, Hernández J (2010) Experimental study on the splash/deposition limit in drop impact onto solid surfaces. In: ILASS Europe (ed.) ILASS Europe 2010, BRNO
Pan KL, Tseng KC, Wang CH (2010) Breakup of a droplet at high velocity impacting a solid surface. Exp Fluids 48(1):143–156
Pasandideh-Fard M, Qiao YM, Chandra S, Mostaghimi J (1996) Capillary effects during droplet impact on a solid surface. Phys Fluids 8(3):650–659
Raffel M, Willert CE, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2007) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide ; with 42 tables, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Range K, Feuillebois F (1998) Influence of surface roughness on liquid drop impact. J Colloid Interface Sci 203(1):16–30
Rein, M (eds) (2002) Drop–surface interactions: courses and lectures, courses and lectures / International Centre for Mechanical Sciences, vol 456. Springer and Springer Wien, Wien
Rioboo R, Tropea C, Marengo M (2001) Outcomes from a drop impact on solid surfaces. At Sprays 11(2):155–166
Rioboo R, Marengo M, Tropea C (2002) Time evolution of liquid drop impact onto solid, dry surfaces. Exp Fluids 33(1):112–124
Roisman IV (2010) On the instability of a free viscous rim. J Fluid Mech 661:206–228
Roisman IV, Rioboo R, Tropea C (2002) Normal impact of a liquid drop on a dry surface: model for spreading and receding. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 458(2022):1411–1430
Szilder K, Mcilwain S, Lozowski E (2006) Numerical simulation of complex ice shapes on swept wings. In: German Society for Aeronautics and Astronautics (DGLR) (ed) ICAS 2006 proceedings
Thoroddsen ST, Sakakibara J (1998) Evolution of the fingering pattern of an impacting drop. Phys Fluids 10(6):1359–1374
Thoroddsen ST, Thoraval MJ, Takehara K, Etoh TG (2011) Droplet splashing by a slingshot mechanism. Phys Rev Lett 106(3):034501
Ulbrich CW (1983) Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J Clim Appl Meteorol 22(10):1764–1775
Vander Wal RL, Berger G, Mozes S (2006) The splash/non-splash boundary upon a dry surface and thin fluid film. Exp Fluids 40(1):53–59
Weiss DA (1993) Periodischer aufprall monodisperser tropfen gleicher geschwindigkeit auf feste oberflächen. PhD thesis, Universität Göttingen, Göttingen
Willis PT, Tattelman P (1989) Drop-size distributions associated with intense rainfall. J Appl Meteorol 28(1):3–15
Worthington AM (1908) A study of splashes. Longmans, Green & Co., London [u.a.]
Wright WB, Potapczuk (2005) Semi-empirical modeling of SLD physics. NASA/TM-2004-212916
Xu L, Zhang WW, Nagel SR (2005) Drop splashing on a dry smooth surface. Phys Rev Lett 94(18):184505
Yarin AL (2006) Drop impact dynamics: splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing.... Annu Rev Fluid Mech 38(1):159–192
Yarin AL, Weiss DA (1995) Impact of drops on solid surfaces: self-similar capillary waves, and splashing as a new type of kinematic discontinuity. J Fluid Mech 283(1):141–173
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Cameron Tropea for his discerning annotation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faßmann, B.W., Bansmer, S.E., Möller, T.J. et al. High velocity impingement of single droplets on a dry smooth surface. Exp Fluids 54, 1516 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-013-1516-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-013-1516-4