Abstract
Purpose
To update a prior report on web-based networks and frequently visited forums used by patients affected by synthetic mesh and/or tape (SMT) complications and to present the new developments in this dynamic SMT field following recent FDA notifications.
Methods
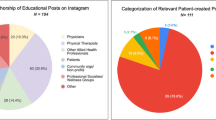
A review of available blogs and forums on SMT complications was conducted using the terms “mesh complications”, “mesh blogs”, and “polypropylene mesh removal” in Internet search engines for the United States and several other countries. Forums from a prior report were analyzed for updates, and new forums with their founders were identified using same search methodology. The number of posts and new fields from 07/2011 to 10/2013 was recorded, and then divided into categories based on broad content (personal stories, supportive replies to complaints, patients recommending physicians, legal stories, newspaper/article stories with reactions, other).
Results
Although four social networks became inactive, four expanded and at least five new major ones surfaced. While personal stories and support remained a prominent topic of discussion, other categories increased, such as the number of posts discussing physician referrals and reactions to news stories. Additionally, the number of posts designated to personal stories decreased. Finally, discussion about the topic expanded internationally.
Conclusion
Web-based social networks for women suffering from SMT have expanded and the contents have broadened with new domains being introduced. Patient networking remains a dynamic force in the current debate on the future of these procedures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee D, Dillon B, Lemack G, Gomelsky A, Zimmern P (2013) Transvaginal mesh kits–how “serious” are the complications and are they reversible? Urology 81(1):43–48. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2012.07.098
Yanagisawa M, Rhodes M, Zimmern P (2011) Mesh social networking: a patient-driven process. BJU Int 108(10):1539–1541. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10645.x
Truthinmedicine-lor.blogspot.com. Accessed 11 Jan 2013
www.truthinmedicine.org. http://www.truthinmedicine.org. Accessed 11 Jan 2013
Theladyisachamp.blogspot.com. Theladyisachamp.blogspot.com Accessed 11 Jan 2013
Bladderslingsurgerymystory.blogspot.com. Bladderslingsurgerymystory.blogspot.com. Accessed 11 Jan 2013
www.aboutlawsuits.com. www.aboutlawsuits.com. Accessed 16 Dec 2013
www.topix.com. www.topix.com. Accessed 15 Jan 2014
www.healthcentral.com. www.healthcentral.com. Accessed 14 Jan 2014
www.hystersisters.com. www.hystersisters.com. Accessed 15 Jan 2014
www.tvt-messed-u-mesh.org.uk (tvt mum). www.tvt-messed-up-mesh.org.uk. Accessed 3 Jan 2014
www.tvtno.org. www.tvtno.org. Accessed 3 Jan 2014
Alas A, Sajadi KP, Goldman HB, Anger JT (2013) The rapidly increasing usefulness of social media in urogynecology. Female pelvic med reconstr surg 19(4):210–213. doi:10.1097/SPV.0b013e3182909872
Konety BR (2013) Physicians, internet and the vox populi. J Urol 190(4):1157–1158. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.07.014
http://www.tvtinfo.wordpress.com. Accessed 1 Mar 2014
Conflict of interest
Authors have no disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephens, C., Zimmern, P.E. Expansion of the role of web-based social networks related to synthetic mesh/tape complications. World J Urol 33, 999–1004 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1364-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-014-1364-8