Abstract
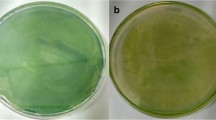
In the present study, a microcosm test was used to explore the effects of the zoobenthos on macrophyte allelopathy. Four representative zoobenthos showed low algal inhibition ranging within 0.05–0.16 in separate co-culture. When zoobenthos and tested microalgae were mixed completely, the inhibition rate was enhanced by 0.68. The inhibition potential followed the order: Corbicula fluminea > Palaemonetes sinensis > Chironomus plumosus > Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri. Furthermore, the benthic fauna significantly enhanced algal inhibition of the emergent plant Typha angustifolia and the submerged plant Potamogeton crispus by 0.43 and 0.32, respectively. Meanwhile, there was a significant difference in algal inhibition between five growth phases of macrophytes combined with zoobenthos community. In addition, a significant positive relationship occurred between the algal inhibition of allelopathic macrophytes and the mean individual biomass of the zoobenthos. Through the determination of physiological and biochemical traits of macrophytes, it was concluded that the zoobenthos would be a significant disturbance factor and induce strong stress-resistance response in macrophytes. Subsequently, the specific response will facilitate the algal inhibition of allelopathic macrophytes. Therefore, to keep a reasonable biodiversity will fully display strong function of the aquatic ecosystem and efficiently control harmful algal bloom.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazzanti M, Coccia C, Dowgiallo MG (2010) Microdistribution of macroinvertebrates in a temporary pond of Central Italy: taxonomic and functional analyses. Limnologica 40:291–299
Beaulieu SE, Sengco MR, Anderson DM (2005) Using clay to control harmful algal blooms: deposition and resuspension of clay/algal flocs. Harmful Algae 4:123–138
Boyd CE (2005) Copper treatments control phytoplankton. Glob Aquacul Advo 8:69–70
Bozic M, Nikolic G, Rudic Z, Raicevic V, Lalevic B (2013) Constructed wetlands as an alternative restoration measure for shallow lakes. Water Sci Technol 68:1672–1678
Calbet A, Vaque D, Felipe J, Vila M, Sala MM, Alcaraz M, Estrada M (2003) Relative grazing impact of microzooplankton and mesozooplankton on a bloom of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Mar Eco Prog Ser 259:303–309
Cao QJ, Wang D (2012) Fragment growth of rooted and rootless submerged aquatic macrophytes: effects of burial modes and decapitation of shoot apex. J Freshwater Ecol 27:315–324
Chen J, Zhang H, Han Z, Ye J, Liu Z (2012) The influence of aquatic macrophytes on Microcystis aeruginosa growth. Ecol Eng 42:130–133
Dermott R, Bonnell R (2010) Benthic fauna in Hamilton Harbour and adjacent Lake Ontario 2002–2005 in comparison to 1964. Aquat Ecosyst Health 13:413–428
Devlin SP, Vander Zanden MJ, Vadeboncoeur Y (2013) Depth-specific variation in carbon isotopes demonstrates resource partitioning among the littoral zoobenthos. Freshwater Biol 58:2389–2400
Draper HH, Squires EJ, Mahmoodi H, Wu J, Agarwal S, Hadley M (1993) A comparative evaluation of thiobarbituric acid methods for the determination of malondialdehyde in biological materials. Free Radic Biol Med 15:353–363
Gross EM (2003) Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:313–339
Harman WN, Hingula LP, Macnamara CE (2005) Does Long-Term Macrophyte Management in Lakes Affect Biotic Richness and Diversity? J Aquat Plant Manage 43:57–64
Hodgkiss JI, Lu S (2004) The effects of nutrients and their ratios on phytoplankton abundance in Junk Bay, Hong Kong. Hydrobiologia 512:215–229
Hu MM, Zhou HD, Wang YC, Wang YC, Wang Z, Wu WJ, Zhao GF, Cheng Y, Liu YD (2014) Ecological characteristics of plankton and aquatic vegetation in Lake Qiluhu. Water Sci Technol 69:1620–1625
Karlson AML, Mozūraitis R (2011) Deposit-feeders accumulate the cyanobacterial toxin nodularin. Harmful Algae 12:77–81
Karlson AML, Nascimento FJA, Suikkanen S, Elmgren R (2012) Benthic fauna affects recruitment from sediments of the harmful cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Harmful Algae 20:126–131
Li FM, Hu HY (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel antialgal allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Appl Environ Microb 71:6545–6553
Li P, Song Y, Yu S (2014) Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa using hydrodynamic cavitation: performance and mechanisms. Water Res 62:241–248
Liu Y, Xie P, Wu XP (2009) Grazing on toxic and non-toxic Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7820 by Unio douglasiae and Corbicula fluminea. Limnology 10:1–5
Lürling M, van Geest G, Scheffer M (2006) Importance of nutrient competition and allelopathic effects in suppression of the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus by the macrophytes Chara, Elodeaand, Myriophyllum. Hydrobiologia 556:209–220
Mermillod-Blondin F, Poggiale JC, Tolla C, Auger P, Thuiller W, des Chatelliers MC (2008) Using a mathematical model to simulate the influence of tubificid worms (Oligochaeta) on oxygen concentrations in hyporheic sediments. Fund Appl Limnol 172:135–145
Nakai S, Inoue Y, Hosomi M, Murakami A (1999) Growth inhibition of blue-green algae by allelopathic effects of macrophytes. Water Sci Technol 39:47–53
Nakai S, Zou G, Okuda T, Nishijima W, Hosomi M, Okada M (2012) Polyphenols and fatty acids responsible for anti-cyanobacterial allelopathic effects of submerged macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum. Water Sci Technol 66:993–999
Nemoto F, Fukuhara H (2012) The antagonistic relationship between chlorophyll a concentrations and the growth areas of Trapa during summer in a shallow eutrophic lake. Limnology 13:289–299
Nordhaus I, Salewski T, Jennerjahn TC (2011) Food preferences of mangrove crabs related to leaf nitrogen compounds in the Segara Anakan Lagoon, Java, Indonesia. J Sea Res 65:414–426
Pakdel FM, Sim L, Beardall J, Davis J (2013) Allelopathic inhibition of microalgae by the freshwater stonewort, Chara australis, and a submerged angiosperm, Potamogeton crispus. Aquat Bot 110:24–30
Penha-Lopes G, Flindt MR, Ommen B, Kristensen E, Garret P, Paula J (2012) Organic carbon dynamics in a constructed mangrove wastewater wetland populated with benthic fauna: a modelling approach. Ecol Model 232:97–108
Rajasekhar P, Fan L, Nguyen T, Roddick FA (2012) A review of the use of sonication to control cyanobacterial blooms. Water Res 46:4319–4329
Ristau K, Faupel M, Traunspurger W (2012) The effects of nutrient enrichment on a freshwater meiofaunal assemblage. Freshwater Biol 57:824–834
Shang J, Liao Q, Zhang L, Fan C (2014) The influence of different benthic fauna on inorganic nitrogen flux and denitrification in a large shallow hyper-eutrophic lake. Fund Appl Limnol 184:101–108
Takamura N, Ito T, Ueno R, Ohtaka A, Wakana I, Nakagawa M, Ueno Y, Nakajima H (2009) Environmental gradients determining the distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in Lake Takkobu, Kushiro wetland, Northern Japan. Ecol Res 24:371–381
Wang HQ, Zhu HJ, Zhang LY, Xue WJ, Yuan B (2014) Identification of antialgal compounds from the aquatic plant Elodea nuttallii. Allelopathy J 34:207–213
Wu Z, Deng P, Wu X, Luo S, Gao Y (2007) Allelopathic effects of the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton malaianus on Scenedesmus obliquus. Hydrobiologia 592:465–474
Wu H, Liu X, You L, Zhang L, Zhou D, Feng J, Zhao J, Yu J (2012) Effects of salinity on metabolic profiles, gene expressions, and antioxidant enzymes in halophyte Suaeda salsa. J Plant Growth Regul 31:332–341
Ye L, Qian J, Jin S, Zuo SP, Mei H, Ma SM (2014) Algicidal effects of four Chinese herb extracts on bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Environ Technol 35:1150–1156
Yongvanich T, Juntarajumnong W, Nakapong S, Chulalaksananukul W (2002) Allelopathic effect of flavonoids from Typha angustifolia on seed growth of Mimosa pigra. Thai J Agr Sci 35:361–367
Zuo SP, Wan K, Ying L, Ma SM, Mei H (2013) Effects of environmental pollution on algal suppression of Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb: field and laboratory observations. Allelopathy J 32:149–156
Zuo SP, Ye LT, Wan K, Ma SM (2014) Combined allelopathic potential of aquatic plants species to control algae. Allelopathy J 34:315–323
Zuo SP, Wan K, Ma SM (2015) Combined effect of predatory zooplankton and allelopathic aquatic macrophytes on algal suppression. Environ Technol 36:54–59
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Q. Q. Ni for his useful comments and language editing, which have improved the manuscript greatly. Professor Y. L. Xi provided valuable assistance by identifying the zoobenthos types and the aquatic macrophyte. This study was supported by National Natural Science Fund of China (30900186), Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province of China for Universities (KJ2015A122), Anhui Province and Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of the People’s Republic of China (MOHRSS) for studying abroad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, S., Fang, Z., Zhou, S. et al. Benthic Fauna Promote Algicidal Effect of Allelopathic Macrophytes on Microcystis aeruginosa . J Plant Growth Regul 35, 646–654 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9566-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9566-x