Abstract
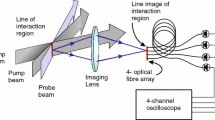
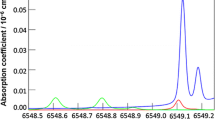
We have studied the effects of random laser speckle and self-mixing interference on TDLS based gas measurements made using integrating spheres. Details of the theory and TDLS apparatus are given in Part 1 of this paper and applied here to integrating spheres. Experiments have been performed using two commercial integrating spheres with diameters of 50 mm and 100 mm for the detection of methane at 1651 nm. We have calculated the expected levels of laser speckle related uncertainty, considered to be the fundamental limiting noise, and imaged subjective laser speckle in a sphere using different sized apertures. For wavelength modulation spectroscopy, noise equivalent absorbances (NEAs) of around 5×10−5 were demonstrated in both cases, corresponding to limits of detection of 1.2 ppm methane and 0.4 ppm methane respectively. Longer-term drift was found to be at an NEA of 4×10−4. This lies within our broad range of expectations. For a direct spectral scan with no wavelength dither, a limit of detection of 75 ppm or fractional measured power uncertainty of 3×10−3 corresponded well with our prediction for the objective speckle uncertainty.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.U. White, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 32, 285 (1942)
D.R. Herriott, H. Kogelnik, R. Kompfner, Appl. Opt. 3, 523 (1964)
S.M. Chernin, E.G. Barskaya, Appl. Opt. 30(1), 51 (1991)
Toptica GmbH, Product specification. Compact Herriott cell for absorption spectroscopy: CMP-30. Available at www.toptica.com (2009)
R. Engeln, G. Berden, R. Peeters, G. Meijer, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 69, 3763 (1998)
A. O’Keefe, D.A.G. Deacon, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59, 2544 (1988)
A.G. Berezin, S.M. Chernin, D.B. Stavrovskii, in Proc. 7th International Conference on Tunable Diode Laser Spectroscopy—TDLS09, Paper E2 (2009)
H.I. Schiff, G.I. Mackay, J. Bechara, in Air Monitoring by Spectroscopic Techniques, ed. by M.W. Sigrist (Wiley, New York, 1994). Chapter 5
Labsphere Inc. A Guide to Integrating Sphere Theory and Applications (Labsphere, North Sutton, 1998)
P. Elterman, Appl. Opt. 9(9), 2140 (1970)
L.M. Hanssen, K.A. Snail, in Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy, vol. 2, ed. by J.M. Chalmers, P.R. Griffiths (Wiley, Chichester, 2002), p. 1175
E.S. Fry, G.W. Kattawar, R.M. Pope, Appl. Opt. 31(12), 2055 (1992)
I. Fecht, M. Johnson, Meas. Sci. Technol. 10, 612 (1999)
J. Hodgkinson, M. Johnson, J.P. Dakin, Appl. Opt. 44, 4360 (2005)
E. Hawe, P. Chambers, C. Fitzpatrick, E. Lewis, Meas. Sci. Technol. 18, 3187 (2007)
E. Hawe, C. Fitzpatrick, P. Chambers, G. Dooly, E. Lewis, Sensor. Actuat. A 141, 414 (2008)
C.G. Venkatesh, R.S. Eng, A.W. Mantz, Appl. Opt. 19(10), 1704 (1980)
R.M. Abdullin, A.V. Lebedev, Sov. J. Opt. Technol. 55(3), 139 (1988)
S. Tranchart, I.H. Bachir, J.-L. Destombes, Appl. Opt. 35(36), 7070 (1996)
D. Masiyano, J. Hodgkinson, R.P. Tatam, Appl. Phys. B 90, 279 (2008)
J. Hodgkinson, D. Masiyano, R.P. Tatam, Appl. Opt. 48(30), 5748 (2009)
A. Bozeit, J. Burke, H. Helmers, H. Sagehorn, R. Schuh, Opt. Laser Technol. 30, 325 (1998)
D. Masiyano, J. Hodgkinson, S. Schilt, R.P. Tatam, Appl. Phys. B 96(4), 863 (2009)
P. Werle, R. Mücke, F. Slemr, Appl. Phys. B 57, 131 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masiyano, D., Hodgkinson, J. & Tatam, R.P. Gas cells for tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy employing optical diffusers. Part 2: Integrating spheres. Appl. Phys. B 100, 303–312 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-010-4021-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-010-4021-y