Abstract.
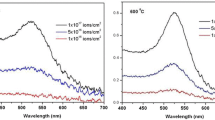
In order to resolve problems concerning the understanding and the control of laser-induced damage of silica optical elements, a collaboration between the CEA and different university laboratories has been undertaken. Ultra-pure silica model samples, seeded with gold nanoparticles whose diameter did not exceed 5 nm, were prepared. The aim in using these samples was to observe the mechanism of damage initiation that could be attributed to inclusions of nanometric size. This paper presents the different steps encountered during this study: preparation of the samples, the laser-induced damage tests, the Nomarski and atomic-force microscope observations of this damage and a series of experiments using a time-of-flight mass spectrometer at Argonne National Laboratory. The experimental data are then interpreted, and, in particular, compared to numerical simulations. A very encouraging result is the existence of a pre-damage phase at very low fluences that is not detectable by classical optical devices. The experimental means developed for such model samples should be transposable to the analysis of industrial glasses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 July 2002 / Revised version: 23 September 2002 / Published online: 11 December 2002
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. Fax: +33-1/6926-7106, E-mail: florian.bonneau@cea.fr
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonneau, F., Combis, P., Rullier, J. et al. Study of UV laser interaction with gold nanoparticles embedded in silica . Appl Phys B 75, 803–815 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-1049-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-1049-7