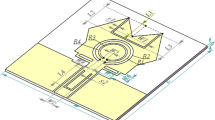
Abstract
Printed circuit board (PCB) fabrication technology has been widely used in metasurfaces in microwave domain. However, such technology still needs a non-negligible fabricating period and cost. To further explore the ultra-low-cost, convenient processing and fast demonstrating method, we present a metasurface using silver ink to produce the digital patterns for abundant scattering field manipulation. By directly painting the conductive ink on the paper to establish the specific metal structure, arbitrary EM properties can be designed, which could be regarded as a manually convenient PCB technology for metasurface fabrication. We design eight coding sequences to, respectively, generate single- and dual beam fields with different scattering angles. Simulations and measurements show good agreements, verifying the feasibility of our design method. We believe the presented metasurface processing method will promote the interests on flexible metasurface design and further stimulate related domain like wireless communication.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Alu, Mantle cloak: invisibility induced by a surface Phys. Rev. B 80(24), (2009). doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.245115 (Art no. 245115)
Q. Ma, Z.L. Mei, S.K. Zhu, T.Y. Jin, T.J. Cui, Experiments on active cloaking and illusion for Laplace equation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(17) (2013). doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.173901 (Art no. 173901)
X. Ni, Z.J. Wong, M. Mrejen, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, An ultrathin invisibility skin cloak for visible light. Science 349(6254), 1310–1314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac9411
Q. Ma, F. Yang, T.Y. Jin, Z.L. Mei, T.J. Cui, "Open active cloaking and illusion devices for the Laplace equation. J. Opt. 18(4), 044004 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/18/4/044004
N. Fang, H. Lee, C. Sun, X. Zhang, Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 308(5721), 534–537 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1108759
Q. Ma, C.B. Shi, T.Y. Chen, M.Q. Qi, Y.B. Li, T.J. Cui, Broadband metamaterial lens antennas with special properties by controlling both refractive-index distribution and feed directivity. J. Opt. 20(4), 045101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8986/aaacbf
X. Zou et al., Imaging based on metalenses. PhotoniX 1(1), 2 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43074-020-00007-9.
D. Wang, C. Liu, C. Shen, Y. Xing, Q.-H. Wang, Holographic capture and projection system of real object based on tunable zoom lens. PhotoniX 1(1), 6 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43074-020-0004-3.
X. Ding et al., Metasurface holographic image projection based on mathematical properties of Fourier transform. PhotoniX 1(1),16 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43074-020-00016-8.
Q. Ma, C.B. Shi, G.D. Bai, T.Y. Chen, A. Noor, T.J. Cui, Beam-editing coding metasurfaces based on polarization bit and orbital-angular-momentum-mode bit. Adv. Opt. Mater. 5(23). doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201700548 (Art no. 1700548)
X. Yin, Z. Ye, J. Rho, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, Photonic spin Hall effect at metasurfaces. Science 339(6), 1405–1407, 2013. Available: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/sci/339/6126/1405.full.pdf
T.J. Cui, M.Q. Qi, X. Wan, J. Zhao, Q. Cheng, Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials. Light Sci. Appl. 3(10), e218 (2014). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2014.99 (Art no. e218)
Q. Ma, T.J. Cui, Information metamaterials: bridging the physical world and digital world. PhotoniX 1(1), 1–32 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43074-020-00006-w
T.J. Cui et al., Information metamaterial systems. Iscience 23(8), 101403 (2020)
L. Chen, Q. Ma, H.B. Jing, H.Y. Cui, Y. Liu, T.J. Cui, Space-energy digital-coding metasurface based on an active amplifier. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11(5), 6 (2019). doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.11.054051 (Art no. 054051)
Q. Ma et al., Editing arbitrarily linear polarizations using programmable metasurface. Phys. Rev. Appl. 13(2), 021003 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.13.021003
L. Chen et al., Dual-polarization programmable metasurface modulator for near-field information encoding and transmission. Photonics Res. 9(2) (2021). doi: https://doi.org/10.1364/prj.412052.
Y. Shuang, H. Zhao, W. Ji, T.J. Cui, L. Li, Programmable high-order OAM-carrying beams for direct-modulation wireless communications. IEEE J. Emerg. Selected Topics Circ. Syst. 10(1), 29–37 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/jetcas.2020.2973391
Q. Ma et al., Controllable and programmable nonreciprocity based on detachable digital coding metasurface. Adv. Opt. Mater. 7(24), 1901285 (2019). doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201901285
Q. Ma, G.D. Bai, H.B. Jing, C. Yang, L. Li, T.J. Cui, Smart metasurface with self-adaptively reprogrammable functions. Light Sci. Appl. 8(1), 98 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-019-0205-3
Q. Ma et al., Smart sensing metasurface with self-defined functions in dual polarizations. Nanophotonics 9(10), 3271–3278 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2020-0052
A. Grbic, G.V. Eleftheriades, Overcoming the diffraction limit with a planar left-handed transmission-line lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(11) (2004). doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.117403 (Art no. 117403)
D. Schurig et al., Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 314(5801), 977–980 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1133628
R.A. Shelby, D.R. Smith, S. Schultz, Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction. Science 292(5514), 77–79 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1058847
O. R. Bilal et al., A flexible spiraling-metasurface as a versatile haptic interface. Adv. Mater. Technol. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202000181 (Art no. 2000181)
C.-Y. Chang et al., Flexible localized surface plasmon resonance sensor with metal-insulator-metal nanodisks on PDMS substrate. Sci. Rep. 8 (2018). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30180-8 (Art no. 11812)
S. Chejarla, S.R. Thummaluru, R.K. Chaudhary, Flexible metamaterial absorber with wide incident angle insensitivity for conformal applications. Electron. Lett. 55(3), 133–134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2018.7501
J. Sidén, M.K. Fein, A. Koptyug, H.E. Nilsson, Printed antennas with variable conductive ink layer thickness. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 1(2) (2007), doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map:20060021.
A. Rida, Y. Li, R. Vyas, M.M. Tentzeris, Conductive inkjet-printed antennas on flexible low-cost paper-based substrates for RFID and WSN applications. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 51(3), 13–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/map.2009.5251188
A.M. Mansour, N. Shehata, B.M. Hamza, M.R.M. Rizk, Efficient design of flexible and low cost paper-based inkjet-printed antenna. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2015, 1–6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/845042
Y. Lee, C.H. Kim, D.Y. Shin, Y.G. Kim, Printed UHF RFID antennas with high efficiencies using nano-particle silver ink. J Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(7), 6425–6428 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.4390
H. Koga, T. Inui, I. Miyamoto, T. Sekiguchi, M. Nogi, K. Suganuma, A high-sensitivity printed antenna prepared by rapid low-temperature sintering of silver ink. RSC Adv. 6(87), 84363–84368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra19687j
R. Zichner, R.R. Baumann, Printed antennas: from theory to praxis, challenges and applications. Adv. Radio Sci. 11, 271–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5194/ars-11-271-2013
H.K. Kim, D. Lee, S. Lim, A fluidically tunable metasurface absorber for flexible large-scale wireless ethanol sensor applications. Sensors (Basel) 16(8) (2016) doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081246
S. Jun et al., Circular polarised antenna fabricated with low-cost 3D and inkjet printing equipment. Electron. Lett. 53(6), 370–371 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2016.4605
E. Li, XJ. Li, B.-C. Seet, X. Lin, Ink-printed flexible wideband dipole array antenna for 5G applications. Phys. Commun. 43 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101193
W.G. Whittow et al., Inkjet-printed microstrip patch antennas realized on textile for wearable applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13, 71–74 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2013.2295942
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.62001232, 11404207), Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. BK20180457), SHIEP Foundation K2014-054 and Z2015-086, the Local Colleges and Universities Capacity Building Program of the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee, China (Grant Nos. 15110500900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Luo, S.S., Ye, F.J. et al. Flexible painted metasurface using conductive silver ink for scattering fields digital manipulation. Appl. Phys. A 127, 666 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04800-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04800-6