Abstract
Actinobacillus (A.) pleuropneumoniae is among the most important pathogens in pig. The agent causes severe economic losses due to decreased performance, the occurrence of acute or chronic pleuropneumonia, and an increase in death incidence. Since therapeutics cannot be used in a sustainable manner, and vaccination is not always available, new prophylactic measures are urgently needed. Recent research has provided evidence for a genetic predisposition in susceptibility to A. pleuropneumoniae in a Hampshire × German Landrace F2 family with 170 animals. The aim of the present study is to characterize the expression response in this family in order to unravel resistance and susceptibility mechanisms and to prioritize candidate genes for future fine mapping approaches. F2 pigs differed distinctly in clinical, pathological, and microbiological parameters after challenge with A. pleuropneumoniae. We monitored genome-wide gene expression from the 50 most and 50 least susceptible F2 pigs and identified 171 genes differentially expressed between these extreme phenotypes. We combined expression QTL analyses with network analyses and functional characterization using gene set enrichment analysis and identified a functional hotspot on SSC13, including 55 eQTL. The integration of the different results provides a resource for candidate prioritization for fine mapping strategies, such as TF, TFRC, RUNX1, TCN1, HP, CD14, among others.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auld KL, Berasi SP, Liu Y, Cain M, Zhang Y, Huard C, Fukayama S, Zhang J, Choe S, Zhong W, Bhat BM, Bhat RA, Brown EL, Martinez RV (2012) Estrogen-related receptor α regulates osteoblast differentiation via Wnt/β-catenin signalling. J Mol Endocrinol 48:177–191
Baltes N, Topitak W, Gerlach GF, Hennig-Pauka I, Hoffmann-Moujahid M, Ganter M, Rothkotter HJ (2001) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae iron transport and urease activity: effects on bacterial virulence and host immune response. Infect Immun 69:472–478
Baltes N, Hennig-Pauka I, Jacobsen I, Gruber AD, Gerlach GF (2003a) Identification of dimethyl sulfoxide reductase in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and its role in infection. Infect Immun 71:6784–6792
Baltes N, Tonpitak W, Hennig-Pauka I, Gruber AD, Gerlach GF (2003b) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 7 siderophore receptor FhuA is not required for virulence. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220:41–48
Beisser D, Klau GW, Dandekar T, Müller T, Dittrich MT (2010) BioNet: an R-package for the functional analysis of biological networks. Bioinformatics 26:1129–1130
Benga L, Hoeltig D, Rehm T, Rothkoetter HJ, Pabst R, Valentin-Weigand P, the FUGATO consortium IRAS (2009) Expression levels of immune markers in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infected pigs and their relation to breed and clinical symptoms. BMC Vet Res 5:13
Bishop SC, Axford RFE, Nicholas FW, Owen JB (2010) Breeding for disease resistance in farm animals, 3rd edn. CAB International, Wallingford
Bossé JT, Jansona H, Sheehana BJ, Beddekb AJ, Rycroftb AN, Krolla JS, Langford PR (2002) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae: pathobiology and pathogenesis of infection. Microbes Infect 4:225–235
Bray PJ, Cotton RGH (2003) Variations of the human glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1): pathological and in vitro mutations and polymorphisms. Hum Mutat 21:557–568
Casanova JL, Holland SM, Notarangelo LD (2012) Inborn errors of human JAKs and STATs. Immunity 36:515–528
Chiers K, De Waele T, Pasmans F, Ducatelle R, Hasebrouck F (2010) Virulence factors of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae involved in colonization, persistence and induction of lesions in its porcine host. Vet Res 41:65
Cho JY, Akbarali Y, Zerbini LF, Gu Z, Boltax J, Wang Y, Oettgen P, Zhang DE, Libermann TA (2004) Isoforms of the Ets transcription factor NERF/ELF-2 physically interact with AML1 and mediate opposing effects on AML1-mediated transcription of the B cell-specific blk gene. J Biol Chem 279:19512–19522
Cho WS, Jung K, Kim J, Ha Y, Chae C (2005) Expression of mRNA encoding Interleukin (IL)-10, IL-12p35 and IL-12p40 in lungs from pigs experimentally infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Vet Res Commun 29:111–122
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mA. pleuropneumoniaeing. Genetics 138:963–971
Cleveland-Nielsen A, Nielsen EO, Ersbol AK (2002) Chronic pleuritis in Danish slaughter pig herds. Prev Vet Med 55:121–135
Cooley J, McDonald B, Accurso FJ, Crouch EC, Remold-O’Donnel E (2008) Patterns of neutrophile serine proteases-dependent cleavage of surfactant protein D in inflammatory lung disease. J Leukoc Biol 83:946–955
Danilowicz E, Martinez-Arias R, Dolf G, Singh M, Probst I, Tümmler B, Höltig D, Waldmann KH, Gerlach GF, Stanke F, Leeb T, the IRAS consortium (2009) Characterization of the porcine transferrin gene (TF) and its association with disease severity following an experimental Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection. Anim Genet 41:424–427
De Bruijn M, Speck NA (2004) Core-binding factors in hematopoiesis and immune function. Oncogene 23:4238–4248
De Pooter RF, Kee BL (2010) E proteins and the regulation of early lymphocyte development. Immunol Rev 238:93–109
Dos Santos MM, Grond-Ginsbach C, Aksay SS, Chen B, Tchatchou S, Wolff NI, Van der Knaap MS, Grau AJ (2012) Adult-onset autosomal dominant leukodystrophy due to LMNB1 gene duplication. J Neurol 259:579–581
Dreyfuß A, Schaller A, Nivollet S, Segers RPAM, Kobisch M, Mieli L, Soerensen V, Hussy D, Miserez R, Zimmermann W, Inderbitzin F, Frey J (2004) Use of recombinant ApxIV in serodiagnosis of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infections, development and prevalidation of the Apx IV Elisa. Vet Microbiol 99:227–238
Dziegielewska KM, Andersen NA, Saunders NR (1998) Modification of macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by fetuin. Immunol Lett 60:31–35
Ertan P, Berdeli A, Yilmaz O, Gonulal DA, Yuksel H (2010) LY96, UPKIB mutations and TLR4, CD14, MBL polymorphisms in children with urinary tract infection. Indian J Pediatr 78:1229–1233
Fenwick B, Henry S (1994) Porcine pleuropneumonia. J Am Vet Med Assoc 204:1334–1340
Gottschalk M (2012) Actinobacillosis. In: Zimmermann JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ, Stevenson GW (eds) Diseases of swine. Wiley Blackwell, West Sussex, pp 653–669
Gottschalk M, Taylor DJ (2006) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. In: Straw BE, Zimmermann JJ, D’Allaire S, Taylor DJ (eds) Diseases of swine. Blackwell Publishing, Ames, pp 563–576
Green P, Falls K, Crooks S (1990) Documentation for CRI-MAP, version 2.4. Washington University, School of Medicine, St. Louis
Gregersen VR, Sørensen KK, Christensen OF, Busch ME, Vingborg RKK, Velander IH, Lund MS, Bendixen C (2010) Identification of QTL for dorso-caudal chronic pleuritis in 12 crossbred porcine families. Anim Genet 41:509–514
Gutiérrez-Martín CB, García Del Blanco N, Blanco M, Navas J, Rodríguez-Ferri EF (2006) Changes in antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae isolated from pigs in Spain during the last decade. Vet Microbiol 115:218–222
Haesebrouck F, Chiers K, Van Overbeke I, Ducatelle R (1997) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infections in pigs: the role of virulence factors in pathogenesis and protection. Vet Microbiol 58:49–239
Haley CS, Knott SA, Elsen JM (1994) MA. pleuropneumoniaeing quantitative trait loci in crosses between outbred lines using least squares. Genetics 136:1195–1207
Hannan PC, Bhogal BS, Fish JP (1982) Tylosin tartrate and tiamutilin effects on experimental piglet pneumonia induced with pig lung homogenate containing mycoplasmas, bacteria and viruses. Res Vet Sci 33:76–88
Hedegaard J, Skovgaard K, Mortensen S, Sørensen P, Jensen TK et al (2007) Molecular characterisation of the early response in pigs to experimental infection with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae using cDNA microarrays. Acta Vet Scand 49:11
Higgins R, Lariviere S, Mittal KR, Martineau GP, Rousseau P, Cameron J (1985) Evaluation of a killed vaccine against porcine pleuropneumoniae due to Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can Vet J 26:86–89
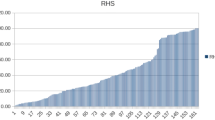
Hoeltig D, Hennig-Pauka I, Thies K, Rehm T, Beyerbach M, Strutzberg-Minder K, Gerlach GF, Waldmann KH, FUGATO-consortium IRAS (2009) A novel respiratory health score (RHS) supports a role of acute lung damage and pig breed in the course of an Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection. BMC Vet Res 5:14
Inge-Vechtomov S, Zhouravleva G, Philippe M (2003) Eukaryotic release factors (eRFs) history. Biol Cell 95:195–209
Jacobsen MJ, Nielsen JP (1995) Development and evaluation of a selective and indicative medium for isolation of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Vet Microbiol 47:191–197
Jacobsen MJ, Nielsen JP, Nielsen R (1996) Comparison of virulence of different Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotypes and biotypes using an aerosol infection model. Vet Microbiol 49:159–168
Jacobsen I, Hennig-Pauka I, Baltes N, Trost M, Gerlach GF (2005) Enzymes involved in anaerobic respiration appear to play a role in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae virulence. Infect Immun 73:226–234
Jirawattanapong P, Stockhofe-Zurwieden N, van Leengoed L, Wisselink H, Raymakers R, Cruijsen T, van der Peet-Schwering C, Nielen M, van Nes A (2008) Pleuritis in slaughter pigs: relations between lung lesions and bacteriology in 10 herds with high pleuritis. Res Vet Sci 88:11–15
Johnston J, Yang-Feng T, Berliner N (1992) Genomic structure and mapping of the chromosomal gene for transcobalamin I (TCNI): comparison to human intrinsic factor. Genomics 12:459–464
Kahlisch D, Büttner FFR, Naim HY, Gerlach GF, the IRAS consortium (2009) Glycoprotein analysis of porcine bronchoalveolar lavage fluid reveals potential biomarkers corresponding to resistance to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection. Vet Res 40:60
Kamburov A, Pentchev K, Galicka H, Wierling C, Lehrach H, Herwig R (2011) ConsensusPathDB: toward a more complete picture of cell biology. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Database issue):D712–D717
Krysiak K, Chen TH, Tibbitts J, Martin MG, Walter MJ (2011) B-cell progenitors are reduced in Hspa9 haploinsufficient mice. Blood 118:1636
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9:559
Leiner G, Franz B, Strutzberg K, Gerlach GF (1999) A novel enzymelinked immunosorbent assay using the recombinant Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ApxII antigen for diagnosis of pleuropneumonia in pig herds. Clinic Diagn Lab Immunol 6:630–632
Linhart C, Halperin Y, Shamir R (2008) Transcription factor and microRNA motif discovery: the Amadeus platform and a compendium of metazoan target sets. Genome Res 18:1180–1189
Lucarini N, Verrotti A, Napolioni V, Bosco G, Curatolo P (2007) Genetic polymorphisms and idiopathic generalized epilepsies. Pediatric Neurol 37:157–164
Maas A, Meens J, Baltes N, Hennig-Pauka I, Gerlach GF (2006) Development of a DIVA subjunit vaccine against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection. Vaccine 24:7226–7237
MAQC Consortium (2006) The MicroArray Quality Control (MAQC) project shows inter- and intraplatform reproducibility of gene expression measurements. Nat Biotechnol 24:1151–1161
Noyes EP, Feeney D, Pijoan C (1990) Comparison of the effect of pneumonia detected during lifetime with pneumonia detected at slaughter on growth in swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc 197:1025–1029
Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, Otsuki T, Sugiyama T, Irie R, Wakamatsu A, Hayashi K, Sato H, Nagai K, Kimura K, Makita H, Sekine M, Obayashi M, Nishi T, Shibahara T, Tanaka T, Ishii S, Sugano S (2004) Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs. Nat Genet 36:40–45
Peterson ML, Ma C, Spear BT (2011) Zhx2 and Zbtb20: novel regulators of postnatal alpha-fetoprotein repression and their potential role in gene reactivation during liver cancer. Sem Cancer Biol 21:21–27
Reiner G (2009) Investigations on genetic disease resistance in swine: a contribution to the reduction of pain, suffering and damage in farm animals. Appl Anim Behav Sci 118:217–221
Reiner G, Melchinger E, Kramarova M, Pfaff E, Büttner M, Saalmüller A, Geldermann H (2002) Detection of quantitative trait loci for resistance/susceptibility to the Pseudorabies Virus in swine. J Gen Virol 83:167–172
Reiner G, Willems H, Berge T, Fischer R, Köhler F, Hepp S, Hertrampf B, Kliemt D, Daugschies A, Zahner H, Geldermann H, Mackenstedt U (2007) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for resistance/susceptibility to Sarcocystis miescheriana in swine. Genomics 89:638–646
Reiner G, Bertsch N, Hoeltig D, Selke M, Willems H, Gerlach GF, Tuemmler B, Probst I, Herwig R, Drungowski M, Waldmann KH (2014) Identification of QTL affecting resistance/susceptibility to acute Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine. Mamm Genome 25:180–191
Renkema GH, Boot RG, Au FL, Donker-Koopman WE, Strijland A et al (1998) Chitotriosidase, a chitinase, and the 39-kDa human cartilage glycoprotein, a chitin-binding lectin, are homologues of family 18 glycosyl hydrolases secreted by human macrophages. Eur J Biochem 251:504–509
Seaton G, Hernandez J, Grunchec JA, White I, Allen J, De Koning DJ, Wei W, Berry D, Haley C, Knott S (2006) GridQTL: A Grid Portal for QTL MA. pleuropneumoniaeing of compute intensive datasets. In: Proceedings of the 8th world congress on genetics A. pleuropneumoniaelied to livestock production, August 13–18, 2006, Belo Horizonte
Shao M, Wang Y, Wang C, Guo Y, Peng Y, Liu J, Li G, Liu H, Liu S (2010) Evaluation of multicomponent recombinant vaccines against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in mice. Acta Vet Scand 52:52
Shen Z, Seppänen H, Vainionpää S, Ye Y, Wang S, Mustonen H, Puolakkainen P (2012) IL10, IL11, IL18 are differently expressed in CD14 + TAMs and play different role in regulating the invasion of gastric cancer cells under hypoxia. Cytokine 59:352–357
Sjölund S, Wallgren P (2010) Field experience with two different vaccination strategies aiming to control infections with. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in a fattening pig herd. Acta Vet Scand 52:23
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:15545–15550
Tietzel I, Mosser DM (2002) The modulation of macrophage activation by tyrosine phosphorylation. Front Biosci 7:d1494–d1502
Tonpitak W, Baltes N, Hennig-Pauka I, Gerlach GF (2002) Construction of an Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 2 prototype live negative-marker vaccine. Infect Immun 70:7120–7125
Tsai TH, Chen SF, Huang TY, Tzeng CF, Chiang AS, Kou YR, Lee TS, Shyue SK (2011) Impaired CD14 and CD36 expression, bacterial clearance, and Toll-like receptor 4YMYD88 signaling in Caveolin-1Y deleted macrophages and mice. Shock 35:92–99
Tumamao JQ, Bowles RE, van den Bosch H, Klaasen HL, Fenwick BW, Storie GJ, Blackall PJ (2004) Comparison of the efficacy of a subunit and a live streptomycin-dependent porcine pleuropneumonia vaccine. Aust Vet J 82:370–374
Vaandrager AB, Van Golde LM (2000) Lung surfactant proteins A and D in innate immune defense. Biol Neonate 77(Suppl 1):9–13
Van Oirschot JT (1994) Vaccination in food animal populations. Vaccine 12:415–418
Wang H, Zhang M, Bianchi M, Sherry B, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1998) Fetuin (alpha2-HS-glycoprotein) opsonises cationic macrophage deactivating molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14429–14434
Wang Y, Ren J, Lan L, Yan X, Huang X, Peng Q, Tang H, Zhang B, Ji H, Huang L (2007) Characterization of polymorphisms of transferrin receptor and their association with susceptibility to ETEC F4ab/ac in pigs. J Anim Breed Genet 124:225–229
Wang Y, Couture OP, Qu L, Uthe JJ, Bearson SM et al (2008) Analysis of porcine transcriptional response to Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis suggests novel targets of NFkappaB are activated in the mesenteric lymph node. BMC Genomics 20:1–20
Wanschers B, van de Vorstenbosch R, Wijers M, Wieringa B, King SM, Fransen J (2008) Rab6 family proteins interact with the dynein light chain protein DYNLRB1. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 65:183–196
Wessel J, Zapala MA, Schork NJ (2007) Accommodating pathway information in expression quantitative trait locus analysis. Genomics 90:132–142
White DG, Zhao S, Simjee S, Wagner DD, McDermott PF (2002) Antimicrobial resistance of food born pathogens. Microbes Infect 4:405–412
Willcocks LC, Carr EJ, Niederer HA, Rayner TF, Williams TN et al (2010) A defunctioning polymorphism in FCGR2B is associated with protection against malaria but susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:7881–7885
Wu C, Delano DL, Mitro N, Su SV, Janes J, McClurg P, Batalov S, Welch GL, Zhang J, Orth AP, Walker JR, Glynne RJ, Cooke MP, Takahashi JS, Shimomura K, Kohsake A, Bass J, Saez E, Wiltshire T, Su AI (2008) Gene enrichment in eQTL data identifies novel annotations and pathway regulators. PLoS Genet 4:e1000070
Xiao S, Jia J, Mo D, Wang Q, Qin L et al (2010) Understanding PRRSV infection in porcine lung based on genome-wide transcriptome response identified by deep sequencing. PLoS One 5:e11377
Yang Y, Chung EK, Wu YL, Savelli SL, Nagaraja HN et al (2007) Gene copy-number variation and associated polymorphisms of complement component C4 in human systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): low copy number is a risk factor for and high copy number is a protective factor against SLE susceptibility in European Americans. Am J Hum Genet 80:1037–1054
Yvert G, Brem RB, Whittle J, Akey JM, Foss E et al (2003) Trans-acting regulatory variation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the role of transcription factors. Nat Genet 35:57
Zhang X, Grusche FA, Harvey KF (2012) Control of tissue growth and cell transformation by the Salvador/Warts/Hippo pathway. PLoS One 7:e31994
Zhu R, Ou Z, Ruan X, Gong J (2012) Role of liver X receptors in cholesterol efflux and inflammatory signaling. Mol Med Rep 5:895–900
Zutic M, Ruzica A, Milic N (2008) Isolation and identification of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in pig’s lungs at farms and their sensitivity to antibiotics. Acta Vet 58:499–507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Suppl Fig. 1
Correlation of gene expression and severity of disease in the parental landrace strain. a IL10: Comparison of RT-PCR (red) and Affymetrix (green) expression profiles with the corresponding lung-scores. Bars show microarray expression fold-changes from 4 infected animals (disease scores = 5.7, 7.8, 11.9 and 12.2) and averaged expression from 4 uninfected animals (disease score = 0). b TLR4: Comparison of RT-PCR (red) and Affymetrix (green) expression profiles with the corresponding lung-scores (TIFF 508 kb)
Suppl Fig. 2
WGCNA results. a Based on the expression profiles across the 100 animals co-expression clusters were computed with the R implementation of the method which yielded 11 clusters of co-expressed genes (colored panel at the bottom). b Clusters (left colored panel) were correlated with phenotypic disease scores (range [−1,1]). Significance of the observation is shown for each cluster by correlation value and P value. Two large clusters of genes (brown 1,179 genes, and blue 2,617 genes) are particularly significantly correlated with the disease scores. Genes belonging to these clusters are shown in Suppl Table 5 (TIFF 3907 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reiner, G., Dreher, F., Drungowski, M. et al. Pathway deregulation and expression QTLs in response to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine. Mamm Genome 25, 600–617 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-014-9536-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-014-9536-9