Abstract
Purpose
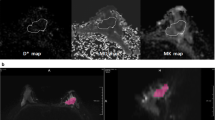
To examine heterogeneous breast cancer through intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) histogram analysis.
Materials and methods
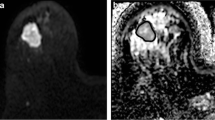
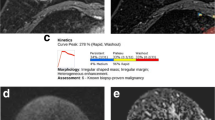
This HIPAA-compliant, IRB-approved retrospective study included 62 patients (age 48.44 ± 11.14 years, 50 malignant lesions and 12 benign) who underwent contrast-enhanced 3 T breast MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and IVIM biomarkers of tissue diffusivity (Dt), perfusion fraction (fp), and pseudo-diffusivity (Dp) were calculated using voxel-based analysis for the whole lesion volume. Histogram analysis was performed to quantify tumour heterogeneity. Comparisons were made using Mann–Whitney tests between benign/malignant status, histological subtype, and molecular prognostic factor status while Spearman’s rank correlation was used to characterize the association between imaging biomarkers and prognostic factor expression.
Results
The average values of the ADC and IVIM biomarkers, Dt and fp, showed significant differences between benign and malignant lesions. Additional significant differences were found in the histogram parameters among tumour subtypes and molecular prognostic factor status. IVIM histogram metrics, particularly fp and Dp, showed significant correlation with hormonal factor expression.
Conclusion
Advanced diffusion imaging biomarkers show relationships with molecular prognostic factors and breast cancer malignancy. This analysis reveals novel diagnostic metrics that may explain some of the observed variability in treatment response among breast cancer patients.
Key Points
• Novel IVIM biomarkers characterize heterogeneous breast cancer.
• Histogram analysis enables quantification of tumour heterogeneity.
• IVIM biomarkers show relationships with breast cancer malignancy and molecular prognostic factors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meacham CE, Morrison SJ (2013) Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature 501:328–337
Durrett R, Foo J, Leder K, Mayberry J, Michor F (2011) Intratumor heterogeneity in evolutionary models of tumor progression. Genetics 188:461–477
Fisher R, Pusztai L, Swanton C (2013) Cancer heterogeneity: implications for targeted therapeutics. Br J Cancer 108:479–485
Polyak K (2011) Heterogeneity in breast cancer. J Clin Invest 121:3786–3788
Jeh SK, Kim SH, Kim HS et al (2011) Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value and dynamic magnetic resonance imaging findings with prognostic factors in invasive ductal carcinoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:102–109
Choi SY, Chang YW, Park HJ, Kim HJ, Hong SS, Seo DY (2012) Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficiency values on diffusion-weighted imaging with prognostic factors for breast cancer. Br J Radiol 85:e474–e479
Iima M, Le Bihan D, Okumura R et al (2011) Apparent diffusion coefficient as an MR imaging biomarker of low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ: a pilot study. Radiology 260:364–372
Kamitani T, Matsuo Y, Yabuuchi H et al (2013) Correlations between apparent diffusion coefficient values and prognostic factors of breast cancer. Magn Reson Med Sci MRMS Off J Jpn Soc Magn Reson Med 12:193–199
Basser PJ (1995) Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed 8:333–344
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11:102–125
Sinha S, Lucas-Quesada FA, Sinha U, DeBruhl N, Bassett LW (2002) In vivo diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast: potential for lesion characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:693–704
Rahbar H, Partridge SC, Demartini WB et al (2012) In vivo assessment of ductal carcinoma in situ grade: a model incorporating dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted breast MR imaging parameters. Radiology 263:374–382
Partridge SC, Rahbar H, Murthy R et al (2011) Improved diagnostic accuracy of breast MRI through combined apparent diffusion coefficients and dynamic contrast-enhanced kinetics. Magn Reson Med 65:1759–1767
Kim SH, Cha ES, Kim HS et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging of breast cancer: correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value with prognostic factors. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:615–620
Iima M, Yano K, Kataoka M et al (2015) Quantitative non-gaussian diffusion and intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging: differentiation of malignant and benign breast lesions. Investig Radiol 50:205–211
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M et al (2008) Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging--pilot study. Radiology 249:891–899
Lemke A, Laun FB, Klauss M et al (2009) Differentiation of pancreas carcinoma from healthy pancreatic tissue using multiple b-values: comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion derived parameters. Investig Radiol 44:769–775
Gaing B, Sigmund EE, Huang WC et al (2015) Subtype differentiation of renal tumors using voxel-based histogram analysis of intravoxel incoherent motion parameters. Investig Radiol 50:144–152
Lu Y, Jansen JF, Mazaheri Y, Stambuk HE, Koutcher JA, Shukla-Dave A (2012) Extension of the intravoxel incoherent motion model to non-gaussian diffusion in head and neck cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 36:1088–1096
Thoeny HC, Zumstein D, Simon-Zoula S et al (2006) Functional evaluation of transplanted kidneys with diffusion-weighted and BOLD MR imaging: initial experience. Radiology 241:812–821
Song YS, Park CM, Lee SM et al (2014) Reproducibility of histogram and texture parameters derived from intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI of FN13762 rat breast Carcinomas. Anticancer Res 34:2135–2144
Kim S, Decarlo L, Cho GY et al (2012) Interstitial fluid pressure correlates with intravoxel incoherent motion imaging metrics in a mouse mammary carcinoma model. NMR Biomed 25:787–794
Suo S, Lin N, Wang H et al (2014) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging of breast cancer at 3.0 tesla: comparison of different curve-fitting methods. J Magn Reson Imaging. doi:10.1002/jmri.24799:n/a-n/a
Cho GY, Moy L, Zhang JL et al (2014) Comparison of fitting methods and b-value sampling strategies for intravoxel incoherent motion in breast cancer. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.25484
Bokacheva L, Kaplan JB, Giri DD et al (2014) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI at 3.0 T differentiates malignant breast lesions from benign lesions and breast parenchyma. J Magn Reson Imaging 40:813–823
Sigmund EE, Cho GY, Kim S et al (2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of tumor microenvironment in locally advanced breast cancer. Magn Reson Med 65:1437–1447
Liu C, Liang C, Liu Z, Zhang S, Huang B (2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in evaluation of breast lesions: comparison with conventional DWI. Eur J Radiol 82:e782–e789
Wiederer J, Pazahr S, Leo C, Nanz D, Boss A (2014) Quantitative breast MRI: 2D histogram analysis of diffusion tensor parameters in normal tissue. MAGMA 27:185–193
Chandarana H, Rosenkrantz AB, Mussi TC et al (2012) Histogram analysis of whole-lesion enhancement in differentiating clear cell from papillary subtype of renal cell cancer. Radiology 265:790–798
Lutz K, Wiestler B, Graf M et al (2014) Infiltrative patterns of glioblastoma: identification of tumor progress using apparent diffusion coefficient histograms. J Magn Reson Imaging 39:1096–1103
Emblem KE, Scheie D, Due-Tonnessen P et al (2008) Histogram analysis of MR imaging–derived cerebral blood volume maps: combined glioma grading and identification of low-grade oligodendroglial subtypes. Am J Neuroradiol 29:1664–1670
Baltzer PA, Renz DM, Herrmann KH et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in MR mammography (MRM): clinical comparison of echo planar imaging (EPI) and half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin echo (HASTE) diffusion techniques. Eur Radiol 19:1612–1620
Kinoshita T, Yashiro N, Ihara N, Funatu H, Fukuma E, Narita M (2002) Diffusion-weighted half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin echo imaging in breast tumors: differentiation of invasive ductal carcinoma from fibroadenoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:1042–1046
ACR (2003) Breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS). American College of Radiology, Reston, VA
Sharma U, Danishad KKA, Seenu V, Jagannathan NR (2009) Longitudinal study of the assessment by MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging of tumor response in patients with locally advanced breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. NMR Biomed 22:104–113
Wirestam R, Borg M, Brockstedt S, Lindgren A, Holtas S, Stahlberg F (2001) Perfusion-related parameters in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging compared with CBV and CBF measured by dynamic susceptibility-contrast MR technique. Acta Radiol 42:123–128
Moteki T, Horikoshi H (2006) Evaluation of hepatic lesions and hepatic parenchyma using diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR with three values of gradient b-factor. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:637–645
Callot V, Bennett E, Decking UK, Balaban RS, Wen H (2003) In vivo study of microcirculation in canine myocardium using the IVIM method. Magn Reson Med 50:531–540
Yao L, Sinha U (2000) Imaging the microcirculatory proton fraction of muscle with diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging. Acad Radiol 7:27–32
Pekar J, Moonen CT, van Zijl PC (1992) On the precision of diffusion/perfusion imaging by gradient sensitization. Magn Reson Med 23:122–129
Guiu B, Petit JM, Capitan V et al (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion–weighted Imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 3.0–T MR study. Radiology 265:96–103
Sumi M, Nakamura T (2013) Head and neck tumors: assessment of perfusion–related parameters and diffusion coefficients based on the intravoxel incoherent motion model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:410–416
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Adams S, Chakravarthy AB, Donach M et al (2010) Preoperative concurrent paclitaxel-radiation in locally advanced breast cancer: pathologic response correlates with five-year overall survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124:723–732
Prat A, Perou CM (2011) Deconstructing the molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol 5:5–23
Yue W, Wang JP, Li Y et al (2005) Tamoxifen versus aromatase inhibitors for breast cancer prevention. Clin Cancer Res 11:925s–930s
Pequeux C, Raymond-Letron I, Blacher S et al (2012) Stromal estrogen receptor-alpha promotes tumor growth by normalizing an increased angiogenesis. Cancer Res 72:3010–3019
Hyder SM, Murthy L, Stancel GM (1998) Progestin regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 58:392–395
Stendahl M, Ryden L, Nordenskjold B, Jonsson PE, Landberg G, Jirstrom K (2006) High progesterone receptor expression correlates to the effect of adjuvant tamoxifen in premenopausal breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 12:4614–4618
Zhang JL, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H et al (2012) Optimization of b-value sampling for diffusion-weighted imaging of the kidney. Magn Reson Med 67:89–97
Dyvorne HA, Galea N, Nevers T et al (2013) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver with multiple b-values: effect of diffusion gradient polarity and breathing acquisition on image quality and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters--a pilot study. Radiology 266:920–929
Nilsen LB, Fangberget A, Geier O, Seierstad T (2013) Quantitative analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in malignant breast lesions using different b-value combinations. Eur Radiol 23:1027–1033
Neil JJ, Bretthorst GL (1993) On the use of Bayesian probability theory for analysis of exponential decay data: an example taken from intravoxel incoherent motion experiments. Magn Reson Med 29:642–647
Barbieri S, Donati OF, Froehlich JM, Thoeny HC (2015) Impact of the calculation algorithm on biexponential fitting of diffusion-weighted MRI in upper abdominal organs. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.25765
Orton MR, Collins DJ, Koh DM, Leach MO (2014) Improved intravoxel incoherent motion analysis of diffusion weighted imaging by data driven Bayesian modeling. Magn Reson Med 71:411–420
Wurnig MC, Donati OF, Ulbrich E et al (2014) Systematic analysis of the intravoxel incoherent motion threshold separating perfusion and diffusion effects: proposal of a standardized algorithm. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.25506
Freiman M, Voss SD, Mulkern RV, Perez-Rossello JM, Callahan MJ, Warfield SK (2012) Reliable assessment of perfusivity and diffusivity from diffusion imaging of the body. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 15:1–9
Quentin M, Blondin D, Klasen J et al (2012) Comparison of different mathematical models of diffusion-weighted prostate MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 30:1468–1474
Veraart J, Rajan J, Peeters RR, Leemans A, Sunaert S, Sijbers J (2012) Comprehensive framework for accurate diffusion MRI parameter estimation. Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.24529:n/a-n/a
Freiman M, Voss SD, Mulkern RV, Perez-Rossello JM, Callahan MJ, Warfield SK (2012) In vivo assessment of optimal b-value range for perfusion-insensitive apparent diffusion coefficient imaging. Med Phys 39:4832–4839
Freiman M, Perez-Rossello JM, Callahan MJ et al (2013) Reliable estimation of incoherent motion parametric maps from diffusion-weighted MRI using fusion bootstrap moves. Med Image Anal 17:325–336
Wu LM, Hu J, Xu JR (2012) MRI in residual tumor size measurement in patient with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy calls for caution. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135:319–320
Prevos R, Smidt ML, Tjan-Heijnen VC et al (2012) Pre-treatment differences and early response monitoring of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients using magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic review. Eur Radiol 22:2607–2616
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Eric E. Sigmund, Ph.D. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise (James S. Babb). Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was waived by the institutional review board. Some study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported in
• Sigmund EE, Cho GY, Kim S et al (2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of tumour microenvironment in locally advanced breast cancer. Magn Reson Med 65:1437–1447
• Cho GY, Moy L, Kim SG, Klautau Leite AP, Baete SH, Babb JS, Sodickson DK, Sigmund EE (2015) Comparison of contrast enhancement and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in healthy and cancerous breast tissue. Eur J Radiol 84(10):1888–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.06.023. Epub 2015 Jul 2.
• Cho GY, Moy L, Zhang JL et al (2014) Comparison of fitting methods and b-value sampling strategies for intravoxel incoherent motion in breast cancer. Magn Reson Med. 10.1002/mrm.25484
Methodology: retrospective, diagnostic or prognostic study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, G.Y., Moy, L., Kim, S.G. et al. Evaluation of breast cancer using intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) histogram analysis: comparison with malignant status, histological subtype, and molecular prognostic factors. Eur Radiol 26, 2547–2558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-4087-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-4087-3