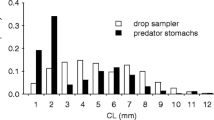
Abstract
Biotic interactions are particularly relevant in stable environments, such as the High Antarctic areas. Among them, predation has a key role in structuring community and population variables, including size-frequency distribution. This study aims to quantify the impact of predation by the notothenioid fish Trematomus bernacchii on the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki-size distribution. We developed a model of this impact that estimates the size distribution of the preyed scallop population, taking into account for the predator-size distribution, sex structure, and daily consumption. Comparing this size distribution of the preyed A. colbecki with the living populations at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), we were able to detect a relevant impact of fish predation. Fish-size frequency resulted to be the major factor shaping prey-size structure, with significant differences between predation by males and females. Our findings, given the key role of the two species in the littoral ecosystem of Terra Nova Bay (Antarctic Special Protected Area 161), fall into the framework of ecosystem management of High Antarctic coastal areas, particularly in the actual context of climate change, and increasing anthropogenic impact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainley DG (2002a) The Ross Sea, Antarctica, where all ecosystem processes still remain for study, but maybe not for long. Mar Ornithol 30:55–62
Ainley DG (2004) Acquiring a ‘base datum of normality’ for a marine ecosystem: the Ross sea, Antarctica. CCAMLR WG-EMM-04/20, Hobart
Ainley DG, Ballard G, Ackley S, Blight LK, Eastman JT, Emslie SD, Lescroël A, Olmastroni S, Townsend SE, Tynan CT, Wilson P, Woehler E (2007) Opinion. Paradigm lost, or is top-down forcing no longer significant in the Antarctic marine ecosystem? Antarct Sci 19:283–290. doi:10.1017/S095410200700051X
Ansell AD, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Chiantore M (1998) Swimming in the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki: analysis of in situ video recordings. Antarct Sci 10:369–375. doi:10.1017/S0954102098000455
Berkman PA, Nigro M (1992) Trace metal concentrations in scallops around Antarctica: extending the mussel watch programme to the Southern Ocean. Mar Pollut Bull 24:322–323. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(92)90594-V
Berkman PA, Tipton-Everett LR (eds) (2001) Latitudinal Ecosystem (LAT-ECO) Responses to climate across Victoria Land, Antarctica. Report of a National Science Foundation Workshop. BPRC, report no. 20. Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus
Berkman PA, Waller TR, Alexander SP (1991) Unprotected larval development in Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Pectinidae). Antarct Sci 3:151–157. doi:10.1017/S0954102091000184
Boyce DG, Frank KT, Leggett WC (2015) From mice to elephants: overturning the ‘one size fits all’ paradigm in marine plankton food chains. Ecol Lett 18:504–515. doi:10.1111/ele.12434
Bradford-Grieve J, Fenwick G (2001) A review of the current knowledge describing the biodiversity of the Ross Sea region. Final research paper for the Ministry of Fisheries Research Project ZBD2000/01, Objective 1. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research
Brose U, Jonsson T, Berlow EL, Warren P, Banasek-Richter C, Bersier LF, Blanchard JL, Brey T, Carpenter SR, Cattin Blandenier MF, Cohen JE, Cushing L, Dawah HA, Dell T, Edwards F, Harper-Smith S, Jacob U, Knapp RA, Ledger ME, Memmott J, Mintenbeck K, Pinnegar JK, Rayner T, Ruess L, Ulrich W, Williams RJ, Woodward G, Martinez ND (2006) Consumer-resource body-size relationships in natural food webs. Ecology 87:2411–2417. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[2411:CBRINF]2.0.CO;2
Bushula T, Pakhomov EA, Kaehler S, Davis S, Kalin RM (2005) Diet and daily ration of two notothenioid fish on the shelf of the sub-Antarctic Prince Edward Islands. Polar Biol 28:585–593. doi:10.1007/s00300-005-0729-2
Carton AG, Montgomery JC (2002) Responses of lateral line receptors to water flow in the Antarctic notothenioid, Trematomus bernacchii. Polar Biol 25:789–793. doi:10.1007/s00300-002-0416-5
Cattaneo-Vietti R, Chiantore M, Albertelli G (1997) The population structure and ecology of the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki (Smith, 1902) at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Sci Mar 61:15–24. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-59607-0_41
CCAMLR (2009a) Report of the workshop on vulnerable marine ecosystems (La Jolla, CA, USA, 3 to 7 August 2009). SC-CAMLR-XXVIII/10. CCAMLR, Hobart
CCAMLR (2009b) CCAMLR VME. Taxa identification guide version 2009. CCAMLR, Hobart
Cerrano C, Puce S, Chiantore M, Bavestrello G, Cattaneo-Vietti R (2001) The influence of the epizoic hydroid Hydractinia angustaon the recruitment of the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki. Polar Biol 24:577–581. doi:10.1007/s003000100254
Cerrano C, Bertolino M, Valisano L, Bavestrello G, Calcinai B (2009) Epibiotic demosponges on the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki (Smith, 1902) and the cidaroid urchins Ctenocidaris perrieri Koehler, 1912 in the nearshore habitats of the Victoria Land, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biol 32:1067–1076. doi:10.1007/s00300-009-0606-5
Chiantore M, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Albertelli G, Misic C, Fabiano M (1998) Role of filtering and biodeposition by Adamussium colbecki in circulation of organic matter in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). J Marine Syst 17:411–424. doi:10.1016/S0924-7963(98)00052-9
Chiantore M, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Berkman PA, Nigro M, Vacchi M, Schiaparelli S, Albertelli G (2001) Antarctic scallop (Adamussium colbecki) spatial population variability along the Victoria Land Coast, Antarctica. Polar Biol 24:139–143. doi:10.1007/s003000000191
Chiantore M, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Elia L, Guidetti M, Antonini M (2002) Reproduction and condition of the scallop Adamussium colbecki (Smith 1902), the sea urchin Sterechinus neumayeri (Meissner 1900) and the sea star Odontaster validus (Koehler 1911) at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea): different strategies related to inter-annual variations in food availability. Polar Biol 25:251–255. doi:10.1007/s00300-001-0331-1
Claessen D, Van Oss C, De Roos AM, Persson L (2002) The impact of size-dependent predation on population dynamics and individual life history. Ecology 83:1660–1675. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[1660:TIOSDP]2.0.CO;2
Coggan R (1997) Growth: ration relationships in the Antarctic fish Notothenia coriiceps Richardson maintained under different conditions of temperature and photoperiod. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 210:23–35. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(96)02717-7
Cowan JH, Houde ED, Rose KA (1996) Size-dependent vulnerability of marine fish larvae to predation: an individual-based numerical experiment. ICES J Mar Sci 53:23–37. doi:10.1006/jmsc.1996.0003
Craig JK, Burke BJ, Crowder LB, Rice JA (2006) Prey growth and size-dependent predation in juvenile estuarine fishes: experimental and model analyses. Ecology 87:2366–2377. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[2366:PGASPI]2.0.CO;2
Fenwick G, Bradford-Grieve JB (2002) Human pressure on Ross Sea region marine communities: recommendation for future marine research. Final research report for Ministry of Fisheries research project ZBD 2000/2001. Objective 3. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research
Floeter J, Temming A (2005) Analysis of prey size preference of North Sea whiting, saithe, and grey gurnard. ICES J Mar Sci 62:897–907. doi:10.1016/j.icesjms.2005.03.004
Flores H, Kock KH, Wilhelms S, Jones CD (2004) Diet of two icefish species from the South Shetland Islands and Elephant Island, Champsocephalus gunnari and Chaenocephalus aceratus. Polar Biol 27:119–129. doi:10.1007/s00300-003-0570-4
Gill AB (2003) The dynamics of prey choice in fish: the importance of prey size and satiation. J Fish Biol 63:105–116. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2003.00214.x
Gill AB, Hart PJB (1994) Feeding behavior and prey choice of the threespine stickleback: the interact effects of prey size, fish size and stomach fullness. Anim Behav 47:921–932. doi:10.1006/anbe.1994.1124
Hammerschlag-Peyer CM, Allgeier AJ, Layman CA (2013) Predator effects on faunal community composition in shallow seagrass beds of The Bahamas. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 446:282–290. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2013.06.002
Hartman KJ (2000) The influence of size on striped bass foraging. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 194:263–268. doi:10.3354/meps194263
Heilmayer O, Brey T, Chiantore M, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Arntz WE (2003) Age and productivity of the Antarctic scallop, Adamussium colbecki, in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 288:239–256. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(03)00020-0
Jacob U, Brey T, Fetzer I, Kaehler S, Mintenbeck K, Dunton K, Beyer K, Struck U, Pakhomov EA, Arntz WE (2006) Towards the trophic structure of the Bouvet Island marine ecosystem. Polar Biol 29:106–113. doi:10.1007/s00300-005-0071-8
Jacob U, Thierry A, Brose U, Arntz WE, Berg S, Brey T, Fetzer I, Jonsson T, Mintenbeck K, Möllmann C, Petchey O, Riede JO, Dunne JA (2011) The role of body size in complex food webs: a cold case. Adv Ecol Res 45:182–223. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386475-8.00005-8
Juanes F, Conover DO (1994) Piscivory and prey size selection in young-of-year bluefish: predator preference or size-dependent capture success? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 114:59–69. doi:10.3354/meps114059
Kato S, Schroeter SC (1985) Biology of the red sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus franciscanus, and its fishery in California. Mar Fish Rev 47:1–20
Kiest KA (1993) A relationship of diet to prey abundance and the foraging behavior of Trematomus bernacchii. Polar Biol 13:291–296. doi:10.1007/BF00238355
Kock KH (1992) Antarctic fish and fisheries. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kondo Y, Sakakibarta S, Tobayama T, Hoshi T (1990) Eggs released by the nototheniid fish Trematomus bernacchii Boulenger in captivity. Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol 3:76–79
La Mesa M, Vacchi M (2001) Review. Age and growth of high Antarctic notothenioid fish. Antarct Sci 13:227–235. doi:10.1017/S0954102001000335
La Mesa M, Arneri E, Giannetti G, Greco S, Vacchi M (1996) Age and growth of the nototheniid fish Trematomus bernacchii Boulenger from Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica. Polar Biol 16:139–145. doi:10.1007/s003000050038
La Mesa M, Dalù M, Vacchi M (2004a) Trophic ecology of the emerald notothen Trematomus bernacchii (Pisces, Nototheniidae) from Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biol 27:721–728. doi:10.1007/s00300-004-0645-x
La Mesa M, Eastman JT, Vacchi M (2004b) The role of notothenioid fish in the foodweb of the Ross Sea shelf waters: a review. Polar Biol 27:321–338. doi:10.1007/s00300-004-0599-z
Lundvall D, Svanback R, Persson L, Bystrom P (1999) Size-dependent predation in piscivores: interactions between predator foraging and prey avoidance abilities. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:1285–1292. doi:10.1139/f99-058
MacArthur RH, Pianka ER (1966) On optimal use of a patchy environment. Am Nat 100:603–609. doi:10.1086/282454
Maynou F, Cartes JE (1998) Daily ration estimates and comparative study of food consumption in nine species of deep-water decapod crustaceans of the NW Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 171:221–231. doi:10.3354/meps171221
Mintenbeck K, Barrera-Oro ER, Brey T, Jacob U, Knust R, Mark FC, Moreira E, Strobel A, Arntz WE (2012) Impact of climate change on fishes in complex Antarctic ecosystems. Adv Ecol Res 46:351–426. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-396992-7.00006-X
Naito Y, Iwami T (1982) Fish fauna in the northern parts of Lutzow-Holm Bay with some notes on the stomach contents. Mem Nat Inst. Polar Res 23:64–72
Nilsson KA (2010) Effects of size-dependent predation and competition on population and community dynamics. Dissertation, Umeå University
Olaso I, Lombarte A, Velasco F (2004) Daily ration of Antarctic silverfish (Pleuragramma antarcticum Boulenger, 1902) in the Eastern Weddell Sea. Sci Mar 68:419–424. doi:10.3989/scimar.2004.68n3419
Pankhurst NW, Montgomery JC (1989) Visual function in four Antarctic nototheniid fishes. J Exp Biol 142:311–324
Pearre S Jr (1986) Ratio-based trophic niche breadths of fish, the Sheldon spectrum, and the size-efficiency hypothesis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 27:299–314. doi:10.3354/meps027287
Peteiro LG, Filgueira R, Labarta U, Fernández-Reiriz MJ (2010) The role of fish predation on recruitment of Mytilusgallo provincialis on different artificial mussel collectors. Aquacult Eng 42:25–30. doi:10.1016/j.aquaeng.2009.09.003
Pinkerton MH, Bradford-Grieve JM, Hanchet SM (2010) A balanced model of the food web of the Ross Sea, Antarctica. CCAMLR Sci 17:1–31
Povero P, Chiantore M, Misic C, Budillon G, Cattaneo-Vietti R (2001) Land forcing controls pelagic-benthic coupling in Adelie Cove (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). Polar Biol 24:875–882. doi:10.1007/s003000100286
Saito H, Imabayashia H, Kawaia K, Cole V (2004) Time and energetic costs of feeding on different sized prey by the predatory polychaete Halla okudai (Imajima). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 311:223–232. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2004.05.010
Sala E, Zabala M (1996) Fish predation and the structure of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus populations in the NW Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 140:71–81. doi:10.3354/meps140071
Scharf FS, Buckel JA, Juanes F, Conover DO (1998) Predation by juvenile piscivorous bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix): the influence of prey to predator size ratio and prey type on predator capture success and prey profitability. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:1695–1703. doi:10.1139/f98-056
Scharf FS, Juanes F, Rountree RA (2000) Predator size–prey size relationships of marine fish predators: interspecific variation and effects of ontogeny and body size on trophic-niche breadth. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 208:229–248. doi:10.3354/meps208229
Scheibling RE (1996) The role of predation in regulating sea urchin population in eastern Canada. Oceanol Acta 19:421–430
Scheibling RE, Hamm J (1991) Interactions between sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis) and their predators in field and laboratory experiments. Mar Biol 110:105–116. doi:10.1007/BF01313097
Schoener TW (1979) Generality of the size–distance relation in models of optimal feeding. Am Nat 14:902–914. doi:10.1086/283537
Schoener TW (1993) On the relative importance of direct vs. indirect effects in ecological communities. In: Kawanabe H, Cohen JE, Iwaski K (eds) Mutualism and community organization. Oxford Scientific, Oxford, pp 365–411
Shears NY, Babcock RC (2002) Marine reserves demonstrate top-down control of community structure on temperate reefs. Oecologia 132:131–142. doi:10.1007/s00442-002-0920-x
Ślusarczyk M (1997) Impact of fish predation on a small-bodied cladoceran: limitation or stimulation? Hydrobiologia 342/343:215–221. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-5648-6_23
Smith WO Jr, Ainley DG, Cattaneo-Vietti R (2007) Trophic interactions within the Ross Sea continental shelf ecosystem. Philos T R Soc B 362:95–111. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1956
Staudinger MD, Juanes F (2010) Size-dependent susceptibility of longfin inshore squid (Loligo pealeii) to attack and capture by two predators. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 393:106–113. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2010.07.005
Stockton WL (1984) The biology and ecology of the epifaunal scallop Adamussium colbecki on the west side of McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Mar Biol 78:171–178. doi:10.1007/BF00394697
Svensson JE (1997) Fish predation on Eudiaptomus gracilis in relation to clutch size, body size, and sex: a field experiment. Hydrobiologia 344:155–161. doi:10.1023/A:1002966614054
Tegner MJ, Dayton PK (1981) Population structure, recruitment and mortality of two sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus franciscanus and purpuratus) in a kelp forest. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 5:255–268. doi:10.3354/meps005255
Tegner MJ, Levin LA (1983) Spiny lobsters and sea urchins: analysis of a predator–prey interaction. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 73:125–150. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(83)90079-5
Trathan PN, Agnew D (2010) Climate change and the Antarctic marine ecosystem: an essay on management implications. Antarct Sci 22:387–398. doi:10.1017/S0954102010000222
Vacchi M, La Mesa M, Castelli A (1994) Diet of two coastal nototheniid fish from Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea. Antarct Sci 8:61–65. doi:10.1017/S0954102094000088
Vacchi M, La Mesa M, Greco S (1999) The coastal fish fauna of Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica. In: Faranda FM, Guglielmo L, Ianora A (eds) Ross sea ecology, Italian Antarctic expeditions (1987–1995). Springer, Berlin, pp 457–468
Vacchi M, Cattaneo-Vietti R, Chiantore M, Dalù M (2000) Predator-prey relationship between the nototheniid fish Trematomus bernacchii and the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea). Antarct Sci 12:64–68
Watzin MC, Joppe-Mercure K, Rowder J, Lancaster B, Bronson L (2008) Significant fish predation on zebra mussels Dreissena polymorpha in Lake Champlain, USA. J Fish Biol 73:1585–1599. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2008.02033.x
Webb KD, Mitsch WJ (2001) Macroinvertebrate diversity and abundance in two experimental wetlands from top-down and bottom-up interpretations. Olentangy River Wetland Research Park Annual Report. The Ohio State University, Columbus, pp 73–80
Winkelmann C, Hellmann C, Rischka S, Petzoldt T, Benndorf J (2011) Fish predation affects the structure of a benthic community. Freshw Biol 56(6):1030–1046. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2010.02543.x
Wootton JT (1993) Indirect effects and habitat use in an intertidal community: interaction chains and interaction modifications. Am Nat 141:71–89. doi:10.1086/285461
Acknowledgements
This study has been possible because of the ACAB project, which was supported by the Progetto Nazionale Ricerche in Antartide (PNRA). We are also grateful to the Alfred Wegener Institute for the support and contribute to the Master Thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dell’Acqua, O., Brey, T., Vacchi, M. et al. Predation impact of the notothenioid fish Trematomus bernacchii on the size structure of the scallop Adamussium colbecki in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Polar Biol 40, 1557–1568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-017-2077-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-017-2077-4