Abstract
Herein, we review and synthesize results from a series of research projects that were conducted to evaluate the role of Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) in the marine ecosystem in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, Norway. A total of 76 sharks were caught on baited lines during the summers of 2008 and 2009 for these investigations. All of these animals, including the largest shark, a female weighing 700 kg, were sexually immature. Approximately half of the gastrointestinal tracts (GITs, N = 33) examined contained seal tissue (42.3 %), and some also contained minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) tissue (18.2 %). Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua), Atlantic wolffish (Anarhichas lupus) and haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus) were the dominant fish species consumed by the sharks. These fish species were found in 39.4, 18.2 and 18.2 % of the GITs, respectively. Many of the fishes were swallowed whole, including an Atlantic wolffish weighing 8.6 kg. Satellite pop-up tags deployed on 20 of the sharks showed that they travelled in the water column from the surface to depths greater than 1500 m, encountering temperatures from −1.5° to 7.4°. Accelerometers deployed on six of the sharks showed that they swim extremely slowly, with average speeds of 0.34 m/s and burst speeds of only twice this value. Various types of circumstantial evidence, including the condition of the seals and fishes found in the sharks’ stomachs, indicate that they are not only scavengers, but also active predators of both fish and mammalian prey. Given the swim speed of these sharks, we suggest that the only way they could successfully capture a healthy seal is via cryptically approaching seals that are asleep in the water. Greenland sharks clearly play a significant role as large predators in the Kongsfjorden marine ecosystem, a fact that has been largely overlooked until recently.

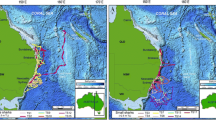
Modified from Leclerc et al. (2012)

From Leclerc et al. (2012)

From Fisk et al. (2012)

From Fisk et al. (2012)

Photograph: Armin Mück, NRK

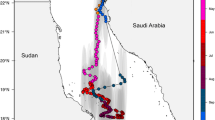
From Watanabe et al. (2012)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (1942) Beretninger vedrørende Grønlands Styrelse, sammendrag av statistiske oplysninger. Afsnit 17. Grønlændernes fiskeri. pp 647–652
Bexton S, Thompson D, Brownlow A, Barley J, Milne R, Bidewell C (2012) Unusual mortality of pinnipeds in the United Kingdom associated with helical (Corkscrew) injuries of anthropogenic origin. Aquat Mamm 38:229–240
Campana SE, Fisk AT, Klimley AP (2015) Movements of Arctic and northwest Atlantic Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) monitored with archival satellite pop-up tags suggest long-range migrations. Deep Sea Res 115:109–115
Carlson L (1958) Håkjerringa og håkjerringfisket (The Greenland shark and the Greenland shark fishery). Fiskeridir Skr Ser Fiskeri 5(1):1–36 (In Norwegian)
Corsolini S, Ancora S, Bianchi N, Mariotti G, Leonzio C, Christiansen JS (2014) Organotropism of persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals in the Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus in NE Greenland. Mar Pollut Bull 87:381–387
Cortés E (1997) A critical review of methods of studying fish feeding based on analysis of stomach contents: application to elasmobranch fishes. Can J Aquat Sci 54:726–738
Fisk AT, Tittlemier SA, Pranschke JL, Norstrom RJ (2002) Using anthropogenic contaminants and stable isotopes to assess the feeding ecology of Greenland sharks. Ecology 83:2162–2172
Fisk AT, Lydersen C, Kovacs KM (2012) Archival pop-off tag tracking of Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) in the High Arctic waters of Svalbard, Norway. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 468:255–265
Horning M, Mellish J-AE (2014) In cold blood: evidence of Pacific sleeper shark (Somniosus pacificus) predation on Steller sea lions (Eumetopias jubatus) in the Gulf of Alaska. Fish Bull 112:297–310
Leclerc L-M, Lydersen C, Haug T, Glover KA, Fisk AT, Kovacs KM (2011) Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) scavenge offal from minke (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) whaling operations in Svalbard (Norway). Polar Res. doi:10.3402/polar.v30i0.7342
LeClerc L-M, Lydersen C, Haug T, Bachmann L, Fisk AT, Kovacs KM (2012) A missing piece in the Arctic food web puzzle? Stomach contents of Greenland sharks sampled in Svalbard, Norway. Polar Biol 35:1197–1208
Liao CH, Pierce CL, Larscheid JG (2001) Empirical assessment of indices of prey importance in the diets of predacious fish. Trans Am Fish Soc 130:583–591
Lu Z, Fisk AT, Kovacs KM, Lydersen C, McKinney MA, Tomy GT, Rosenburg B, McMeans BC, Muir DCG, Wong CS (2014) Temporal and spatial variation in polychlorinated biphenyl chiral signatures of the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) and its Arctic marine food web. Environ Pollut 186:216–225
Lucas ZN, Natanson LJ (2010) Two shark species involved in predation on seals at Sable Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. Proc Nova Scotia Inst Sci 45:64–88
Lyamin OI (1993) Sleep in the harp seals (Pagophilus groenlandicus). Comparison of sleep on land and in water. J Sleep Res 2:170–174
MacNeil MA, McMeans BC, Hussey NE, Vecsei P, Svavarsson J, Kovacs KM, Lydersen C, Treble M, Skomal GB, Ramsey M, Fisk AT (2012) Biology of the Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus. J Fish Biol 80:991–1018
McLaren IA (1958) The biology of the ringed seal (Phoca hispida Schreber) in the eastern Canadian Arctic. Bull Fish Res Bd Can 118:1–97
McMeans BC, Arts MT, Lydersen C, Kovacs KM, Hop H, Falk-Petersen S, Fisk AT (2013) The role of Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) in an arctic ecosystem—assessed via stable isotopes and fatty acids. Mar Biol 160:1223–1238
Molde K, Ciesielski T, Fisk AT, Lydersen C, Kovacs KM, Sørmo EG, Jenssen BM (2013) Associations between vitamins A and E and legacy POP levels in highly contaminated Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus). Sci Total Environ 442:445–454
Murray BM, Wang JY, Yang S-C, Stevens JD, Fisk AT, Svavarsson J (2008) Mitochondrial cytochrome b variation in sleeper sharks (Squaliformes: Somniosidae). Mar Biol 153:1015–1022
Nielsen J, Hedeholm RB, Simon M, Steffensen JF (2014) Distribution and feeding ecology of the Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) in Greenland waters. Polar Biol 37:37–46
Palace VP, Klaverkamp JF, Baron CL, Brown SB (1997) Metabolism of H-3-retinol by lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) pre-exposed to 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126). Aquat Toxicol 39:321–332
Pinkas LM, Oliphant S, Iverson ILK (1971) Food habits of albacore, blue fin tuna and bonito in Californian waters. Cal Fish Game 152:1–105
Ridgway SH, Harrison RJ, Joyce PL (1975) Sleep and cardiac rhythm in the gray seal. Science 187:553–555
Sigler MF, Hulbert LB, Lunsford CR, Thompson NH, Burek K, O’Corry-Crowe G, Hirons AC (2006) Diet of Pacific sleeper shark, a potential Steller sea lion predator, in the north-east pacific Ocean. J Fish Biol 69:392–405
Strid A, Jörundsdóttir H, Päpke O, Svavarsson J, Bergman Å (2007) Dioxins and PCBs in Greenland sharks (Somniosus microcephalus) from the North-East Atlantic. Mar Pollut Bull 54:1514–1522
van den Hoff J, Morrice MG (2008) Sleeper shark (Somniosus antarcticus) and other bite wounds observed on southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) at Macquarie Island. Mar Mammal Sci 24:239–247
van Neer A, Jensen LF, Siebert U (2015) Grey seals (Halichoerus grypus) predation on harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) on the island of Helgoland, Germany. J Sea Res 97:1–4
Watanabe YY, Lydersen C, Fisk AT, Kovacs KM (2012) The slowest fish: swim speed and tail-beat frequency of Greenland sharks. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 426–427:5–11
Yano K, Stevens JD, Compagno LJV (2007) Distribution, reproduction and feeding of the Greenland Shark Somniosus (Somniosus) microcephalus, with notes on two other sleeper sharks, Somniosus (Somniosus) pacificus and Somniosus (Somniosus) antarcticus. J Fish Biol 70:374–390
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by the Norwegian Research Council, the Norwegian Polar Institute, and the National Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC) “Research Chair” program. All animal handling was approved by the Norwegian Animal Research Authority (permit no. 08/51886). We thank G. Christensen, K. Frost, J. I. Karlsen, L. Lowry, H. Lund, L. Leclerc, B. McMeans, K. Molde, Y. Watanabe and the crew on RV Lance for assistance in the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article belongs to the special issue on the “Kongsfjorden ecosystem—new views after more than a decade of research,” coordinated by Christian Wiencke and Haakon Hop.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lydersen, C., Fisk, A.T. & Kovacs, K.M. A review of Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) studies in the Kongsfjorden area, Svalbard Norway. Polar Biol 39, 2169–2178 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-1949-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-1949-3