Abstract.
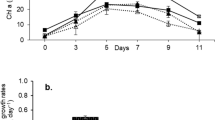
Chlorophyll-specific photosynthetic rates of marine phytoplankton collected under landfast sea ice in the Canadian Arctic were stimulated by additions of a chelator, ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA), and trace metals. This stimulation was imitated by filtered extracts of bottom ice colonized by sea-ice algae. Compared to controls, the assimilation rates for experimental additions averaged 166%, 184%, and 119% for ETDA, trace metals, and ice extracts, respectively. All experimental treatments displayed similar oscillations consistent with tidal forcing where mixing and photosynthetic performance are enhanced during spring tides. These results suggest that some bioactive soluble material(s) produced within the bottom-ice algal layer acts as a "conditioning" agent that enhances the growth of phytoplankton in arctic waters. The bioactive agent(s) remains unidentified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apollonio, S., Pennington, M. & Cota, G.F. Stimulation of phytoplankton photosynthesis by bottom-ice extracts in the Arctic. Polar Biol 25, 350–354 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-001-0349-4
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-001-0349-4