Abstract
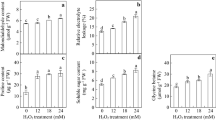
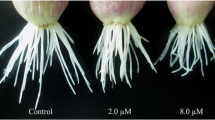
To investigate the rice root proteome, we applied the PEG fractionation technique combined with two-dimensional gel electrophoresis which rendered more well-separated protein spots. Out of the 295 chosen proteins, 93 were identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The proteins were classified as relating to metabolism (38.7%), reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related proteins (22.5%), protein processing/degradation (8.6%), stress/defense (7.5%), energy (6.5%) and signal transduction (5.4%). The high percentage of ROS-related proteins found in rice root brings us to assess the roles of ROS on rice root growth. Treatment with ROS quenching chemicals such as reduced glutathione (GSH), diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) and ascorbate inhibited root growth dose-dependently. Forty-nine proteins identified were either up- or down-regulated by GSH treatment, of which 14 were ROS-related proteins, such noticeably modulated ones as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), superoxide dismutases (SOD) and l-ascorbate peroxidases. The protein levels of four GSTs (NS4, 8, 56 and 57), three APXs (NS46, 49 and 50) and MnSOD (NS45) were strongly reduced by GSH treatment but slightly reduced by ascorbate and DPI. Ascorbate and DPI strongly inhibited expression levels of a catalase A (NP23) and an APX (NS65) but did not affect APXs (NS46, 49 and 50) protein levels. Northern analysis demonstrated that changes in transcript levels of five genes––GST (NS4), GST (NS43), Mn-SOD (NS45), APX (NS50) and APX (NS46/49) in response to ROS quenching chemicals were coherent with patterns shown in two-dimensional electrophoresis analyses. Taken together, we suggest that these proteins may take part in an important role in maintaining cellular redox homeostasis during rice root growth.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azhiri-Sigari T, Yamauchi A, Kamoshita A, Wade LJ (2000) Genotypic variation in response of rainfed lowland rice to drought and rewatering. Plant Prod Sci 3:180–188
Bevan M, Bancroft I, Bent E, Love K, Goodman H, Dean C, Bergkamp R, Dirkse W, van Staveren M, Stiekema W, Drost L, Ridley P, Hudson SA, Patel K, Murphy G, Piffanelli P, Wedler H, Wedler E, Wambutt R, Weitzenegger T, Pohl TM, Terryn N, Gielen J, Villarroel R, De Clerck R, Van Montagu M, Lecharny A, Auborg S, Gy I, Kreis M, Lao N, Kavanagh T, Hempel S, Kotter P, Entian KD, Rieger M, Schaeffer M, Funk B, Mueller-Auer S, Silvey M, James R, Montfort A, Pons A, Puigdomenech P, Douka A, Voukelatou E, Milioni D, Hatzopoulos P, Piravandi E, Obermaier B, Hilbert H, Dusterhoft A, Moores T, Jones JDG, Eneva T, Palme K, Benes V, Rechman S, Ansorge W, Cooke R, Berger C, Delseny M, Voet M, Volckaert G, Mewes HW, Klosterman S, Schueller C, Chalwatzis N (1998) Analysis of 1.9 Mb of contiguous sequence from chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 391:485–488
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot (Lond) 91:179–194
Blum H, Beier H, Gross HJ (1987) Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA, and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93–99
Edwards R, Dixon DP, Walbot V (2000) Plant glutathione S-transferase: enzymes with multiple functions in sickness and in health. Trends Plant Sci 5:193–198
Fang YZ, Yang S, Wu G (2002) Free radical, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition 18:872–879
Foreman J, Demidchik V, Bothwell JHF, Mylona P, Miedema H, Torres MA, Linstead P, Costa S, Brownlee C, Jones JDG, Davies JM, Dolan L (2003) Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature 422:442–446
Gong H, Jiao Y, Hu WW, Pua EC (2005) Expression of glutathione-S-transferase and its role in plant growth and development in vivo and shoot morphogenesis in vitro. Plant Mol Biol 57:53–66
Halliwell B (2006) Reactive species and antioxidants. Redox biology is a fundamental theme of aerobic life. Plant Physiol 141:312–322
Herouatr D, Montagu MV, Inze D (1993) Redox-activated expression of the cytosolic copper/zinc superoxide dismutase gene in Nicotiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:3108–3112
Hochholdinger F, Guo L, Schnable PS (2004) Lateral roots affect the proteome of the primary root of maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Mol Biol 2004:397–412
Hochholdinger F, Woll K, Guo L, Schnable PS (2005) The accumulation of abundant soluble proteins changes early in the development of the primary roots of maize (Zea mays L.). Proteomics 5:4885–4893
International rice genome sequencing project (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Jones AME, Thomas V, Truman B, Lilley K, Mansfield J, Grant M (2004) Specific changes in the Arabidopsis proteome in response to bacterial challenge: differentiating basal and R-gene mediated resistance. Phytochemistry 65:1805–1816
Joo JH, Bae YS, Lee JS (2001) Role of auxin-induced reactive oxygen species in root gravitropism. Plant Physiol 126:1055–1060
Kim ST, Cho KS, Jang YS, Kang KY (2001) Two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of rice proteins by polyethylene glycol fractionation for protein arrays. Electrophoresis 22:2103–2109
Kim ST, Cho KS, Yu S, Kim SG, Hong JC, Han CD, Bae DW, Nam MH, Kang KY (2003a) Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins induced by rice blast fungus and elicitor in suspension-cultured rice cells. Proteomics 3:2368–2378
Kim ST, Kim HS, Kim HJ, Kim SG, Kang SY, Lim DB, Kang KY (2003b) Prefractionation of protein samples for proteome analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Mol Cells 16:316–322
Kim ST, Kim SG, Hwang DH, Kang SY, Kim HJ, Lee BH, Lee JJ, Kang KY (2004) Proteomic analysis of pathogen-responsive proteins from rice leaves induced by rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. Proteomics 4:938–949
Koller A, Washburn MP, Lange BM, Andon NL, Deciu C, Haynes PA, Hays L, Schieltz D, Ulaszek R, Wei J, Wolters D, Yates III JR (2002) Proteomic survey of metabolic pathways in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:11969–11974
Komatsu S, Konishi H (2005) Proteome analysis of rice root proteins regulated by gibberellin. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 3:132–142
Kwak JM, Nguyen V, Schroeder JI (2006) The role of reactive oxygen species in hormonal responses. Plant Physiol 141:323–329
Leamml UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophgae. Nature 227:680–685
Liszkay A, van der Zalm E, Schopfer P (2004) Production of reactive oxygen inermediates (O2 •−, H2O2, and •OH) by maize roots and their role in wall loosening and elongation growth. Plant Physiol 136:3144–3123
Lopez-Bucio J, Cruz-Ramirez A, Herrera-Estrella L (2003) The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:280–287
Marrs KA (1996) The function and regulation of glutathione S-transferase in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:127–158
May MJ, Vernoux T, Leaver C, Montagu MV, Inze D (1998) Glutathione homeostasis in plants: implications for environmental sensing and plant development. J Exp Bot 49:649–667
Miller SS, Driscoll BT, Gregerson RG, Gantt JS, Vance CP (1998) Alfalfa malate dehydrogenase (MDH): molecular cloning and characterization of five different forms reveals a unique nodule-enhanced MDH. Plant J 15:173–184
Morita S, Suga T, Yamazaki K (1988) The relationship between root length density and yield in rice plants. Jpn J Crop Sci 57:438–443
Neuefeind T, Huber R, Dasenbrock H, Prade L, Bieseler B (1997) Crystal structrure of herbicide-detoxifying maize glutathione S-transferase-I in complex with lactoylglutathione: evidence for an induced-fit mechanism. J Mol Biol 274:446–453
O’Donnell BV, Tew DG, Jones OT, England PJ (1993) Studies on the inhibitory mechanism of iodonium compounds with special reference to neutrophil NADPH oxidase. Biochem J 290:41–49
Ostergaard O, Melchior S, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (2002) Initial proteome analysis of mature barley seeds and malt. Proteomics 2:733–739
Pullar JM, Hampton MB (2002) Diphenyleneiodonium triggers the efflux of glutathione from cultured cells. J Biol Chem 277:19402–19407
Reinemer P, Prade L, Hof P, Neuefeind T, Huber R, Zettl R, Palme K, Schell J, Koelln I, Bartunik HD, Bieseler B (1996) Three-dimensional structure of glutathione S-transferase from Arabidopsis thaliana at 2.2 Å resolution: structural characterization of herbicide-conjugating plant glutathione S-transferases and a novel active site architecture. J Mol Biol 255:289–309
Renew S, Heyno E, Schopfer P, Liszkay A (2005) Sensitive detection and localization of hydroxyl radical production in cucumber roots and Arabidopsis seedlings by spin trapping electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Plant J 44:342–347
Rodriguez AA, Grunberg KA, Taleisnik EL (2002) Reactive oxygen species in the elongation zone of maize leaves are necessary for leaf extension. Plant Physiol 129:1627–1632
Ros-Barcelo A, Pomar F, Lopez-Serrano M, Martinez P, Pedreno MA (2002) Developmental regulation of the H2O2-producing system and of a basic peroxidase isoenzyme in the Zinnia elegans lifnifying xylem. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:325–332
Schopfer P, Plachy C, Frahry G (2001) Release of reactive oxygen intermediates (superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals) and peroxidase in germinating radish seeds controlled by light, gibberellin, and abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 125:1591–1602
Schroeder JI, Mori IC (2004) Reactive oxygen species activation of plant Ca2+ channels. A signaling mechanism in polar growth, hormone transduction, stress signaling, and hypothetically mechanotransduction. Plant Physiol 135:702–708
Sheffield J, Taylor N, Fauquet C, Chen S (2006) The cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) root proteome: protein identification and differential expression. Proteomics 6:1588–1598
Smirnoff N (1996) The function and metabolism of ascorbic acid in plants. Ann Bot 78:661–669
Smirnoff N (2000) Ascorbate acid: metabolism and functions of a multi-facetted molecule. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:229–235
Suzuki H, Matsumori A, Matoba Y, Kyu BS, Tanaka A, Funita J, Sasayama S (1993) Enhanced expression of superoxide dismutase messenger RNA in viral myocarditis: SH-dependant reduction of its expression and myocardial injury. J Clin Invest 6:2727–2733
Tanaka N, Konishi H, Khan MMK, Komatsu S (2004) Proteome analysis of rice tissues by two-dimensional electrophoresis: an approach to the investigation of gibberellin regulated proteins. Mol Genet Genomics 270:485–496
Tanaka N, Mitsui S, Nobori H, Yanagi K, Komatsu S (2005) Expression and function of proteins during development of the basal region in rice seedling. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:796–808
Teo YH, Beyrouty CA, Norman RJ, Gbur EE (1995) Nutrient uptake relationship to root characteristics of rice. Plant Soil 171:297–302
Terashima K, OgataT, Akita S (1994) Eco-physiological characteristics related with lodging tolerance of rice in direct sowing cultivation. Jpn J Crop Sci 63:34–41
Ueda M, Matsui K, Ishiguro S, Sano R, Wada T, Paponov I, Palme K, Okada K (2004) The HALTED ROOT gene encoding the 26S proteasome subunit RPT2a is essential for the maintenance of Arabidopsis meristems. Development 131:2101–2111
Yang Y, Kwon HB, Peng HP, Shih MC (1993) Stress response and metabolic regulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 101:209–216
Wingsle G, Karpinski G (1996) Differential redox regulation by glutathione of glutathione reductase and CuZn-superoxide dismutase gene expression in Pinus sylvestris L. needles. Planta 198:151–157
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant No. CG1122 from the Crop Functional Genomic Center; by a grant from KOSEF/MOST to the Environmental Biotechnology National Core Research Center (to S.G. Kim and S.T. Kim); and by scholarships from the Brain Korea 21 Program, Ministry of Education and Human Resources Development, Korea (to S.G. Kim, Y. Wang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W.T. Kim.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.G., Kim, S.T., Kang, S.Y. et al. Proteomic analysis of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related proteins in rice roots. Plant Cell Rep 27, 363–375 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0441-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0441-5