Abstract
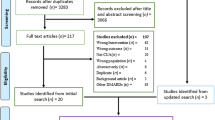
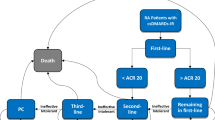
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of using rituximab as first line for patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis in comparison with continuing conventional DMARDs, from a perspective of health service governors. A systematic review was implemented through searching PubMed, Scopus and Cochrane Library. Quality assessment was performed by Jadad scale. After meta-analysis of ACR index results, QALY gain was calculated through mapping ACR index to HAQ and utility index. To measure the direct and indirect medical costs, a set of interviews with patients were applied. Thirty-two patients were selected from three referral rheumatology clinics in Tehran with definite diagnosis of refractory rheumatoid arthritis in the year before and treatment regimen of either rituximab or DMARDs within last year. Incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated for base case and scenario of generic rituximab. Threefold of GDP per capita was considered as threshold of cost-effectiveness. Four studies were eligible to be considered in this systematic review. Total risk differences of 0.3 for achieving ACR20 criteria, 0.21 for ACR50 and 0.1 for ACR70 were calculated. Also mean of total medical costs of patients for 24 weeks were $3985 in rituximab group and $932 for DMARDs group. Thus, the incremental cost per QALY ratio will be $45,900–$70,223 in base case and $32,386–$49,550 for generic scenario. Rituximab for treatment of patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis is not considered as cost-effective in Iran in none of the scenarios.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venables P, Maini R (2014) Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham, MA
Lipsky PE et al (2008) Rheumatoid arthritis. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL et al (eds) Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 17th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 2083
Davatchi F (2009) Rheumatology in Iran. Int J Rheum Dis 12(4):283–287. doi:10.1111/j.1756-185X.2009.01425.x
Selection of results of census 2012 (2014) Statistical Center of Iran. http://www.amar.org.ir/Portals/0/Files/abstract/1390/sarshomari90_nahaii.pdf. Accessed 08 July 2014
Schur PH, Gabriel SE, Crowson CS (2014) Epidemiology of, risk factors for, and possible causes of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham
Yee CS, Filer A, Pace A, Douglas K, Situnayake D, Rowe IF, West Midlands Rheumatology S, Training C (2003) The prevalence of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the West Midlands fulfilling the BSR criteria for anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy: an out-patient study. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 42(7):856–859. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg231
Balk RA (2014) Methotrexate-induced lung injury. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham
Curtis JR, Beukelman T, Onofrei A, Cassell S, Greenberg JD, Kavanaugh A, Reed G, Strand V, Kremer JM (2010) Elevated liver enzyme tests among patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis treated with methotrexate and/or leflunomide. Ann Rheum Dis 69(1):43–47. doi:10.1136/ard.2008.101378
Wallace DJ (2014) Antimalarial drugs in the treatment of rheumatic disease. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham
Weisman MH, Rinaldi RZ (2014) Sulfasalazine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham
Leandro MJ (2014) Rituximab and other B cell targeted therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham
Edwards JCW, Szczepański L, Szechiński J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, Stevens RM, Shaw T (2004) Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350(25):2572–2581
Burton W, Morrison A, Maclean R, E R (2006) Systematic review of studies of productivity loss due to rheumatoid arthritis. Occup Med (Lond) 56(1):18–27
Osiri M, Maetzel A, P T (2007) The economic burden of rheumatoid arthritis in a developing nation: results from a one-year prospective cohort study in Thailand. J Rheumatol 34(1):57–63
GDP per capita (current US$) (2014) World Bank. http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD. Accessed 08 July 2014
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17(1):1–12
Kielhorn A, Porter D, Diamantopoulos A, Lewis G (2008) UK cost-utility analysis of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis that failed to respond adequately to a biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. Curr Med Res Opin 24(9):2639–2650. doi:10.1185/03007990802321683
Bansback NJ, Brennan A, Ghatnekar O (2005) Cost effectiveness of adalimumab in the treatment of patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. Ann Rheum Dis 64(7):995–1002. doi:10.1136/ard.2004.027565
Boggs R, Sengupta N, Ashraf T (2002) Estimating health utility from a physical function assessment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients treated with adalimumab (HUMIRA) [abstract]. International Society of Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research abstract UT3:452–453
Carreno A, Fernandez I, Badia X, Varela C, Roset M (2011) Using HAQ-DI to estimate HUI-3 and EQ-5D utility values for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Spain. Value Health 14(1):192–200. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2010.11.001
Table: threshold values for intervention cost-effectiveness by Region (2014) World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/choice/costs/CER_levels/en/index.html. Accessed 08 July 2014
Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, Keystone EC, Loveless JE, Burmester GR, Cravets MW, Hessey EW, Shaw T, Totoritis MC (2006) Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthr Rheum 54(9):2793–2806. doi:10.1002/art.22025
Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Schechtman J, Szczepanski L, Kavanaugh A, Racewicz AJ, van Vollenhoven RF, Li NF, Agarwal S, Hessey EW, Shaw TM (2006) The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthr Rheum 54(5):1390–1400. doi:10.1002/art.21778
Emery P, Deodhar A, Rigby WF, Isaacs JD, Combe B, Racewicz AJ, Latinis K, Abud-Mendoza C, Szczepanski LJ, Roschmann RA, Chen A, Armstrong GK, Douglass W, Tyrrell H (2010) Efficacy and safety of different doses and retreatment of rituximab: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial in patients who are biological naive with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate (Study Evaluating Rituximab’s Efficacy in MTX iNadequate rEsponders (SERENE)). Ann Rheum Dis 69(9):1629–1635. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.119933
Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of a TNF inhibitor (2010) NICE technology appraisal guidance. http://publications.nice.org.uk/adalimumab-etanercept-infliximab-rituximab-and-abatacept-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-ta195/evidence-and-interpretation. Accessed 08 July 2014
Lindgren P, Geborek P, Kobelt G (2009) Modeling the cost-effectiveness of treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with rituximab using registry data from southern Sweden. Int J Technol Assess Healthc 25(2):181–189. doi:10.1017/s0266462309090230
Drug treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (2014) NICE. http://pathways.nice.org.uk/pathways/rheumatoid-arthritis/drug-treatment-for-rheumatoid-arthritis#. Accessed 08 July 2014
Mota LMHD, Cruz BA, Brenol CV, Pereira IA, Rezende-Fronza LS, Bertolo MB, Freitas MVC, Silva NAD, Louzada-Junior P, Giorgi RDN, Lima RAC, Bernardo WM, Pinheiro GDRC (2012) Guidelines for the drug treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rev Bras Reumatol 53(2):158–183
Schur PH, Cohen S (2014) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis resistant to initial DMARD therapy in adults. In: Basow DS (ed) UpToDate. UpToDate, Waltham
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Any conflict of interest is disclaimed by all of the authors.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Inform consent was obtained from all individual participants prior to interview.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadiani, S., Nikfar, S., Karimi, S. et al. Rituximab as first choice for patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis: cost-effectiveness analysis in Iran based on a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 36, 1291–1300 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3484-5